Routes are the different means of obtaining and selling specific products from a warehouse. Routes might or might not rely upon products/items, the stockroom, the order lines for deliveries, or some other. The system must search for rules relating to routes defined in general by sales order to satisfy a procurement. A procurement is nothing but a demand for a particular place/venue for a certain amount of product. One has to have critical rules on move and procurement to make a path in this route.
For simple product management, Odoo ERP comes with an advanced push/pull path setup.
If you need to know more about Routes and Rules, refer to the following blog: How to Use Push and Procurement Rules in Odoo.
Application of Rules in OdooSales
When applying for sales, assume that we need to take several measures before shipping a product, such as quality control, packaging, and so on. Odoo can manage advanced pull routes configuration. Let us see in detail.
The make-to-order is an example of a pull inventory control process. The aim is to reduce stock levels by giving just enough amount of stock, not pretty much, to fulfill the need of the consumer. By reducing the amount of storage space available for stock and the price of processing items, the MTO program also reduces the wastage of stock.
To learn more about MTO and MTS, refer to Make to Order and Make to Stock in Odoo 12.
Configuration: Rules are part of the routes.
Go to Inventory application -> Configuration -> Settings -> Tick “Multi-step Routes”.
Go to Inventory application -> Configuration -> Routes
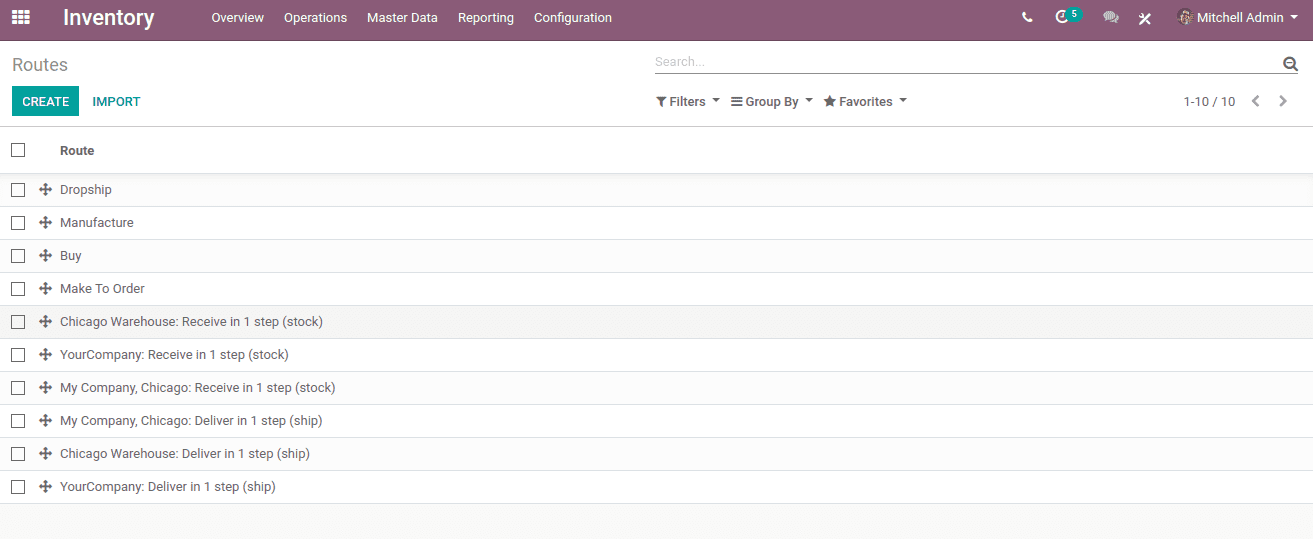
Odoo ERP's default routes include Dropship, Manufacture, Buy and Make To Order
1) Dropship: The supplier does not keep the products in inventory under the Dropship rule, but manages the shipment of the goods directly from the vendor to the customer. During the transit, there will be no stock housing.
2) Manufacture: It proposes to produce it (manufacturing order).
3) Buy: It proposes to buy (purchase order).
4) Make To Order: The function Make to Order triggers a purchase order as soon as a product-related sales order is generated. Here, although the product quantity is insufficient, the function does not assess the current stock and draft a purchase order. It triggers the purchase order irrespective of the quantity of the product in hand.
Under the product's inventory tab we can see the routes for each product.
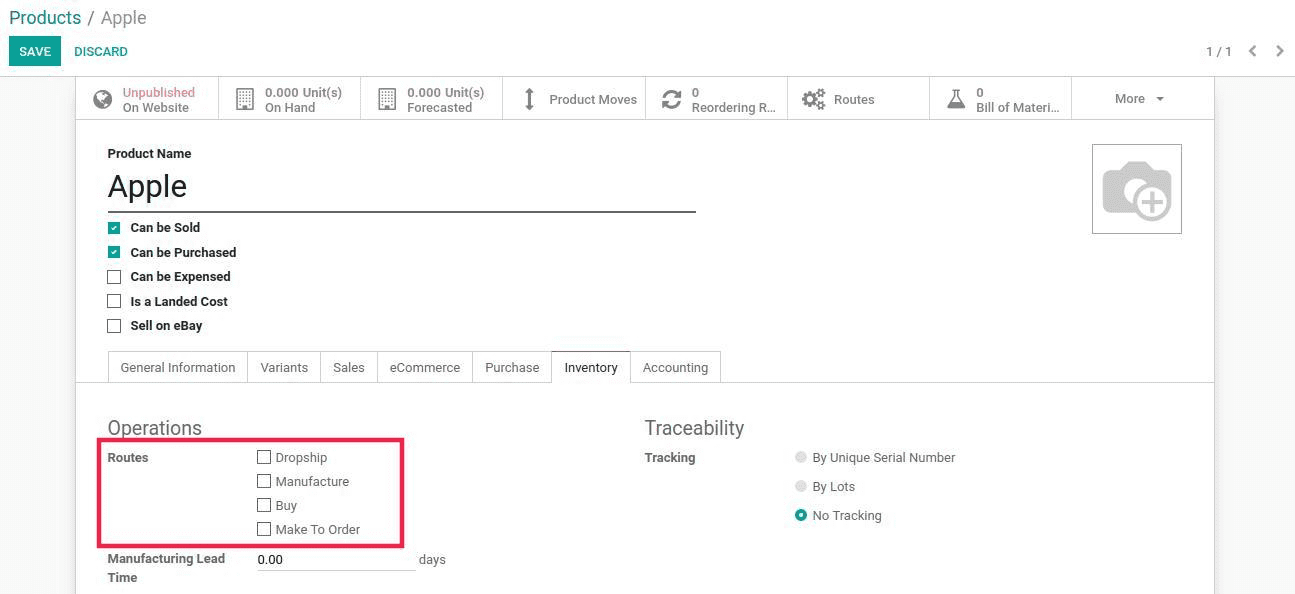
For creating Custom Routes
Go to Inventory application -> Configuration -> Routes -> Create.
