Odoo accounting localization is modifying and adjusting the accounting module to satisfy the unique legal, financial, and regulatory needs of other nations or areas. This guarantees that companies with many locations can effectively oversee their accounting procedures while respecting regional norms and guidelines.
The purpose of Odoo accounting localization for Tunisia is to modify the accounting module according to the unique tax laws, financial rules, and reporting standards of Tunisia. Businesses operating in Tunisia will be able to effectively manage their accounting procedures and follow local legal and regulatory frameworks with this localization.
Installing the modules needed for the Tunisia accounting localization in Odoo is the first step that needs to be done by going to Apps. From here, we can install the required modules for the localization.
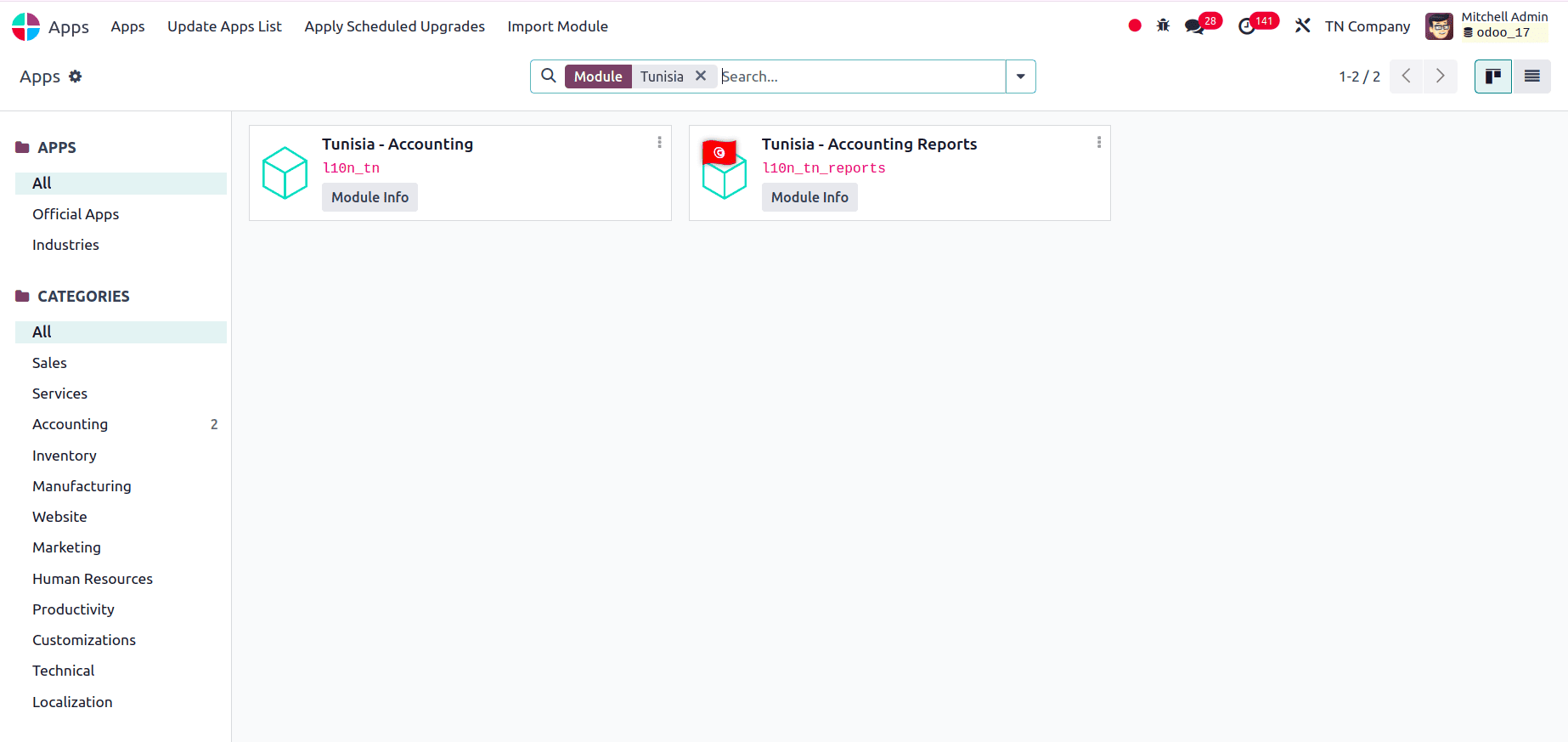
Now, we can set up the company by providing all the details correctly or checking the details of the company that is already set up. Goto Settings > Users and Companies > Companies, and we can select the company to check its configuration.
