Another accounting method in Odoo 17 is called Anglo-Saxon, and it uses the product's cost of revenue record after it is sold out. Generally speaking, Anglo-Saxon accounting is only used by a tiny number of people worldwide. Additionally, the enterprise edition is the only one that offers Anglo-Saxon accounting.
Imagine a situation where products are ordered in large quantities. For example, a manufacturing company buys its raw materials in large quantities. Therefore, the income statement indicates that the company is losing money if all expenses are included. Anglo-Saxon accounting is the best way to fix this. In Anglo-Saxon, an item's cost of income is only recorded if, depending on the business, the purchased goods are used in production or sold out.
To begin with, switch on developer mode and confirm that Anglo-Saxon accounting is activated from the Odoo 17 accounting module configuration settings.
As was already established, expenses in Anglo-Saxon accounting are only documented upon the sale of the purchased object. The things are regarded as assets even though they were bought. Therefore, the inventory valuation in this scenario needs to be automated. Navigate to the product category to locate Automated inventory valuation.
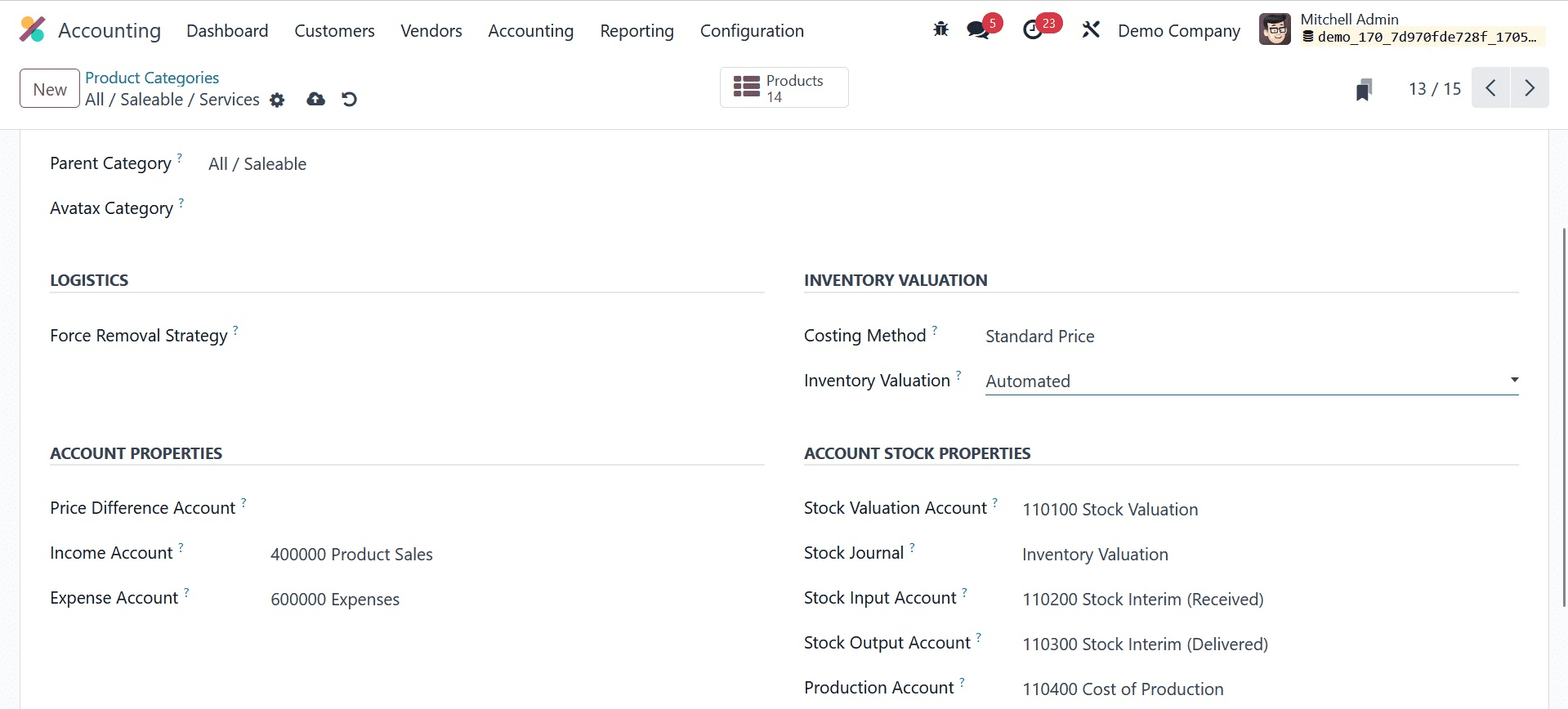
Additionally, either Average Cost (AVCO) or First in First Out (FIFO) should be used as the costing technique.
