Accounting localization modifies financial management systems to adapt to certain local norms and legislation. Accounting software must be customized to manage local tax regulations, reporting standards, and financial practices. Accounting localization promotes accurate and compliant financial operations by adding features like tax calculations and report formats that comply with local rules. Businesses can effectively manage their finances and comply with regionally specific legal and regulatory requirements by using this customized method.
A thorough awareness of local accounting standards and laws is essential for understanding Thailand's financial environment. These particular needs are taken into account in the design of Odoo's accounting localization for Thailand, which provides companies with a customized solution to effectively manage their financial operations. Odoo 17 incorporates key functionalities, including currency management, reporting standards, and Thai tax laws. This technology streamlines the entire accounting process, improves financial reporting accuracy, and simplifies compliance by complying with Thai accounting standards. This frees up organizations to concentrate on strategic decision-making and growth.
Thailand Accounting with Odoo 17
The first step is to set up the Thailand Accounting Localization in Odoo 17. To do this, we can navigate to Apps and install the required modules.
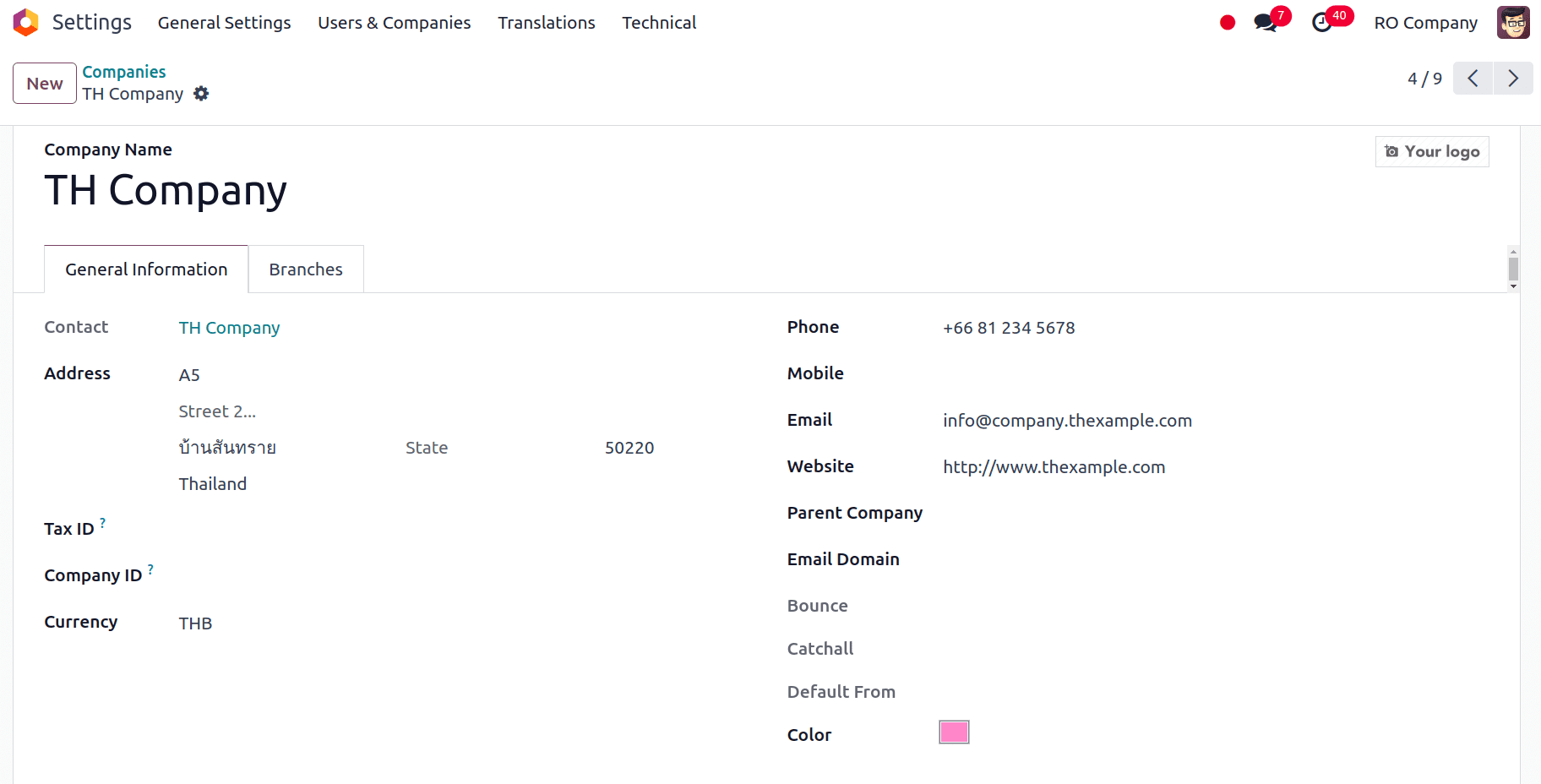