Click the Create button for creating a route.
A new window will appear as shown below,
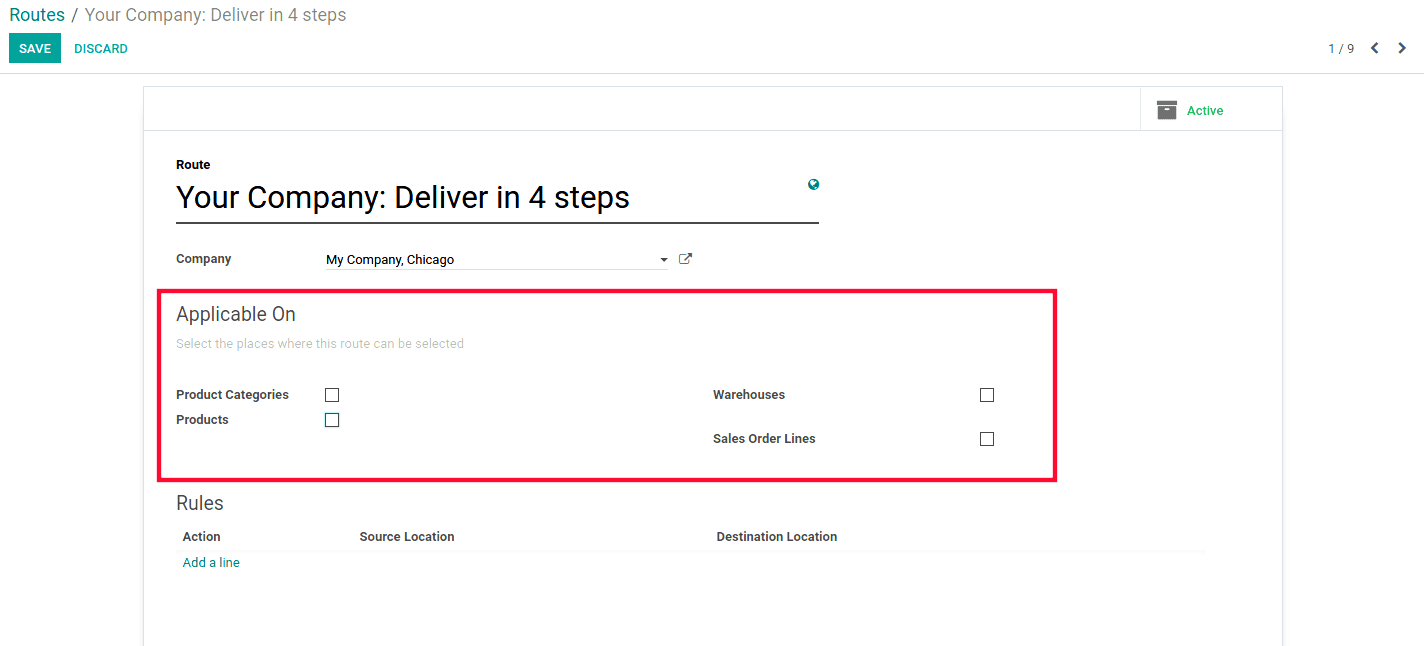
Here under the Applicable section, we can select the places where this route can be used for.
1) If you select Products Categories, the route for the product category will be selectable. This takes precedence over the route of the warehouse.
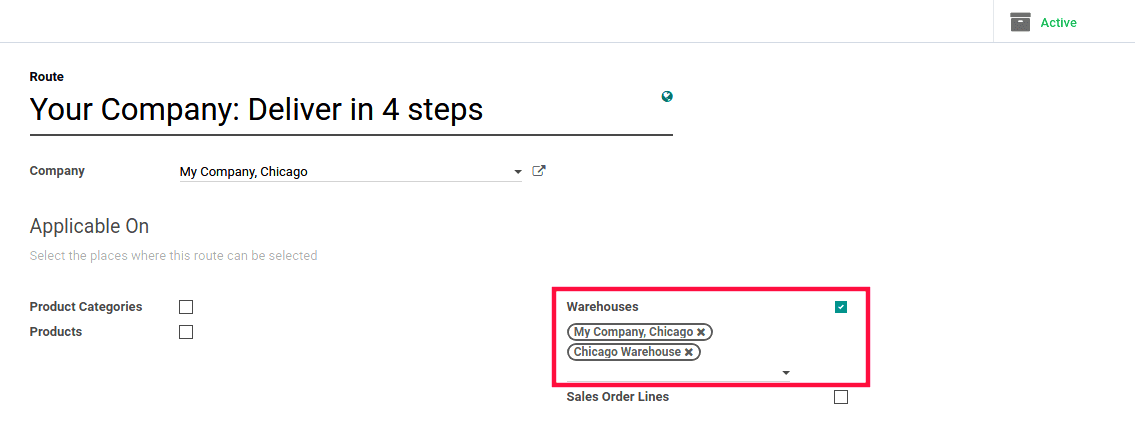
2) If you select Warehouses, as products go through this Warehouse, this route should be seen as the default routes. This action may be overridden by the product/product category routes or the procurement preferred routes.
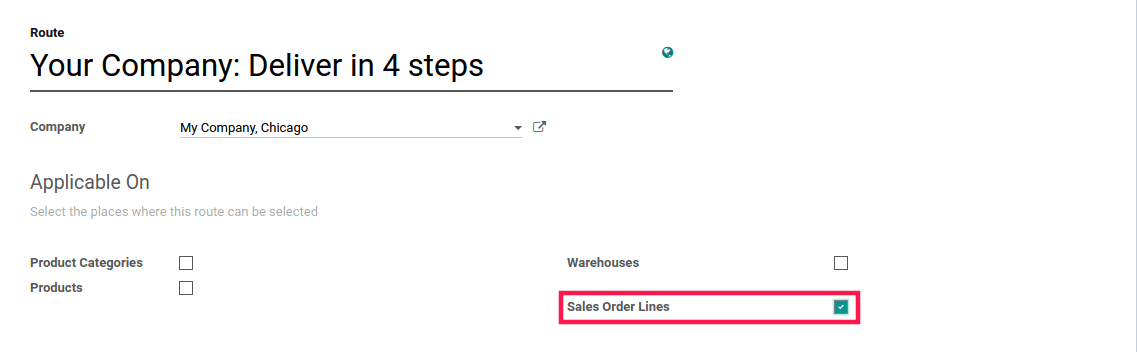
3) If you select Sale Order Line, you need to choose the routes for each line of your sale order.
4) If you select Products, the route will be selectable in the inventory tab of the product form. It will take precedence over the route to the warehouse.

In the case of Product Categories, we need to set the route manually at the Product Category under Logistics.