Let's go ahead and buy something from this category. The accounts are unaffected by the formation of the PO. On the other hand, stock entries will be made as soon as things are received.
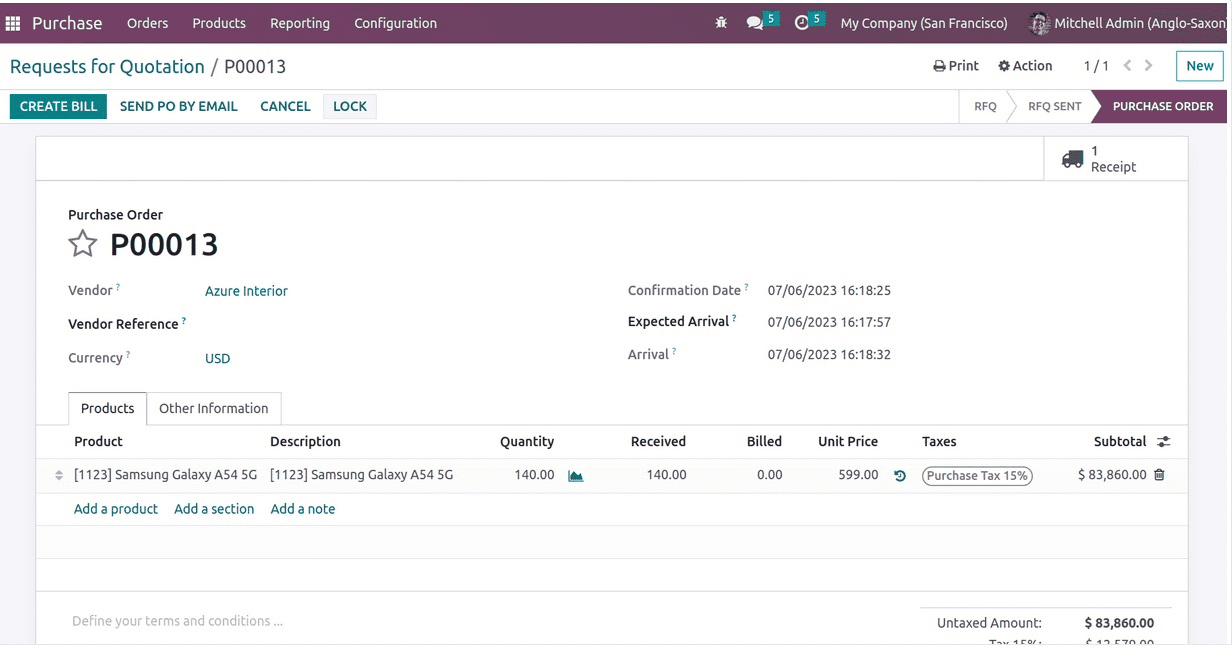
The purpose of creating a PO is to record the commercial transaction of the vendor "buy." Upon delivery, the value of the received stock will be noted in the "stock input account," which will raise the value of the already-existing stock.
Let us analyze the stock journal.