We have to verify the company configuration, it must be appropriately configured failing which we have to establish a new company with the appropriate company settings.
For that, we have to go to Settings > Users and Companies > Companies and select the company for which we want to check from the list of companies that appear.
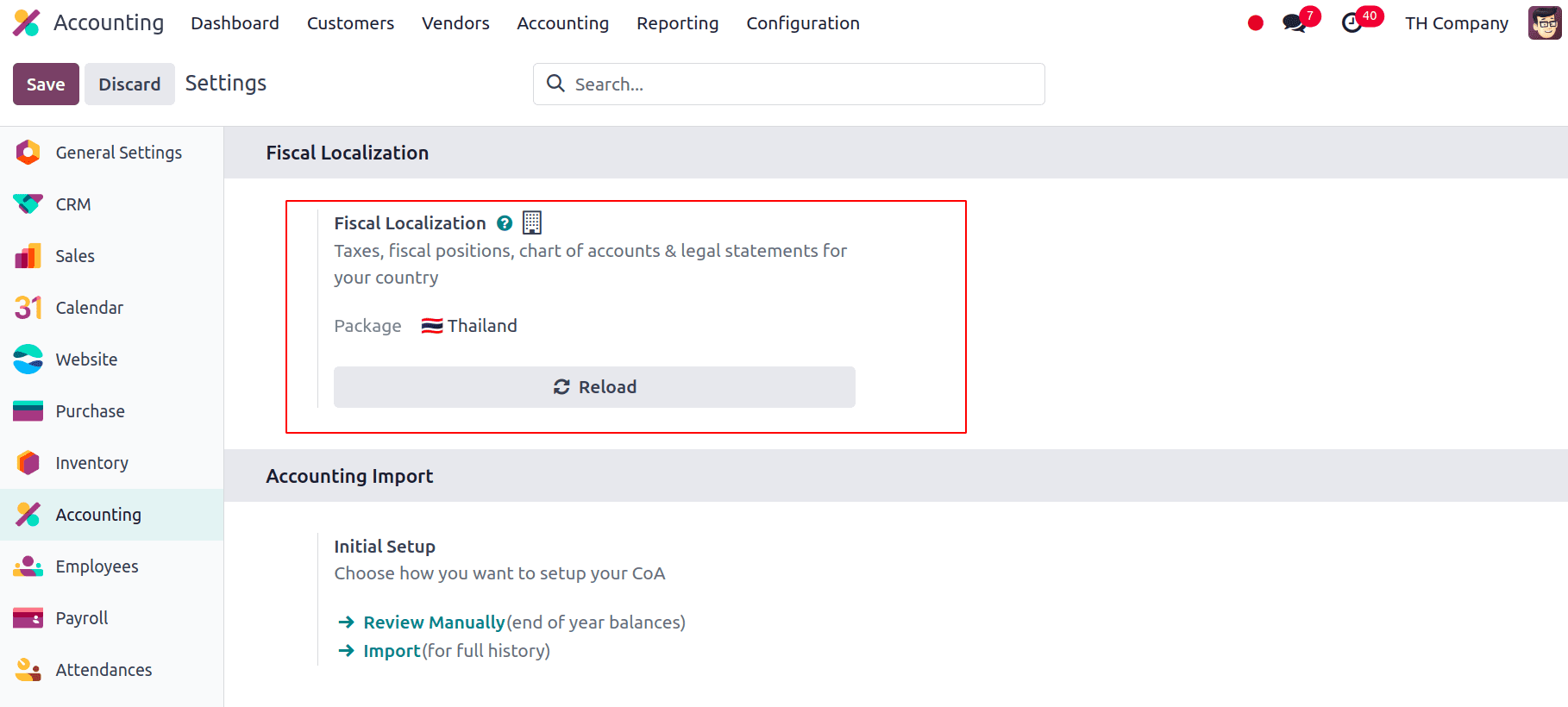
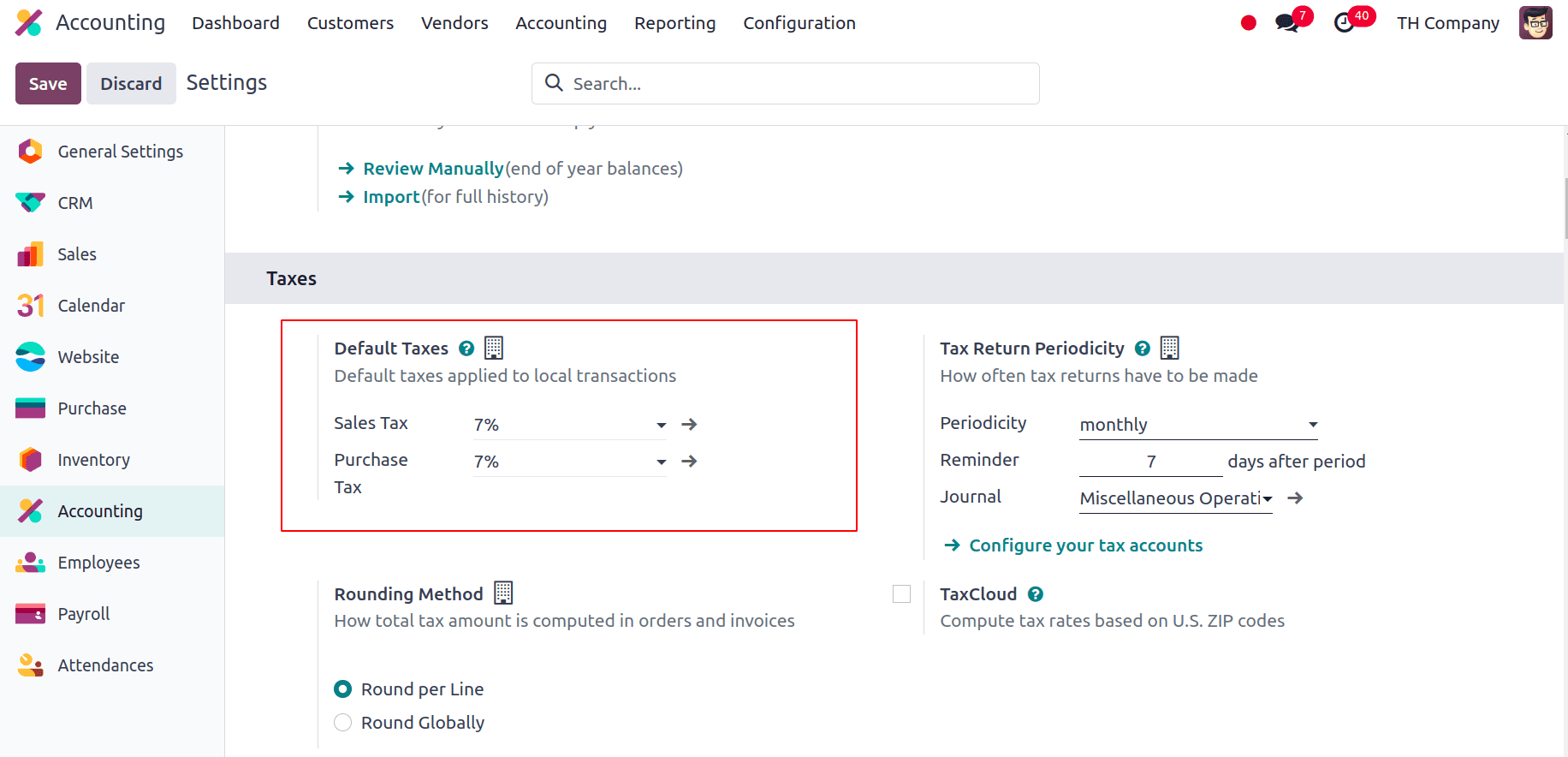
Once we have installed the localization modules and made sure the company configuration is correct, we can check the fiscal localization, main currency, and the default taxes that are applied after installing the localization. To do that, go to Accounting > Configuration > Settings. We can see that Thailand is selected under the fiscal localisation area. Thus, that will determine how the nation's taxes, fiscal positions, chart of accounts, and legal statements are set up.
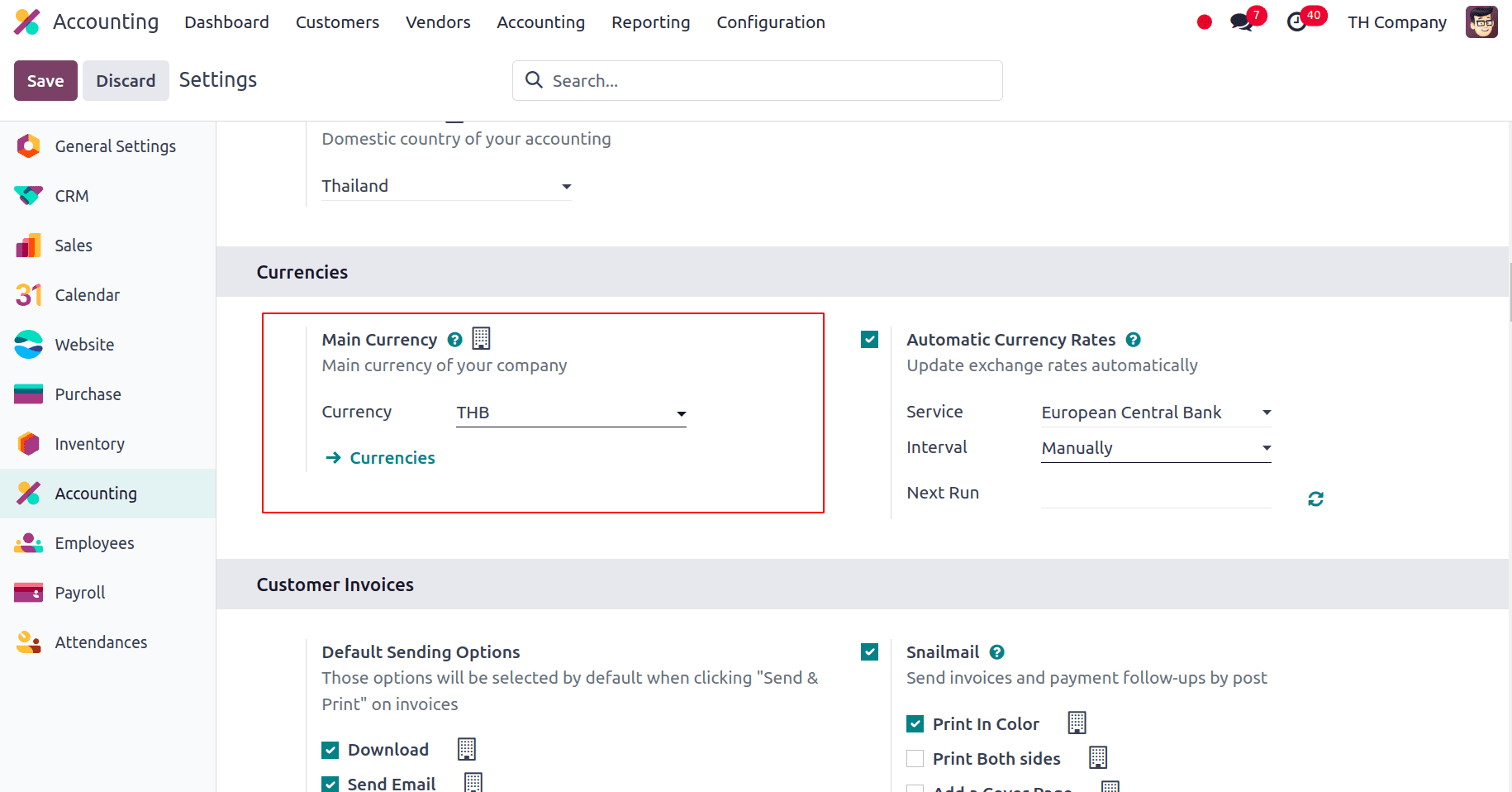
The main currency will be set to Thailand’s official currency, Thai Baht (THB).
The Default Taxes which are the preset tax rates and regulations that are automatically applied to transactions, including sales and purchases, based on the system configurations made. By guaranteeing that the right tax amounts are applied consistently, these default tax settings simplify the accounting process and lessen the need for manual modifications. Here the Default Taxes is applied to 7% Sales and Purchase Tax.