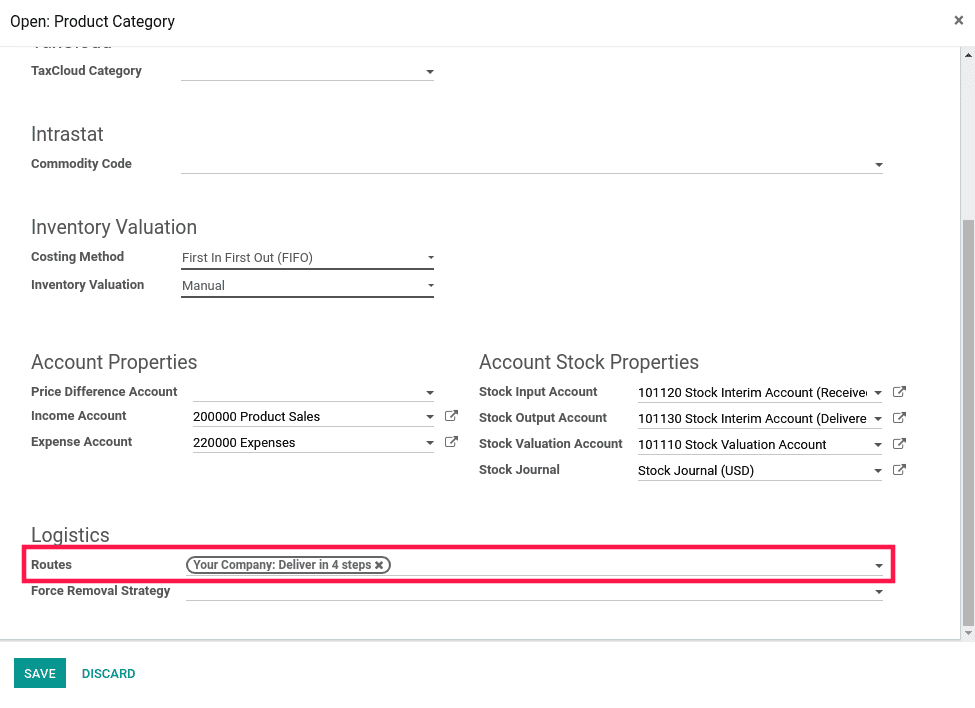
We need to choose which warehouse will be applied when you activate the warehouse. The route will be set in that warehouse for all transfers that would meet the rule's conditions.
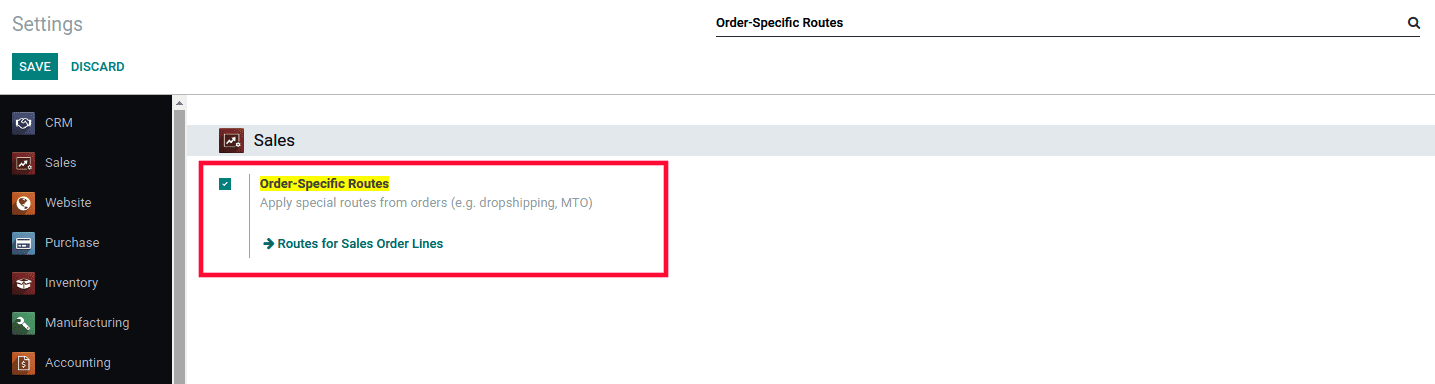
In the case of Sale Order Line, we need to set the route manually at the Sale Order Line. Before that, we need to configure Order-Specific Routes under Sales Settings.
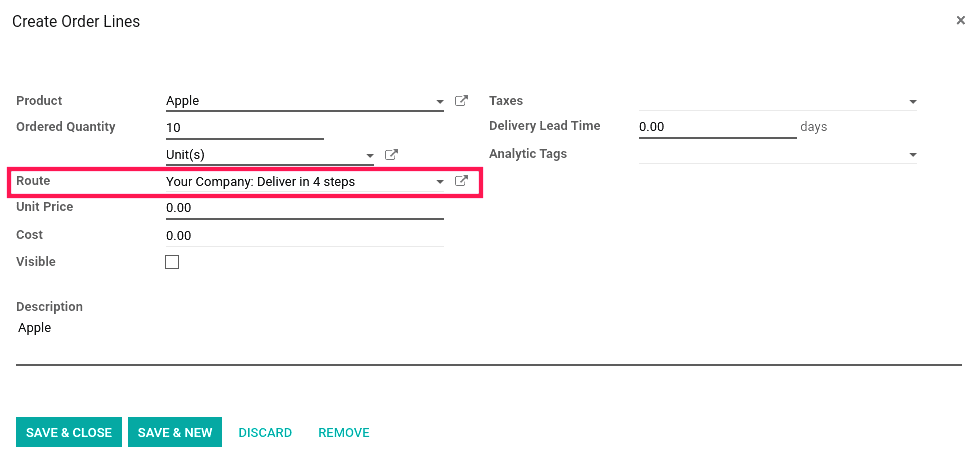
Here we can choose the route to create sale order window.
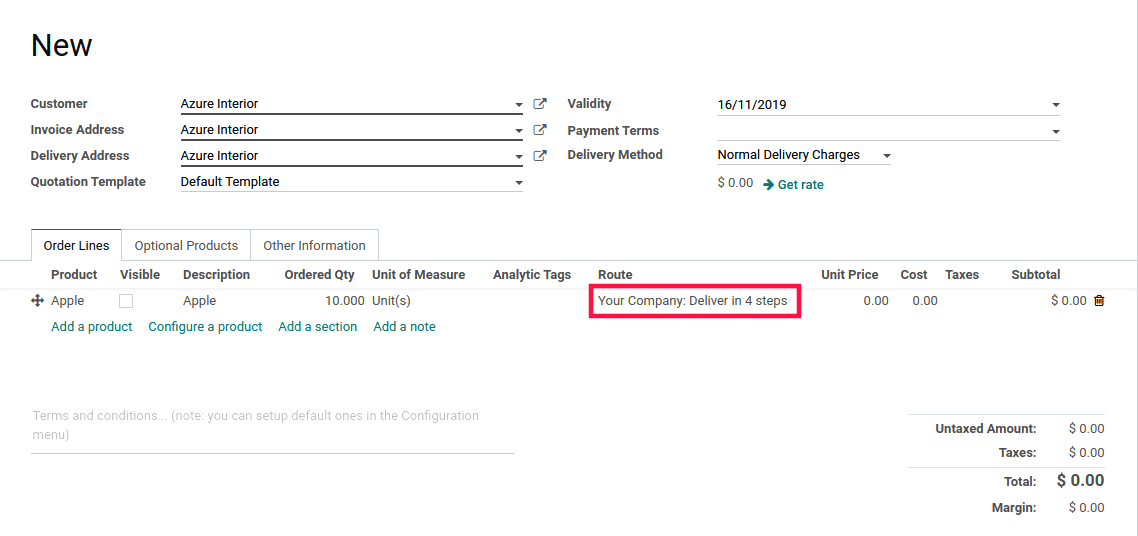
We can see the route under the sales order line.