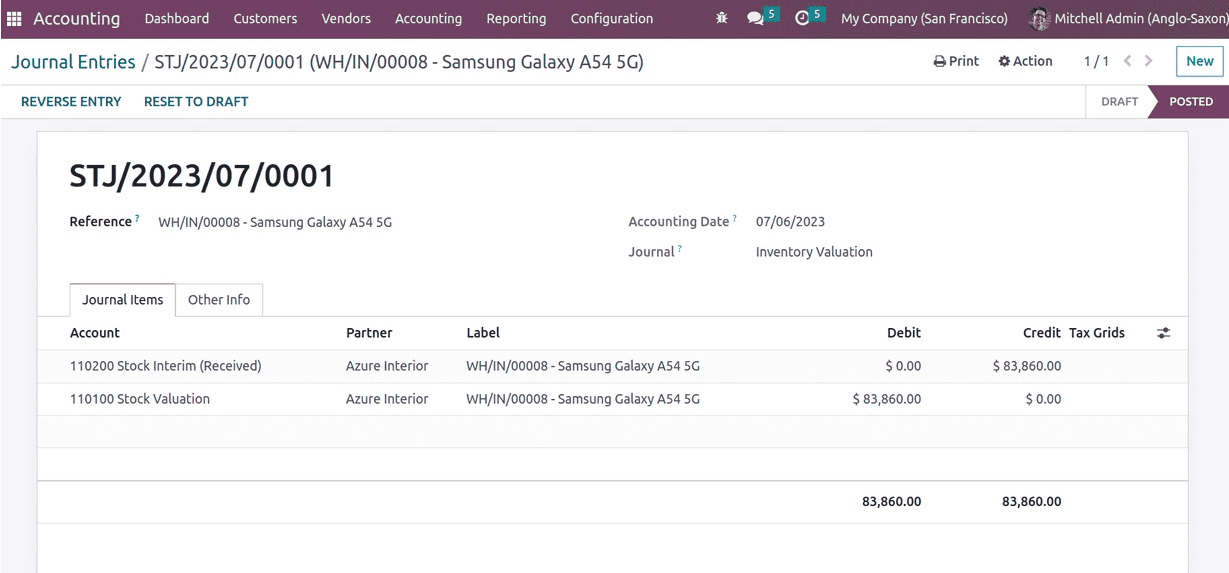
The nature of the stock is seen as a liability. The asset-liability chart will determine how the account is credited or debited when the asset value changes. Consequently, the stock interim received account is credited and the stock valuation account is debited. The current asset value is retained in an account used for stock valuation. As a result, if an asset increases, the stock valuation account is debited.
When the accounts for income and liabilities are increased, accounts are credited, and when the accounts for expenses and assets are increased, accounts are debited which is defined by the asset-liability chart.
The next action that will affect the accounting ledgers is the preparation of the purchase order bill.
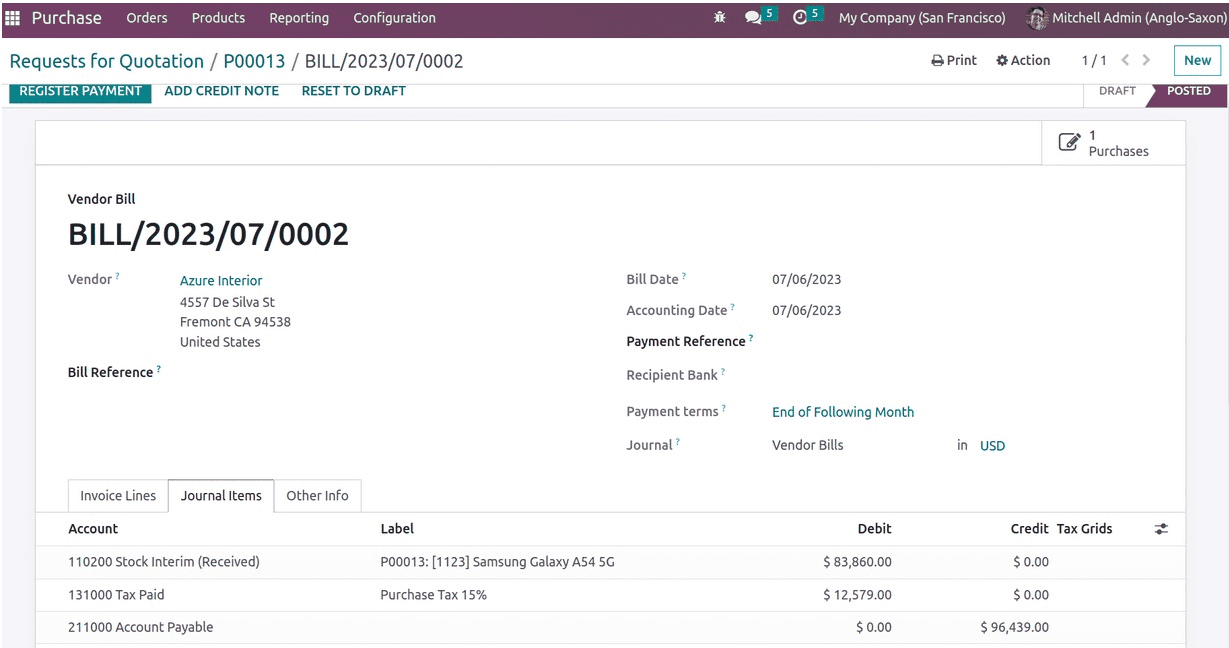
The primary distinction between the accounting of the Anglo-Saxons is as follows. In this case, the account for interim stock receipts is debited rather than the expense. This is a result of the acquired item being recognized as an asset rather than having its expense recorded in the ledger.
The stock interim received account is debited together with the tax paid when the asset value rises. The amount that must be paid to the seller is noted in the account payable which is a liability, and the account payable is credited when liability rises.