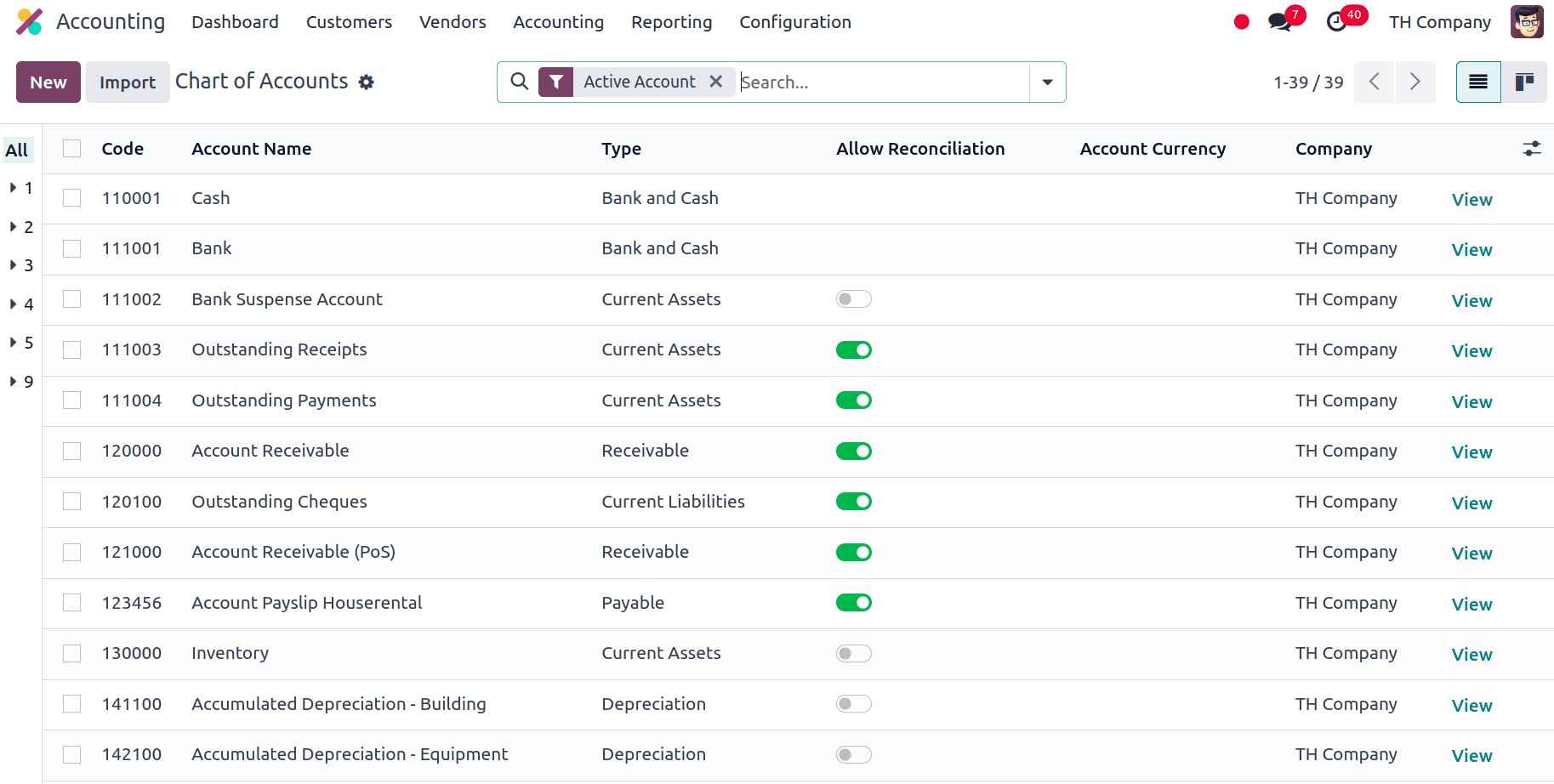
The Chart of Accounts and Taxes will be automatically adjusted in accordance with the localisation upon installation. In order to provide accurate and consistent financial reporting, the Chart of Accounts provides the framework for organising and recording financial transactions. Here we can see all the fundamental chart of accounts along with some other chart of accounts added particularly for this localization.
* Accrued Expenses account within the Chart of Accounts is used to record expenses that have been incurred but not yet paid or invoiced by the end of the accounting period. This account helps ensure that expenses are recognized in the correct financial period, aligning with Thai accounting standards and accrual accounting principles.
* Uninvoiced Receipts account in the Chart of Accounts is used to track amounts received by the business for which invoices have not yet been issued. This account helps manage and account for receipts from customers before formal invoicing takes place, ensuring accurate financial reporting and cash flow management.
* Retained earnings are the amount of a firm's profit that is kept within the company rather than paid out as dividends to shareholders. This account reflects the accumulated profits or losses from previous periods, which are reinvested into the business or used to cover past losses.
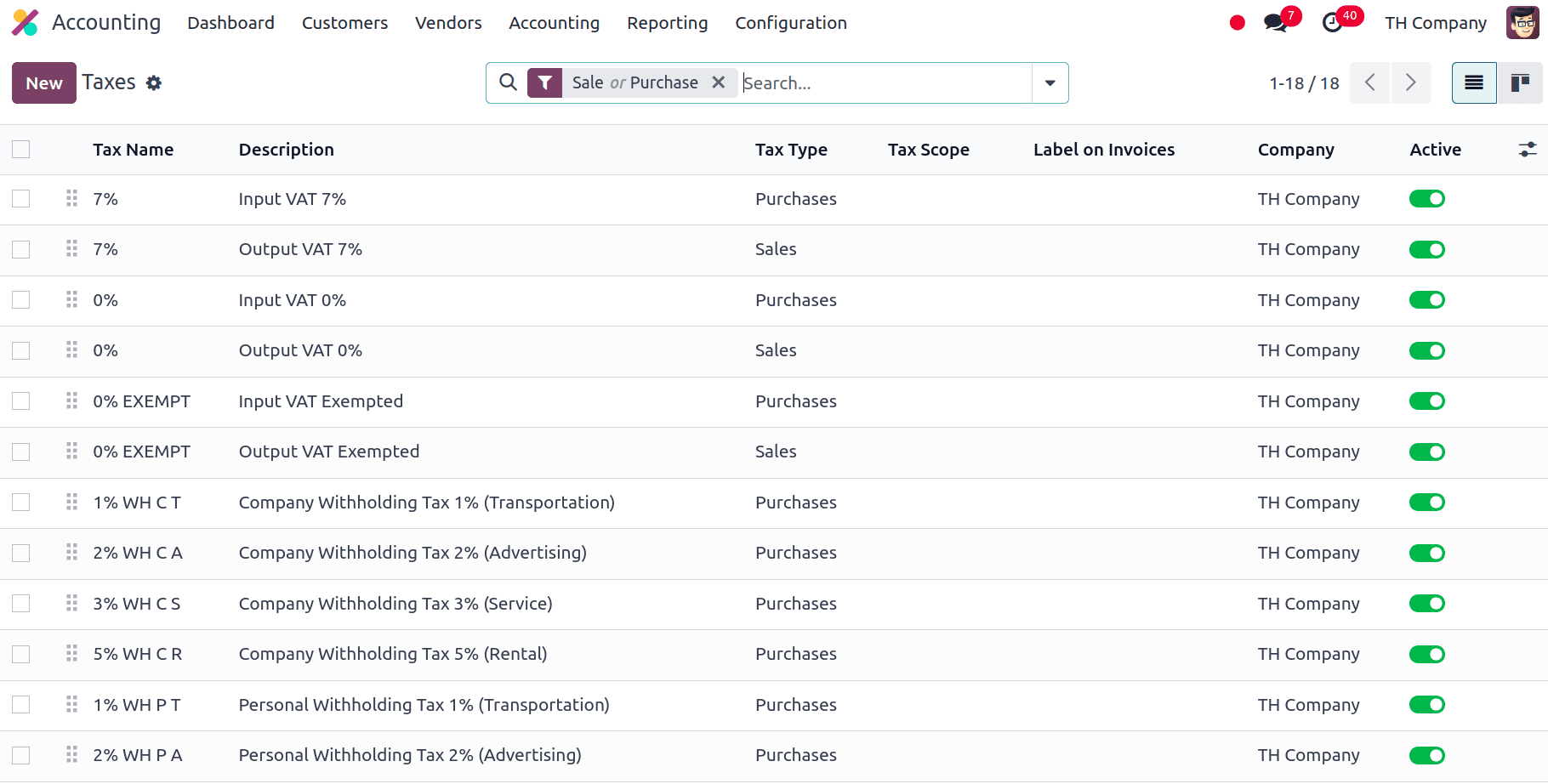
Similarly, we have several other charts of accounts included in this localization with different purposes. Taxes are financial charges that are imposed on sales and purchases in Odoo depending on predetermined rules and rates. In order to guarantee proper application and reporting, the system automatically calculates these taxes and integrates them into the whole accounting procedure. For this localization, the following taxes are included:
* VAT 7%: It is configured to comply with Thailand's Value Added Tax regulations. This tax rate is applied to sales and purchase transactions to reflect the standard VAT rate in Thailand.