In the case of Products, we need to set the route under the inventory tab of that product.
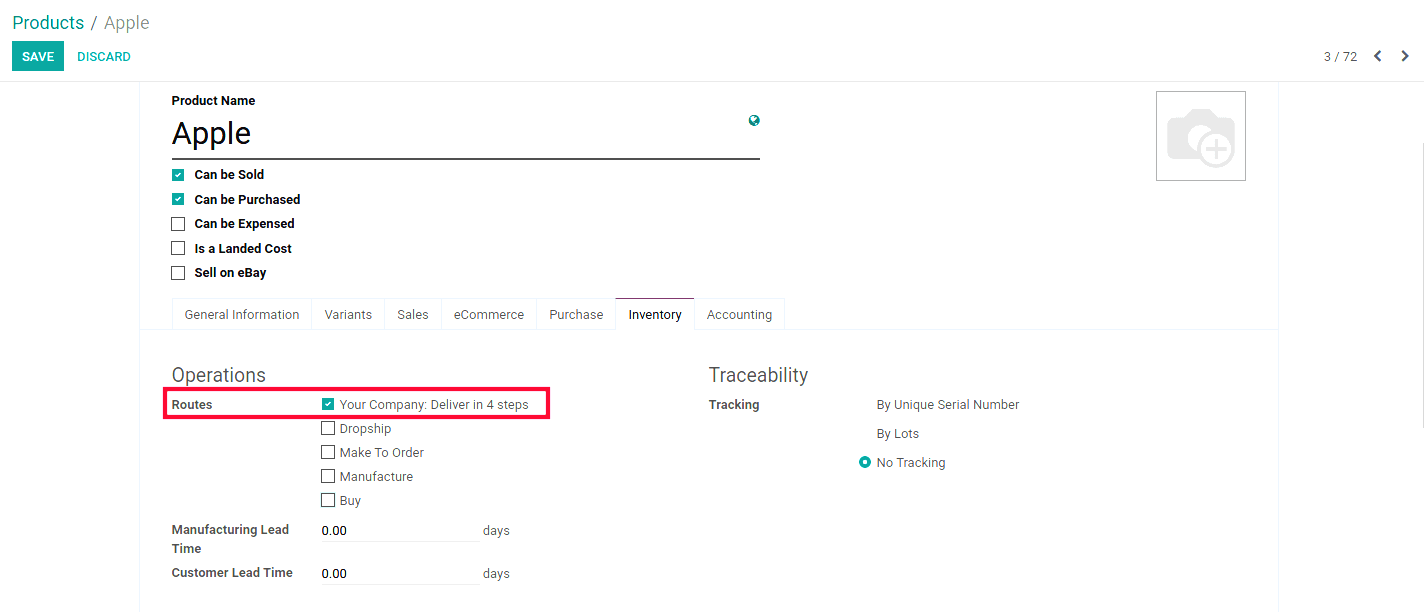
We can see the Route under Operations.
Here an example of how it works for the case of Route Applicable on Products.
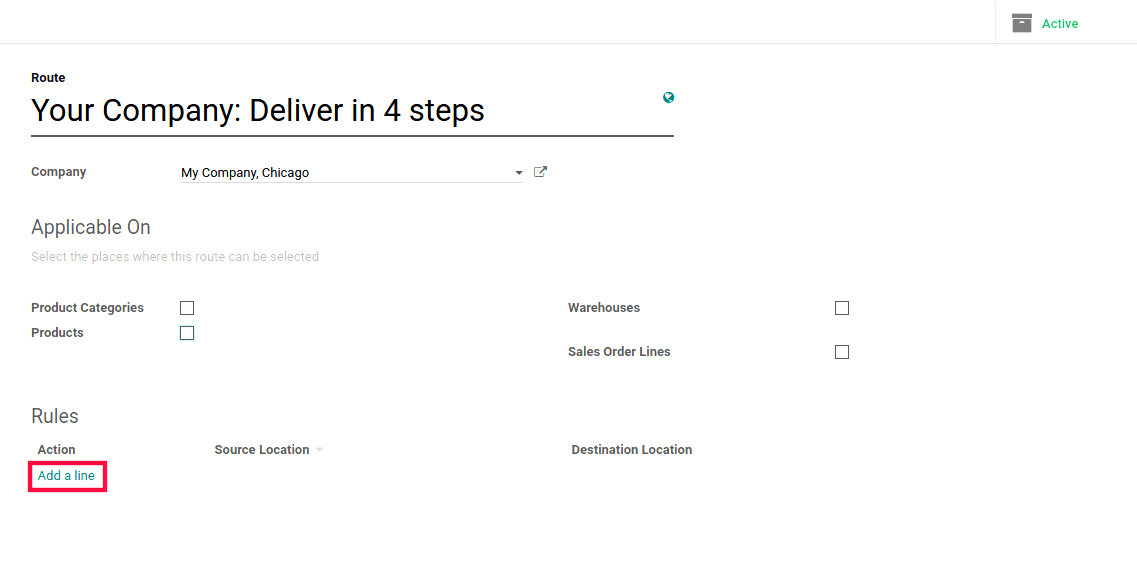
Click Add a line under Rules for creating rules.

One can fill the following fields here.
1) Operation name: This field contains the name of the rule which is created.
2) Action: Possible Actions are:
> Pull From
> Push To
> Pull & Push
> Manufacture
> Buy
3) Operation Type: In this field, one can specify the operation type that will be put on the stock moves.
4) Source Location: This is the location in which the rule can be applied when a move is confirmed.
5) Destination Location: This is the new location where the goods need to go.
6) Automatic move: In Manual Operation, the value will create a stock move after the current one. In the Automatic No Step Added, the location is replaced in the original move.
7) Move Supply Method: In Taking From Stock: The products will be taken from the available stock. Trigger Another Rule: A procurement will be created in the source location and the system will try to find a rule to resolve it.
8) Delay: Under the field, you can specify the delay needed to transfer the goods.