The bill status will change to "In Payment" after the payment has been registered.
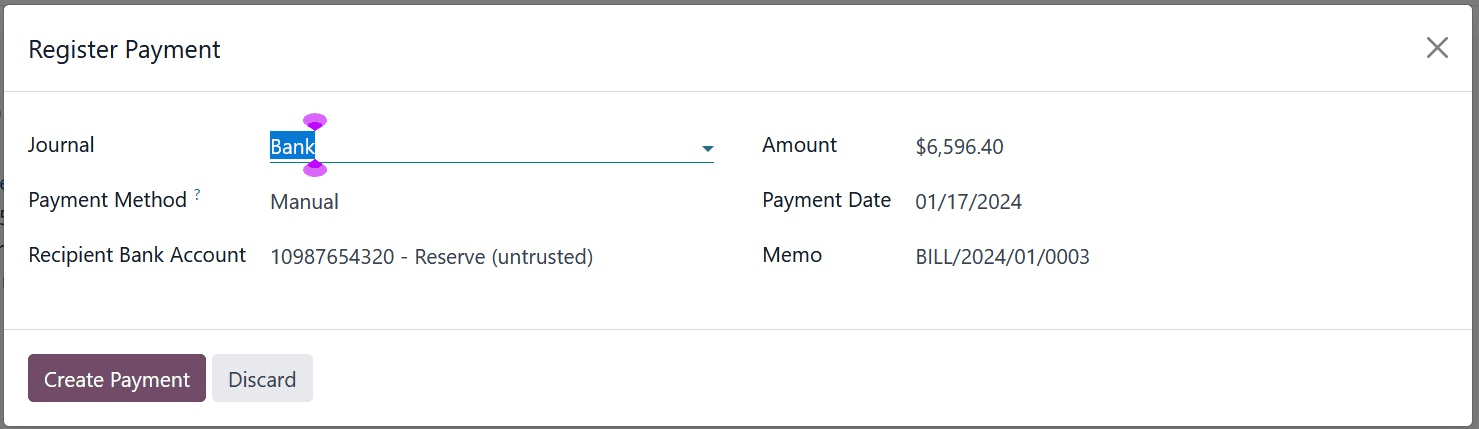
Then the account payable will be debited (as liability falls) and the outstanding payment account will be credited in the payment journal entry.
Later the imported bank statement and payment journal entries can reconciled. The processes of creating statements, uploading ledgers, and reconciling accounts are the same as those covered in our blog Continental Accounting in Odoo 17.
Let's now transition to a sales operation where a portion of the purchased goods are sold. At first, we paid an amount for some quantities. As a result, it does not record the expense; rather, it is retained as a stock. There are currently two quantities sold.
Making a selling order is a similar process to creating a document—no accounts are impacted.
The impact on stock accounts will occur after the delivery is verified.
Let's now examine the stock journal, which shows the debit to the stock interim delivered account. During a sale activity, the account is debited when the responsibility diminishes and the liability is sold out. The account is used for stock valuation, which is by nature an asset. Products that are sold out result in a fall in current stock value, which lowers the asset and credits the account.
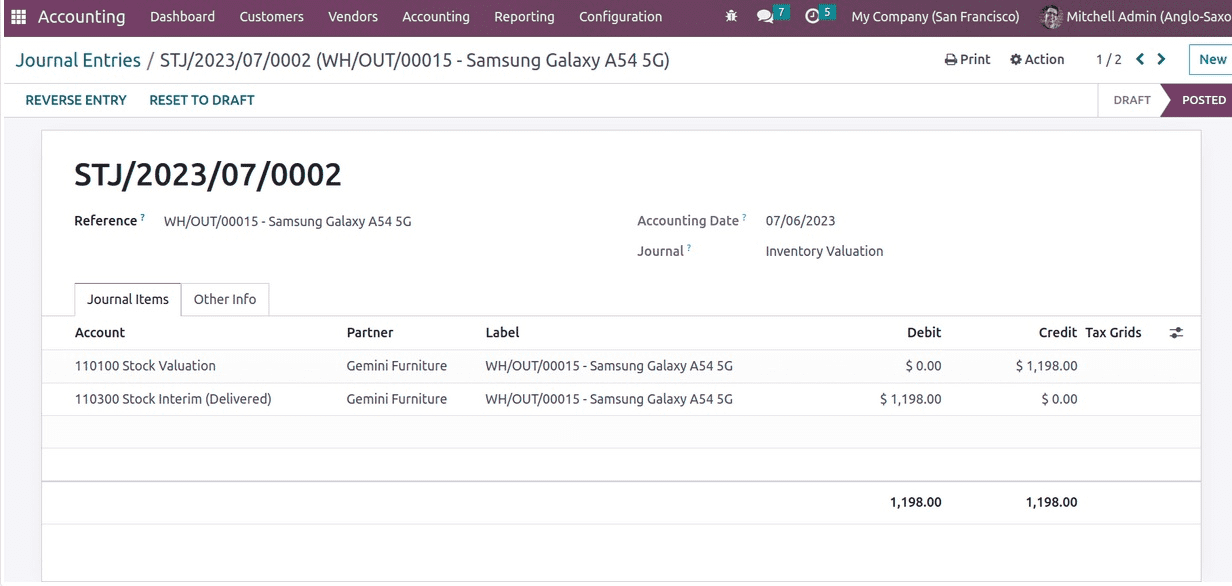
Here, the sold goods are merely $1198 in value. Now that you have an invoice for the order, it will be posted, and the expense will be noted in the ledger called "Expenses."