* VAT-exempted: Some transactions are not subject to Value Added Tax this is used to manage such transactions. This configuration is essential for correctly handling goods or services that fall under VAT-exempt categories as per Thai tax regulations.
* Withholding tax: It is essential for complying with Thai tax regulations. Withholding tax is a portion of the payment that businesses must withhold from certain transactions and remit to the tax authorities.
* Withholding income tax: It is the tax deducted from payments made to individuals or entities and remitted to the Thai Revenue Department. With this we can make sure that taxes will collected on income before it will be received by the taxpayer.
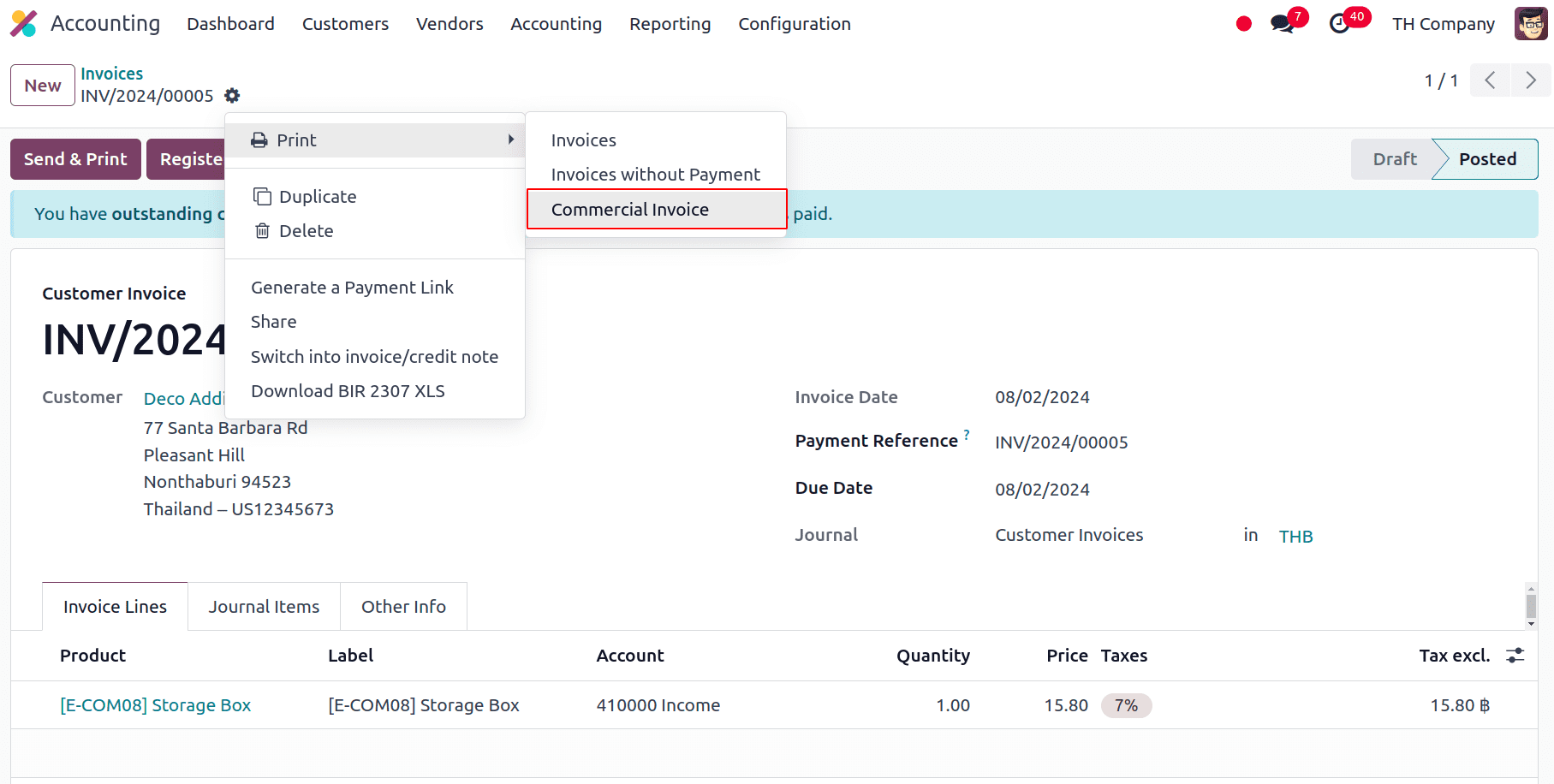
Also, this localization has included the option to print the tax invoices. We can choose to print standard invoices or tax invoices as PDF reports. For that, click on Actions in the invoice and there we have the option to Print under which we have the option to print the Commercial Invoice.
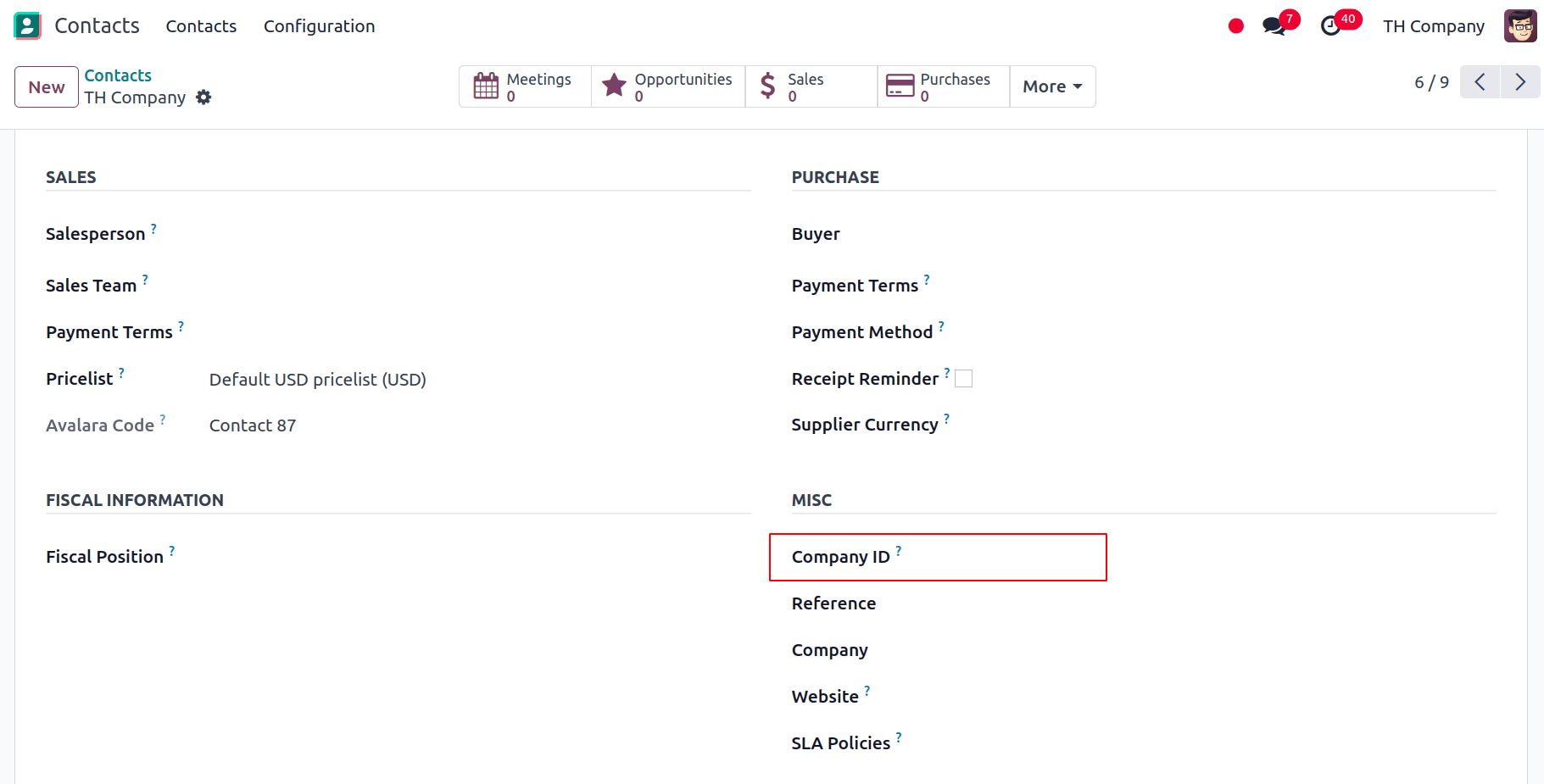
The Contacts app allows us to find a company's headquarters and branch number. Goto Contacts module, and open the company’s contact form; under the Sales & Purchase tab, we have the option to add the Company ID. If the contact is a branch, enter the Branch number, and if it is a Headquarters, leave the Company ID field empty.