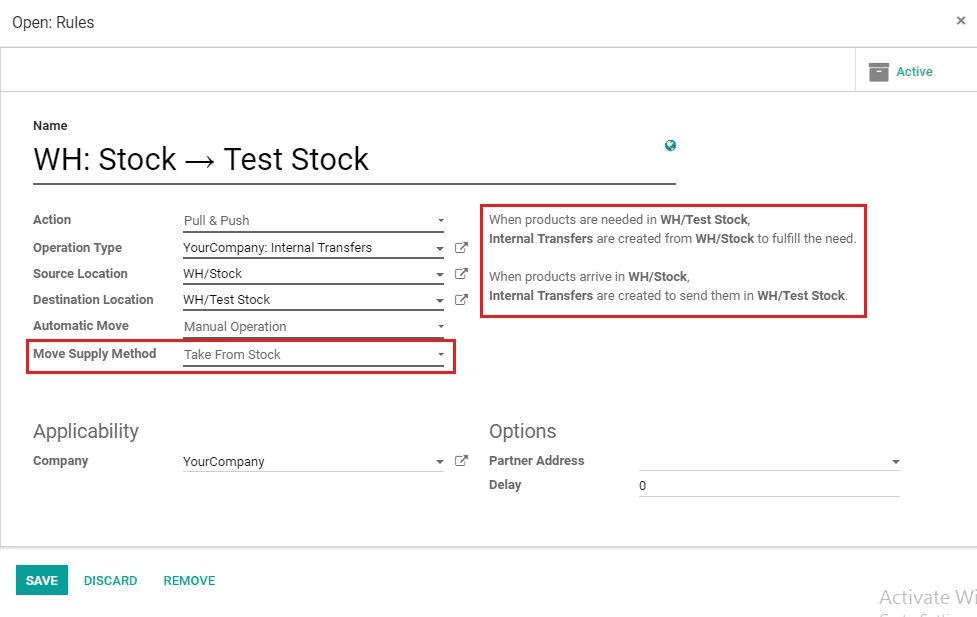
First Rule: Here we have to choose Move Supply Method as Taking From Stock, because of the first move that is from the stock itself.
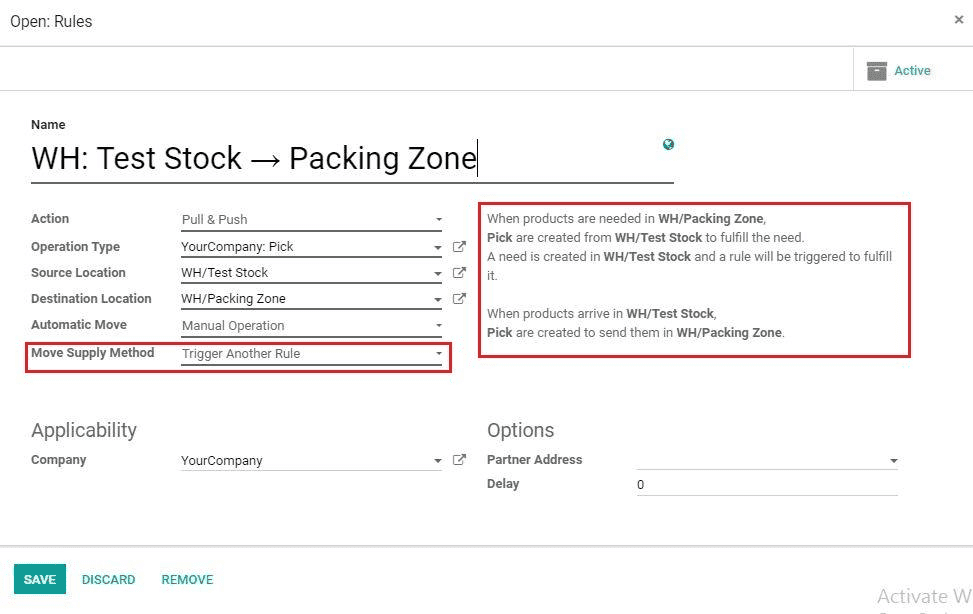
Second Rule: Here we have to choose Move Supply Method as Trigger Another Rule.
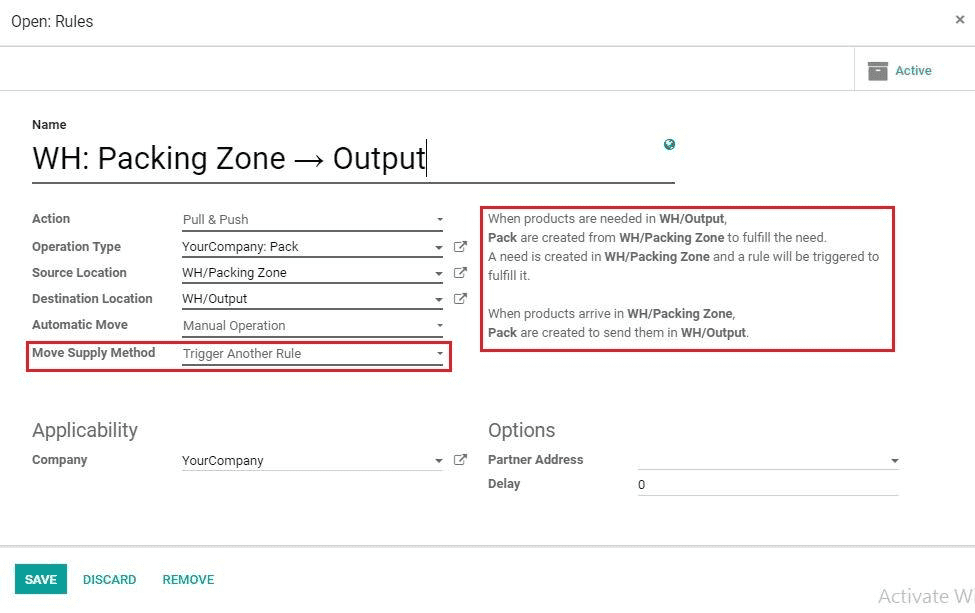
Third Rule:
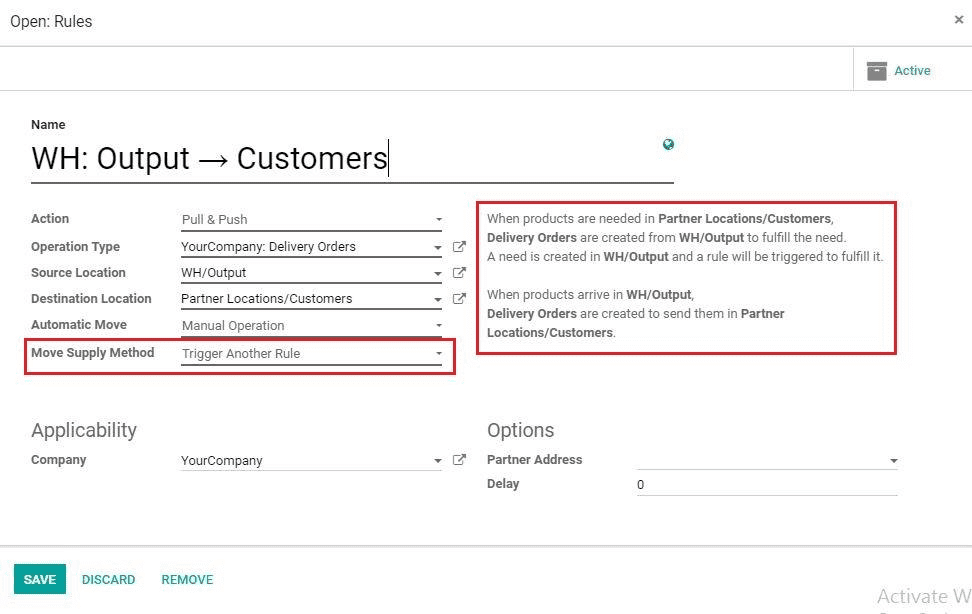
Fourth Rule:
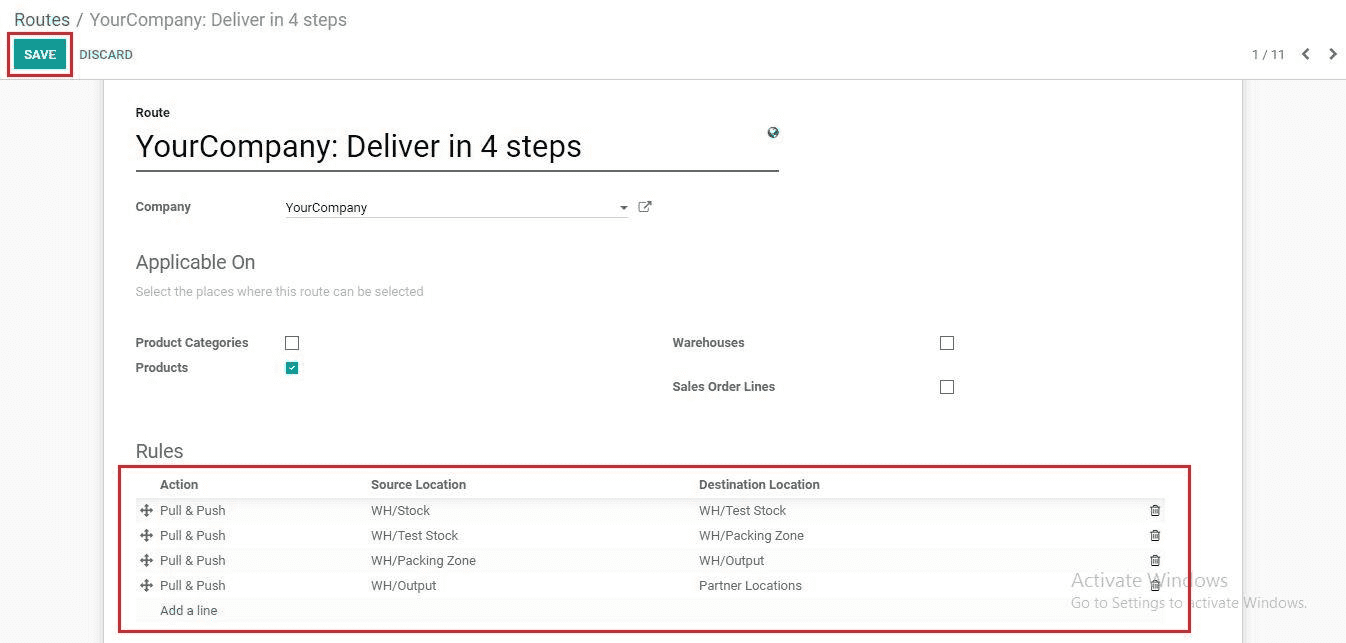
After creating the Rules, we can see the rules. Click the Save button.
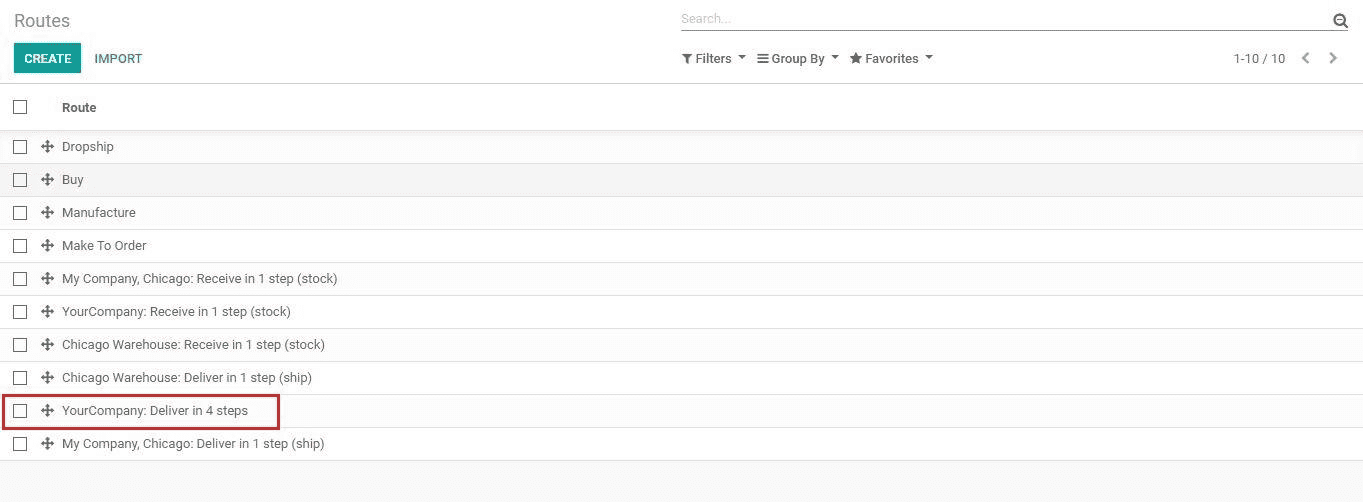
We can see the route we created in Configuration -> Routes.
Now, we have to set the Route under Inventory tab of the product which we want to sell.