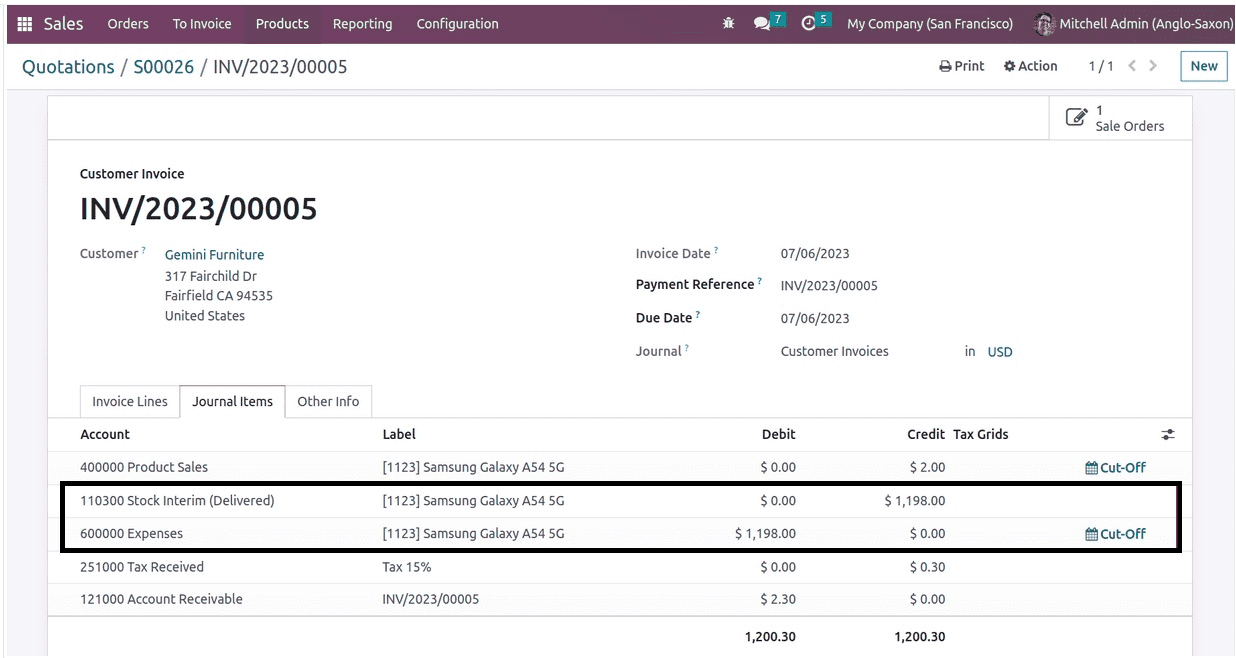
The income account in this case is "Product Sales," which is credited as income rises. Next is the stock interim delivered account. This time, the stock out is displayed and recorded as an asset. For this reason, the expense is debited (expense increases) and the stock account momentarily provided is credited. The expense has now been entered into the Anglo-Saxon accounting system.
Since the liability rises, the "tax received" is likewise credited. Next comes the asset known as the account receivable, which is debited as it grows. This invoice can be settled and reconciled later. The remainder of the procedure and the publishing of ledgers resemble the explanations found in continental accounting. The blog is a resource for you.
The Odoo 17 accounting module's Anglo-Saxon Accounting functions in this manner. The product is recorded as an asset, and only the expense is impacted when it is consumed for any other operations like production or sold out.