PromptPay QR code on Invoices
Customers can use the bank mobile application that supports PromptPay to pay their bills by adding the PromptPay QR code to their invoices. The invoice amount and one of the following merchant details are used to generate the QR code:
* ID for an eWallet
* Tax ID for Merchants
* Mobile Phone Number
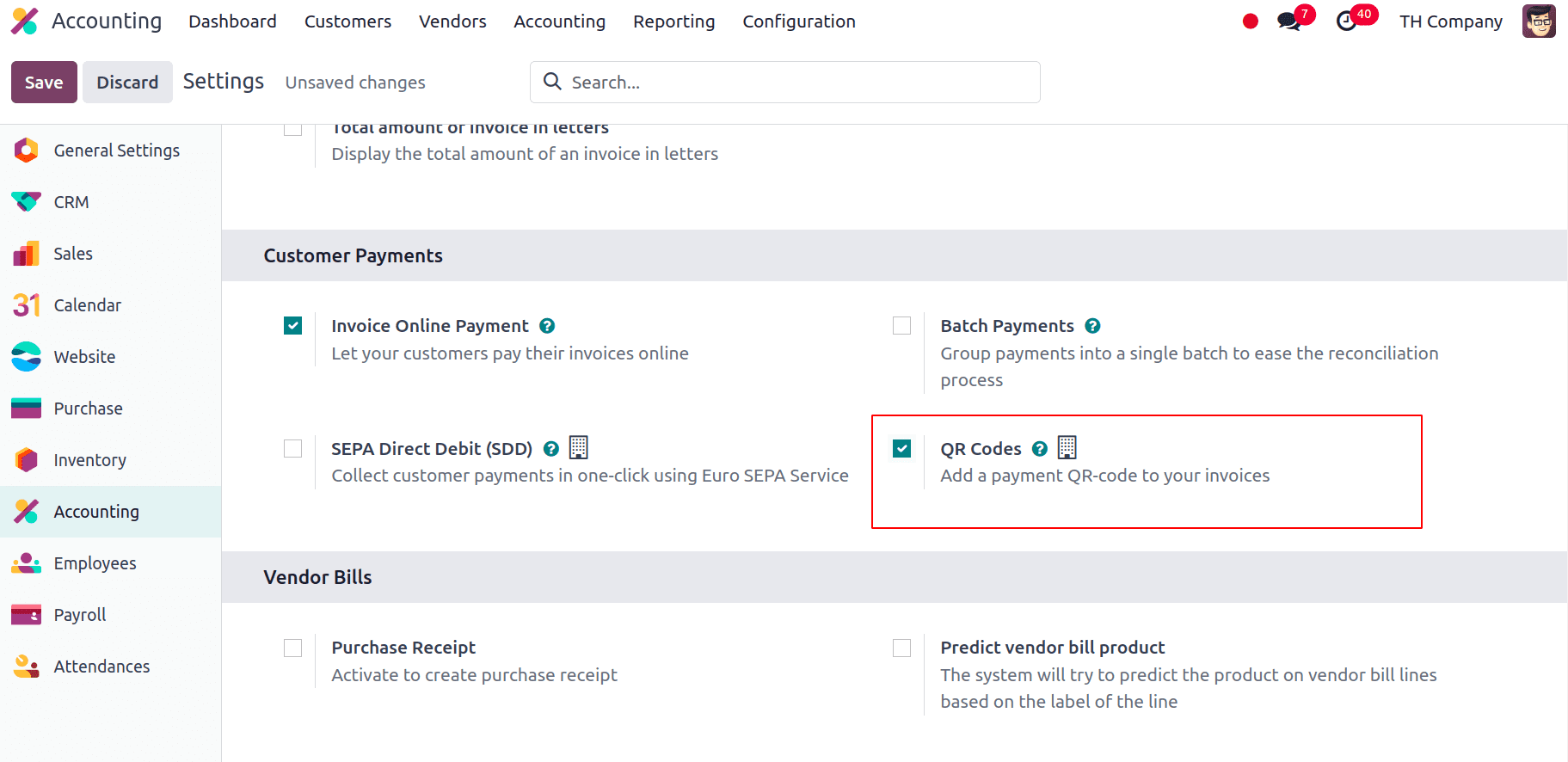
For that we have to activate the QR code and also configure the PromptPay QR bank account. For that goto Accounting > Configuration > Settings and under the Customer Payments we have the QR Codes, enable that and Save the settings.
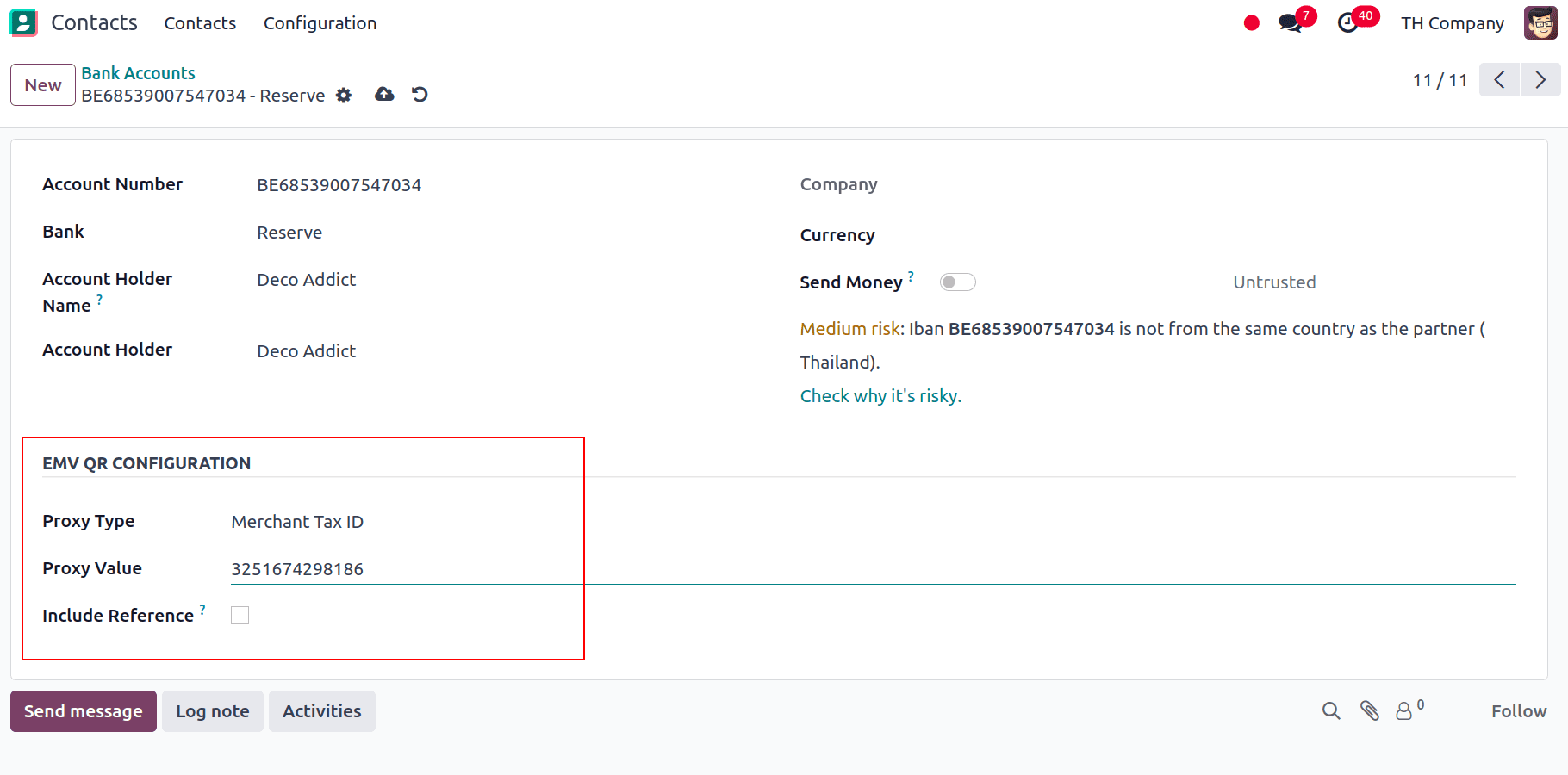
Now, to configure the Promptpay QR bank account, Go to Contacts > Configuration > Bank Accounts, and we can select the bank account for which we want to activate PromptPay QR, and then we have to set the Proxy Type and also fill in the Proxy Value field.