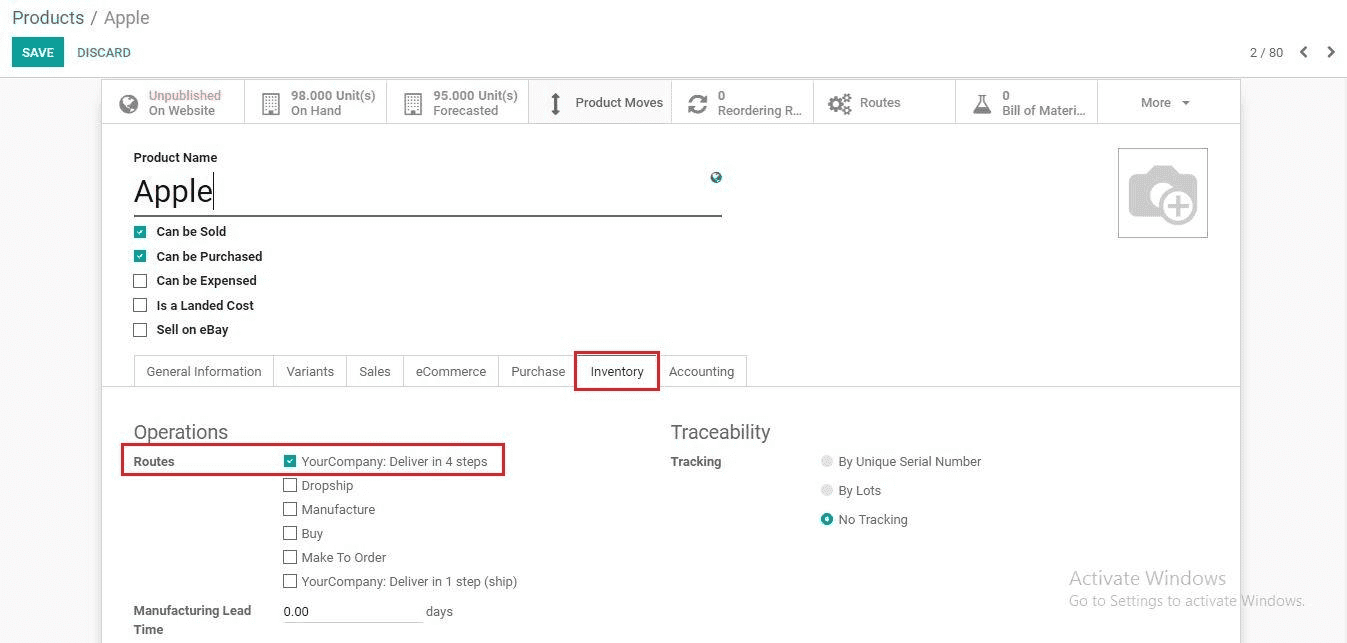
Tick: Your Company: Deliver in 4 steps. Click the Save button.
Then we have to create a Sales Order.
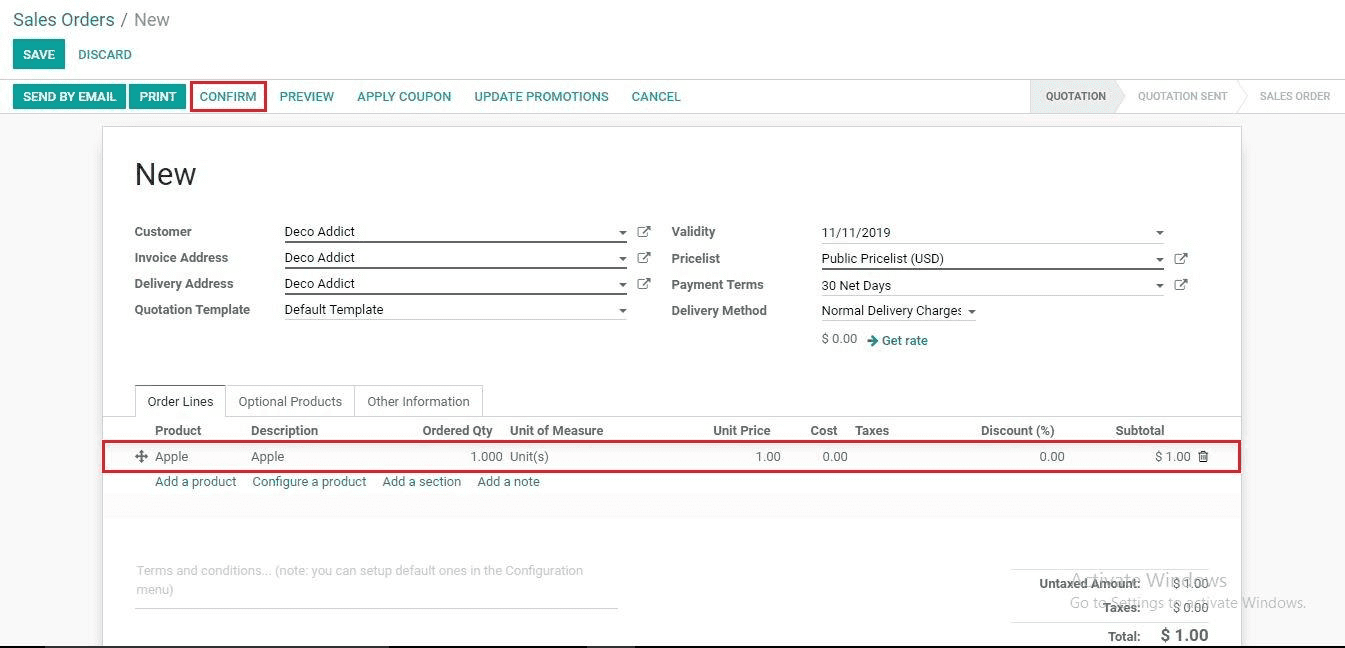
Select the product on the Order line and Confirm the sales order.
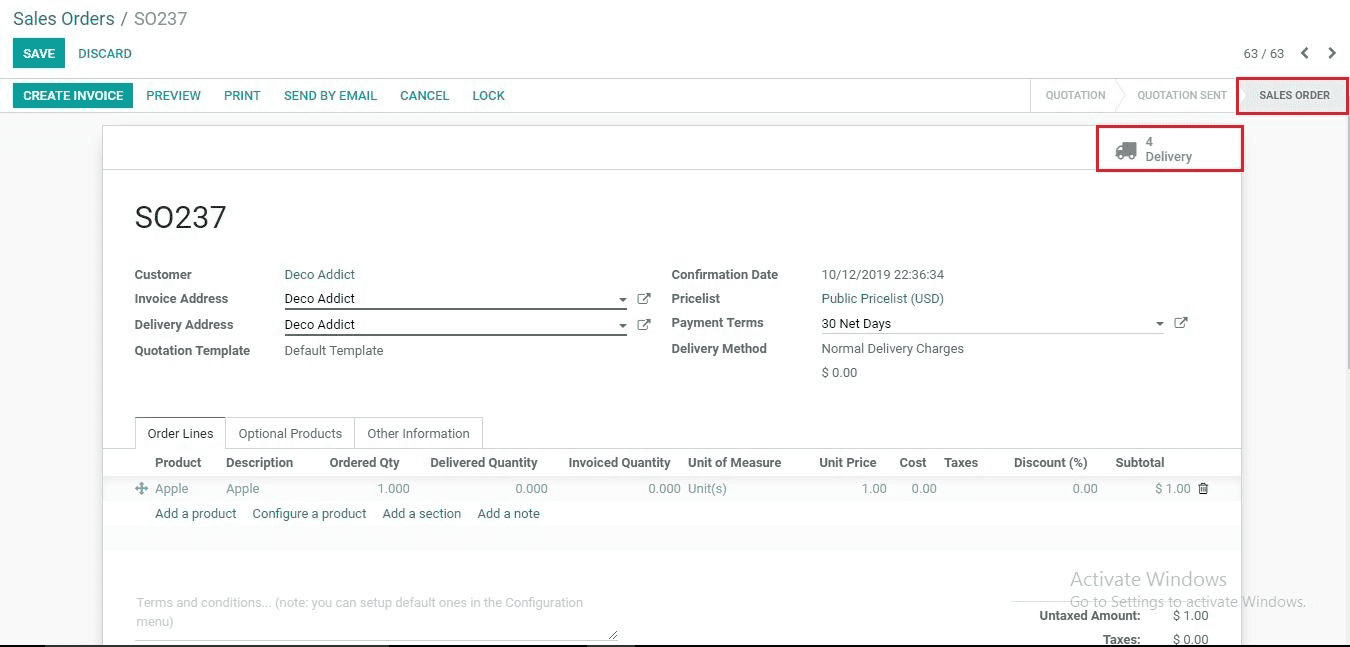
Here we can see the stage is changed. Click the Delivery button to see the four steps.