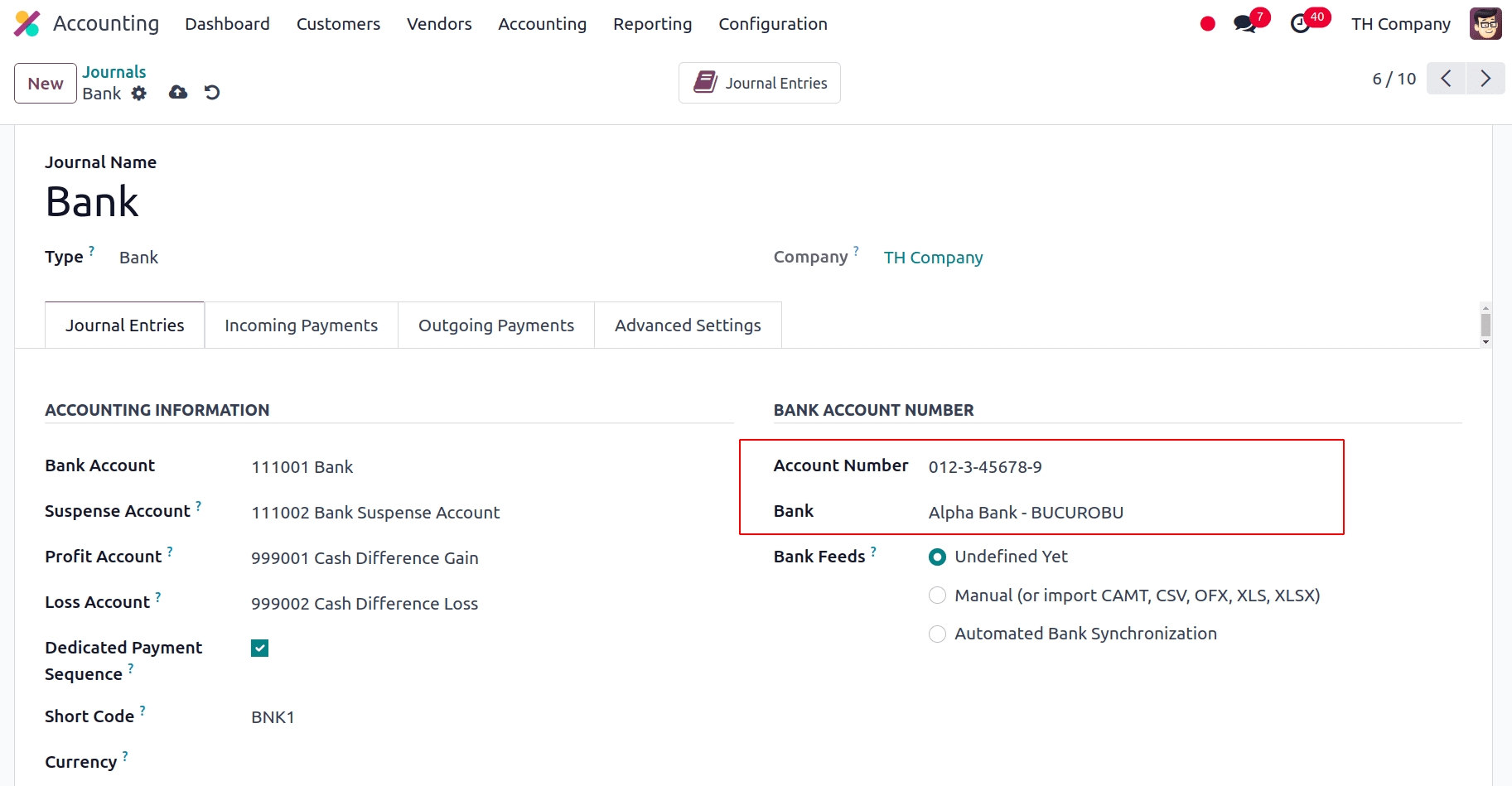
Now we can configure the Bank Journal, for this, go to Accounting > Configuration > Journals and select the Bank journal, and we have to fill the Account Number and Bank under the Journal Entries tab.
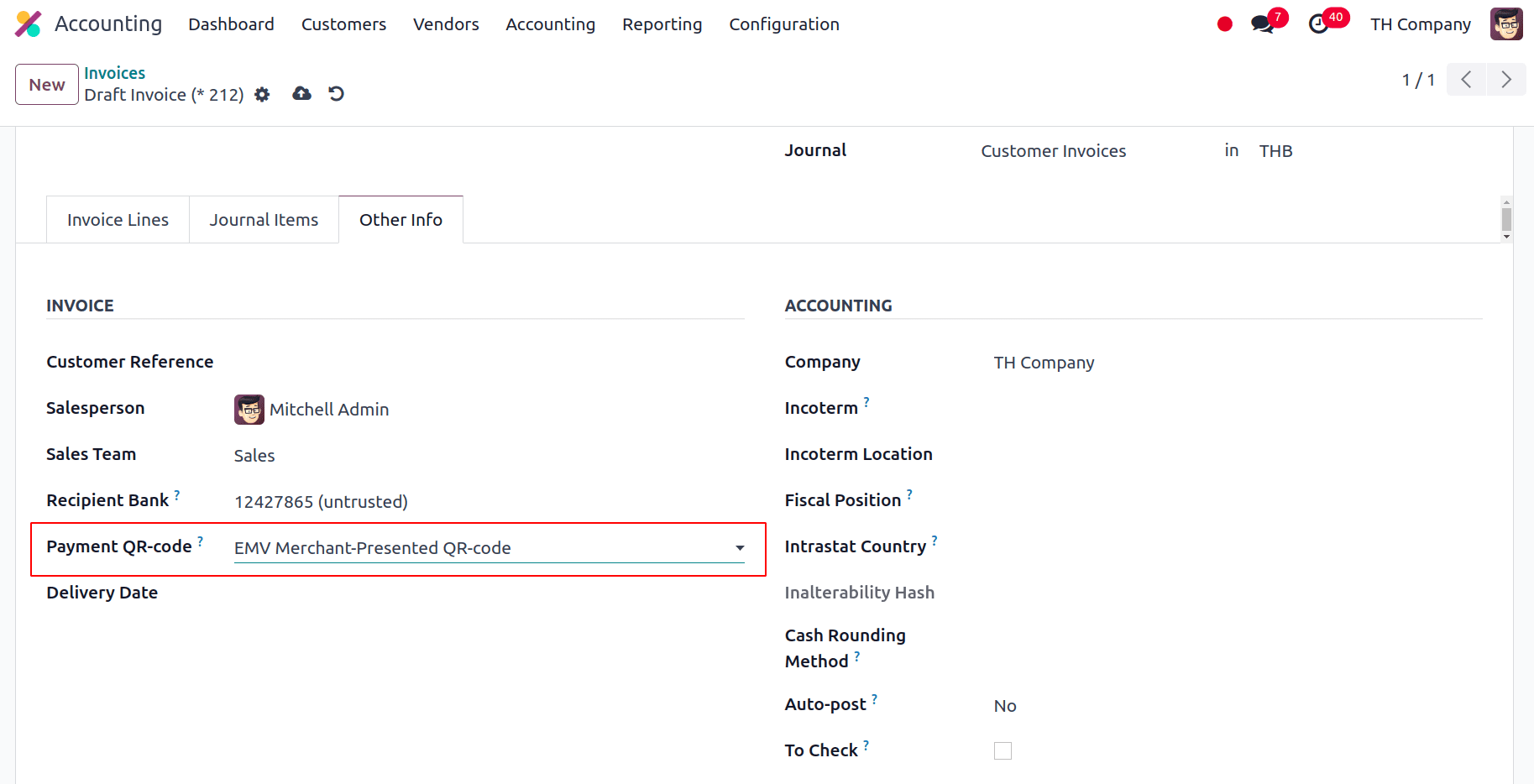
Now, we can issue the invoices with the Promptpay QR code; for that, select EMV Merchant-Presented QR-code under the Payment QR-code option when you create a new invoice by opening the Other Info tab. Choose the option for EMV Merchant-Presented QR-code. Odoo utilizes this field to generate the PromptPay QR code, so make sure it's the same bank that you set.
Now we can look into the Reporting section, where we can find the Balance Sheet, Profit and Loss Report and the Tax Report.
Balance sheet: An organization's balance sheet displays its equity, liabilities, and assets to provide a concise overview of the company's financial situation. Resources that a company or an individual possesses that are valuable commercially and are expected to yield benefits in the future are referred to as assets. A fundamental idea in financial accounting is that assets are often classified based on their type and function within the business. A business's liabilities are the sums of money it owes other people or businesses. Liabilities are entries on the balance sheet that show how much the business owes to suppliers, creditors, lenders, and other organisations. The amount of a company's assets that is left over after subtracting its liabilities is known as equity.
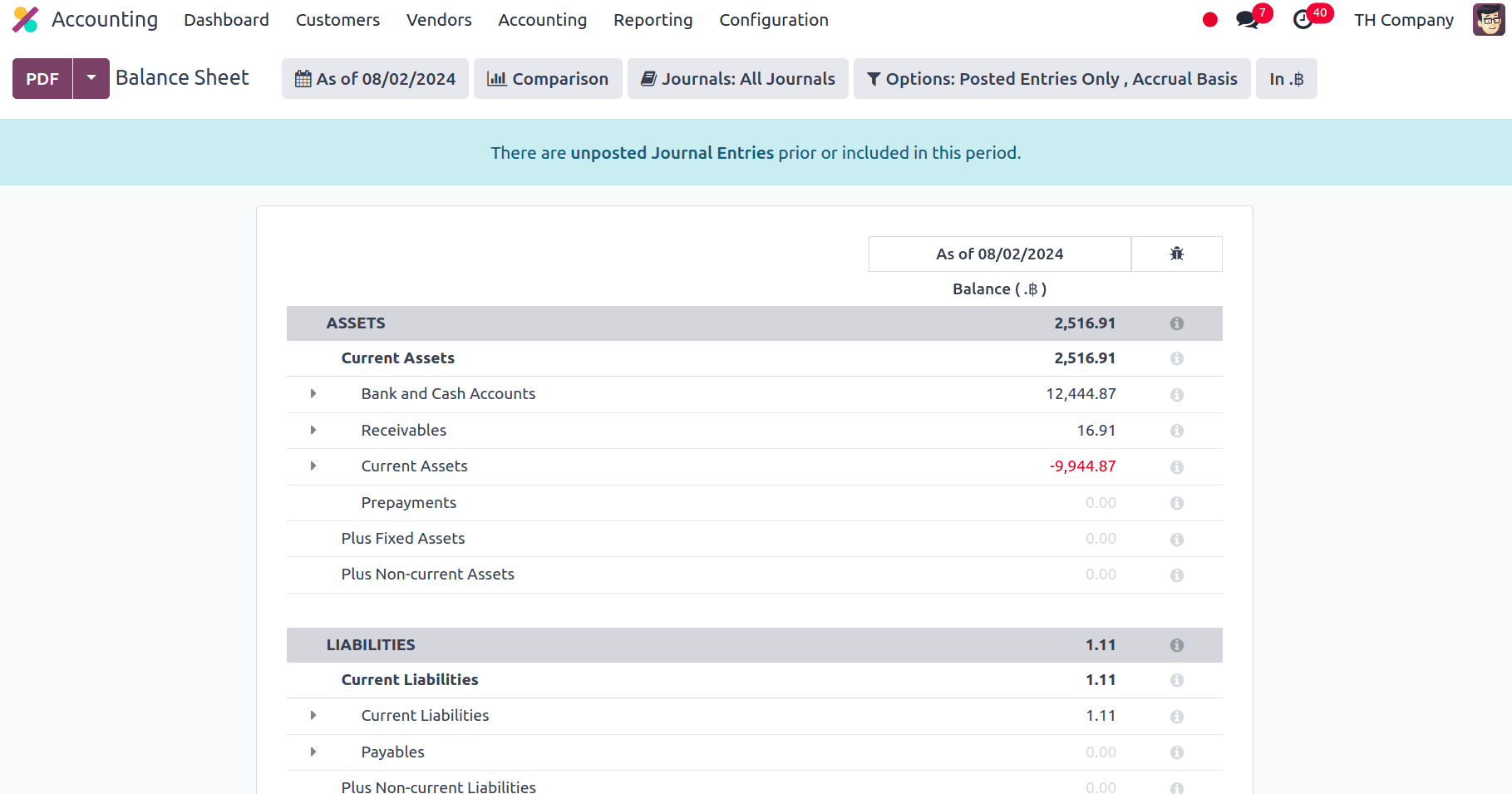
The assets area of the balance sheet includes items such as bank and cash accounts, receivables, current assets, prepayments, fixed assets, non-current assets, etc. Payables, current liabilities, non-current obligations, etc. are all included in the Liabilities section of the balance sheet. Current Year Unallocated Earnings, Current Year Earnings, Current Year Allocated Earnings, Previous Year Unallocated Earnings, and Retained Earnings are all included in the Equity section of the Balance Sheet.
Profit and Loss: A company's payments, expenses, and net earnings or losses for a specific time period are listed in a report called the profit and loss. It gives an overview of the business's financial performance throughout that time frame and is crucial for determining the profitability of the enterprise.
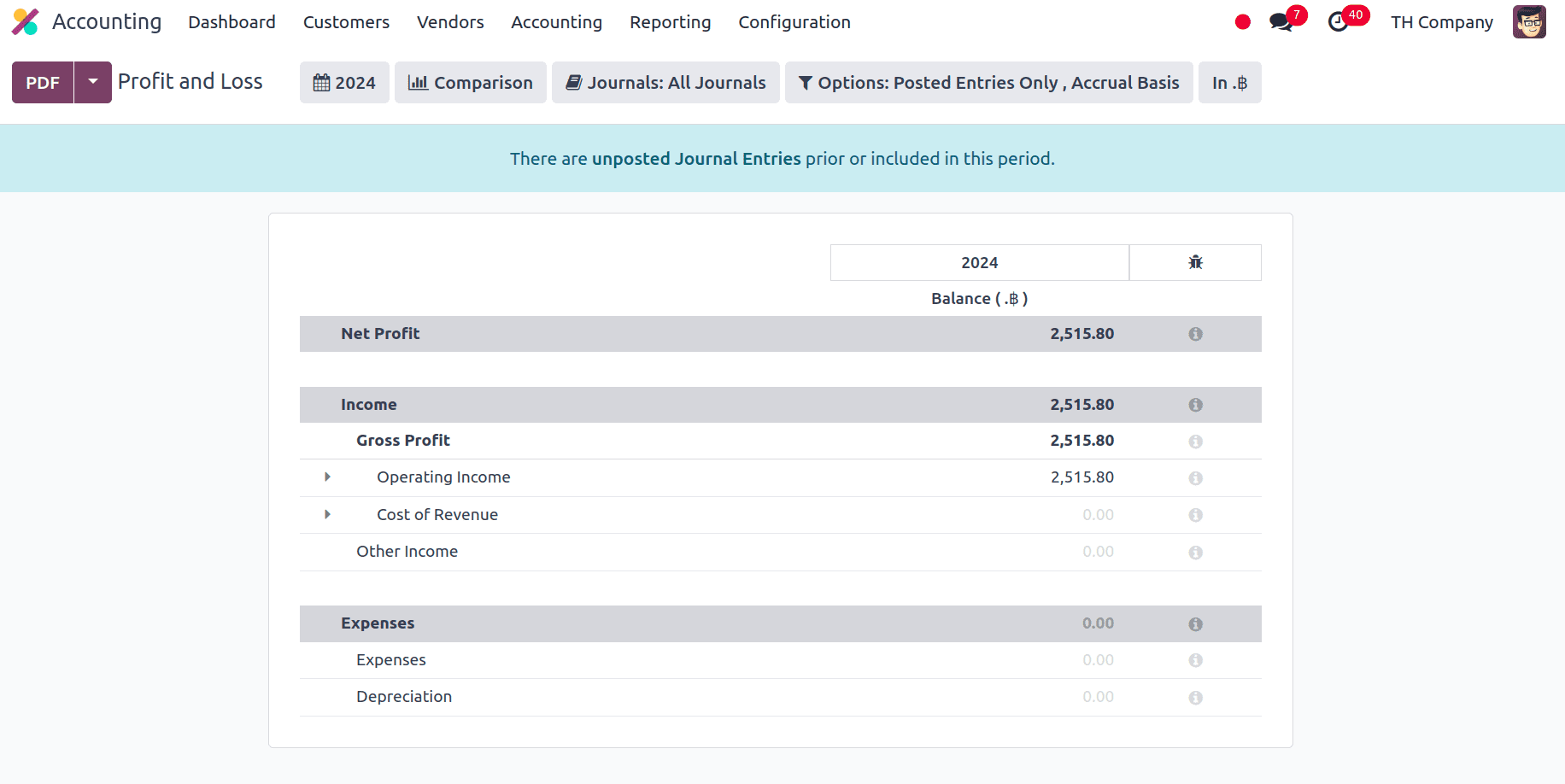
Under Gross profit we can see the operating income, cost of revenue and other income, expenses, and depreciation are under the expenses section, and other items are the primary components of Thailand company's profit and loss report. We can look at the Thailand company's tax report next.