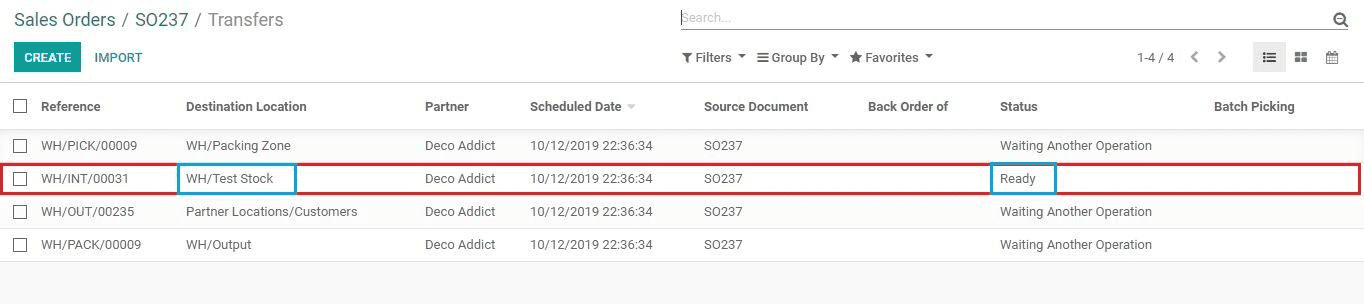
The status of the first step as Ready and all others are in Waiting for another operation.
Click to open the first step.
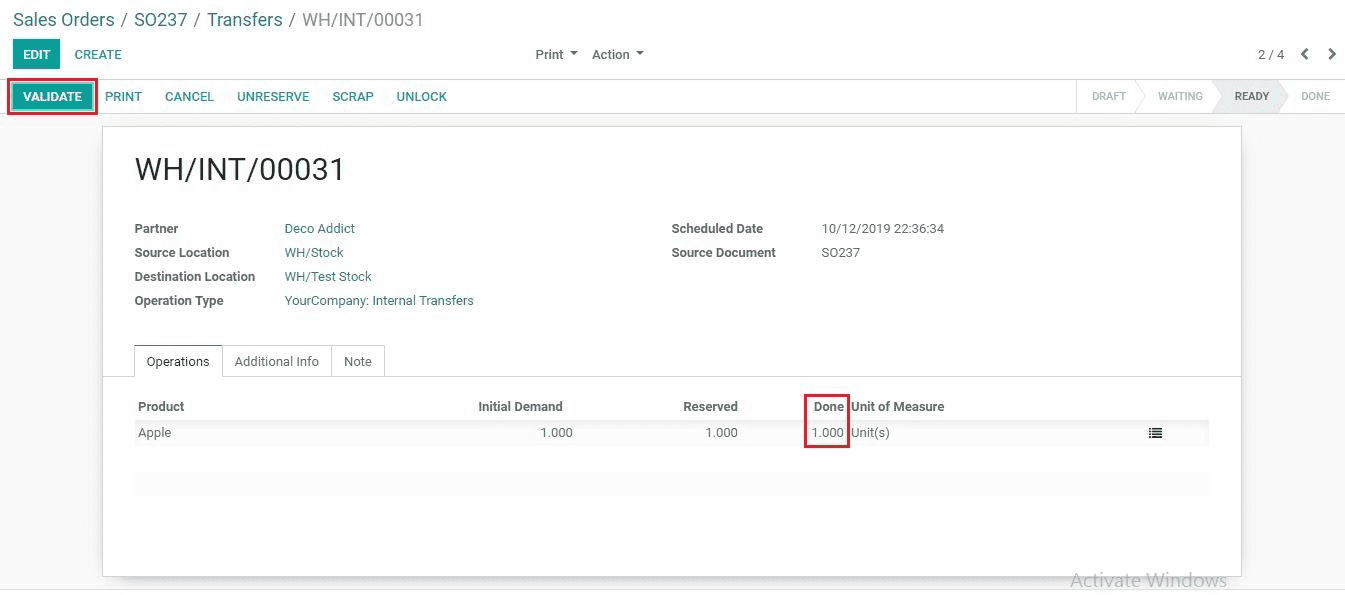
Mark the done quantity and click the validate button.
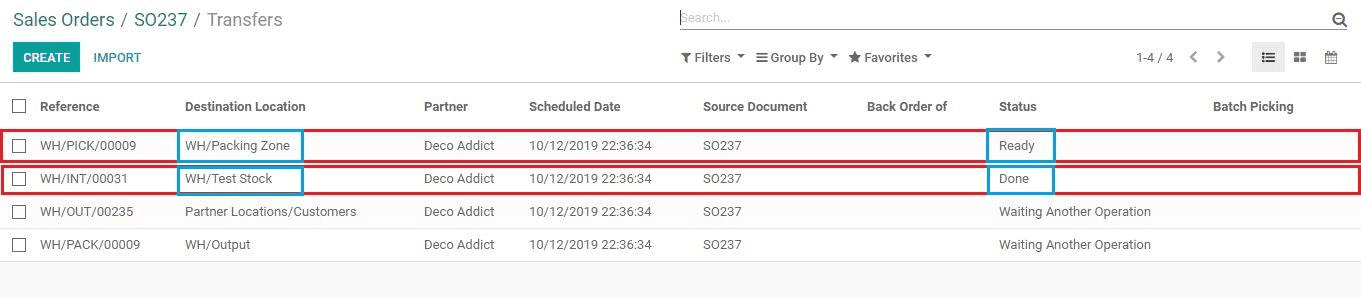
Here we can see the status of the first move as Done and the second move as Ready.
By clicking each move and validating it, delivery will be done and the product is reached at Partner Locations/Customers.
Under the transfers, we can see all the statuses are in the Done state. That means the delivery is successfully reached to the customer using four-step method.
In this method, we can add several steps to the rules for the transfer of the product before selling.
This is how the application of rules in sales happens.