From the Tax Report, we can create Excel files to submit the VAT to Thailand's Revenue Department. Go to Accounting > Reporting > Tax Report to create a sales and purchase tax report. Click Purchase Tax Report (xlsx) for purchase tax and Sales Tax Report (xlsx) for sales tax after choosing a certain period or range on the tax report.
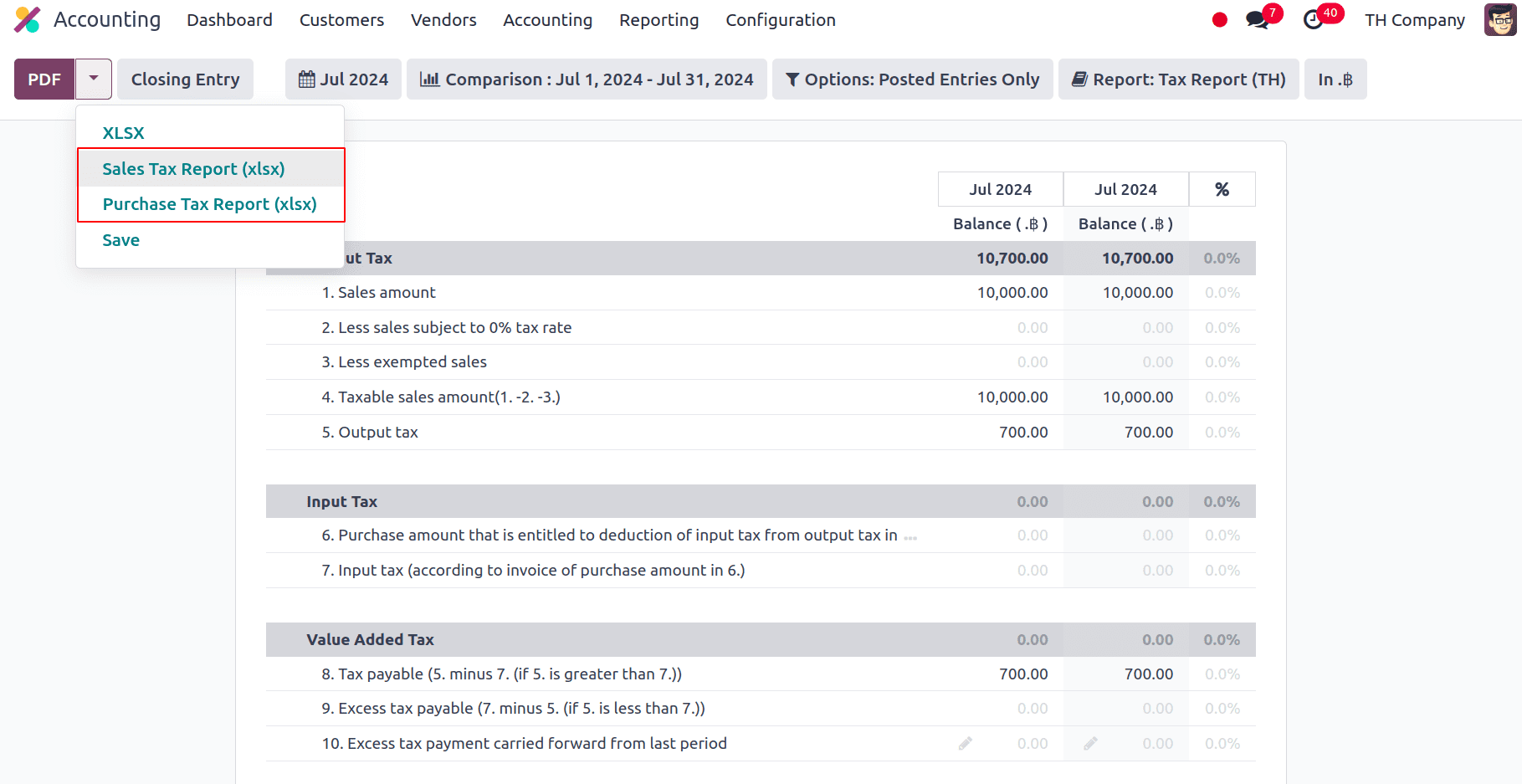
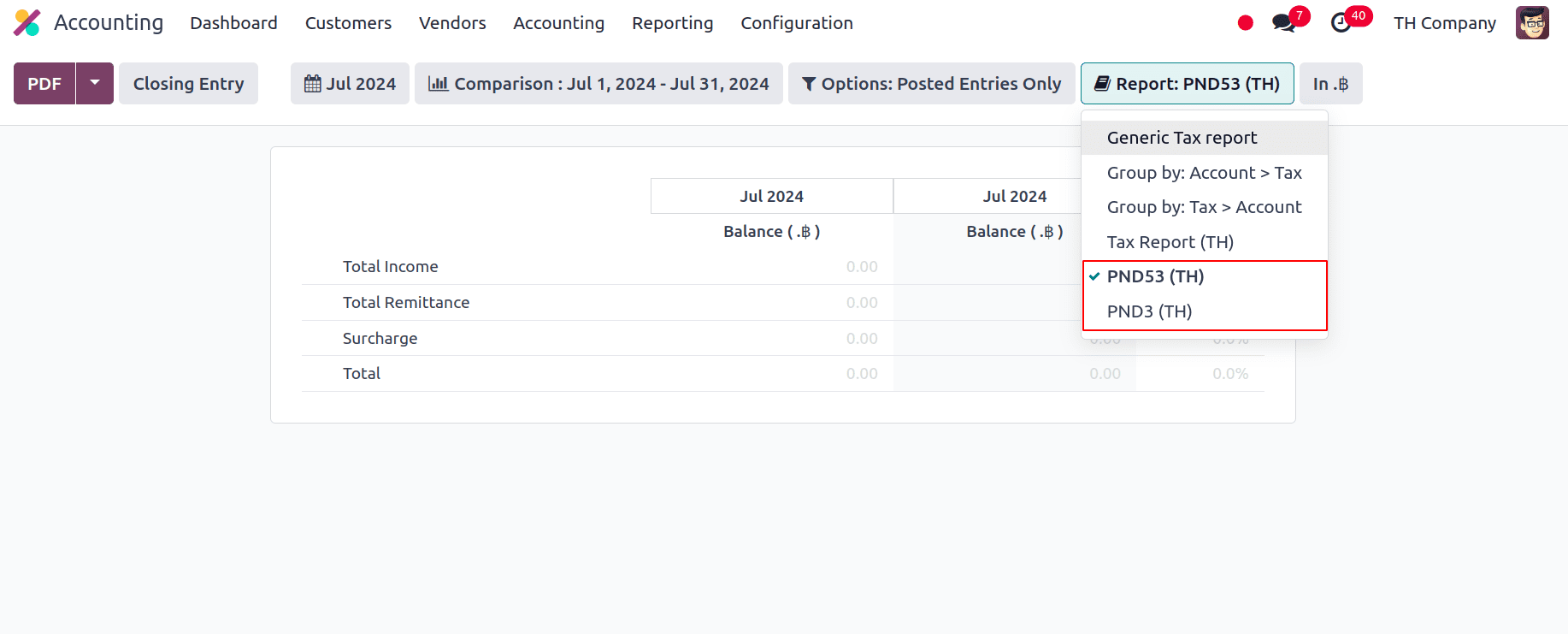
With the installation of Thai localization, under the Tax Reports we have PND53 (TH) and PND3 (TH) tax reports, PND report data presents the aggregated amounts of the relevant withholding corporate income tax returns (domestic) from vendor invoices.
In this blog, we have seen the changes that took place when we installed the Thailand Accounting Localisation. We have the option to print the tax invoice locally, and it also provides a very useful feature of Promptpay QR code on invoices, which enables users to pay their bills through their mobile phone with a Promptpay-supported mobile application. The localization facilitates compliance with Thai tax rules, improves financial reporting accuracy, and simplifies intricate accounting procedures. Businesses gain from increased operational effectiveness and a solid foundation for overseeing their financial operations in Thailand as a result.
To read more about An Overview of Accounting Localization for Japan in Odoo 17, refer to our blog An Overview of Accounting Localization for Japan in Odoo 17.