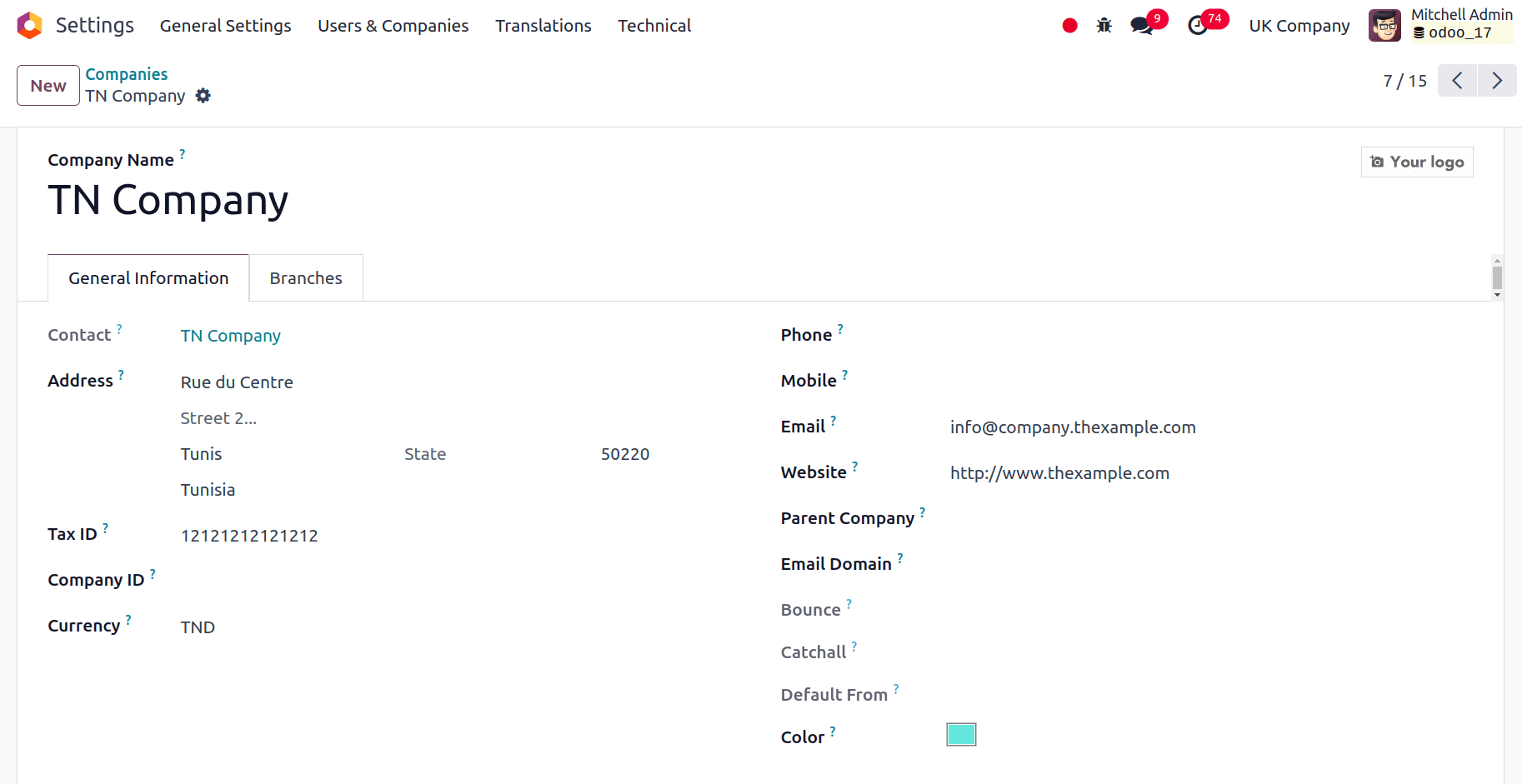
Fiscal Localisation will be set to Tunisia in the accounting module configuration settings.
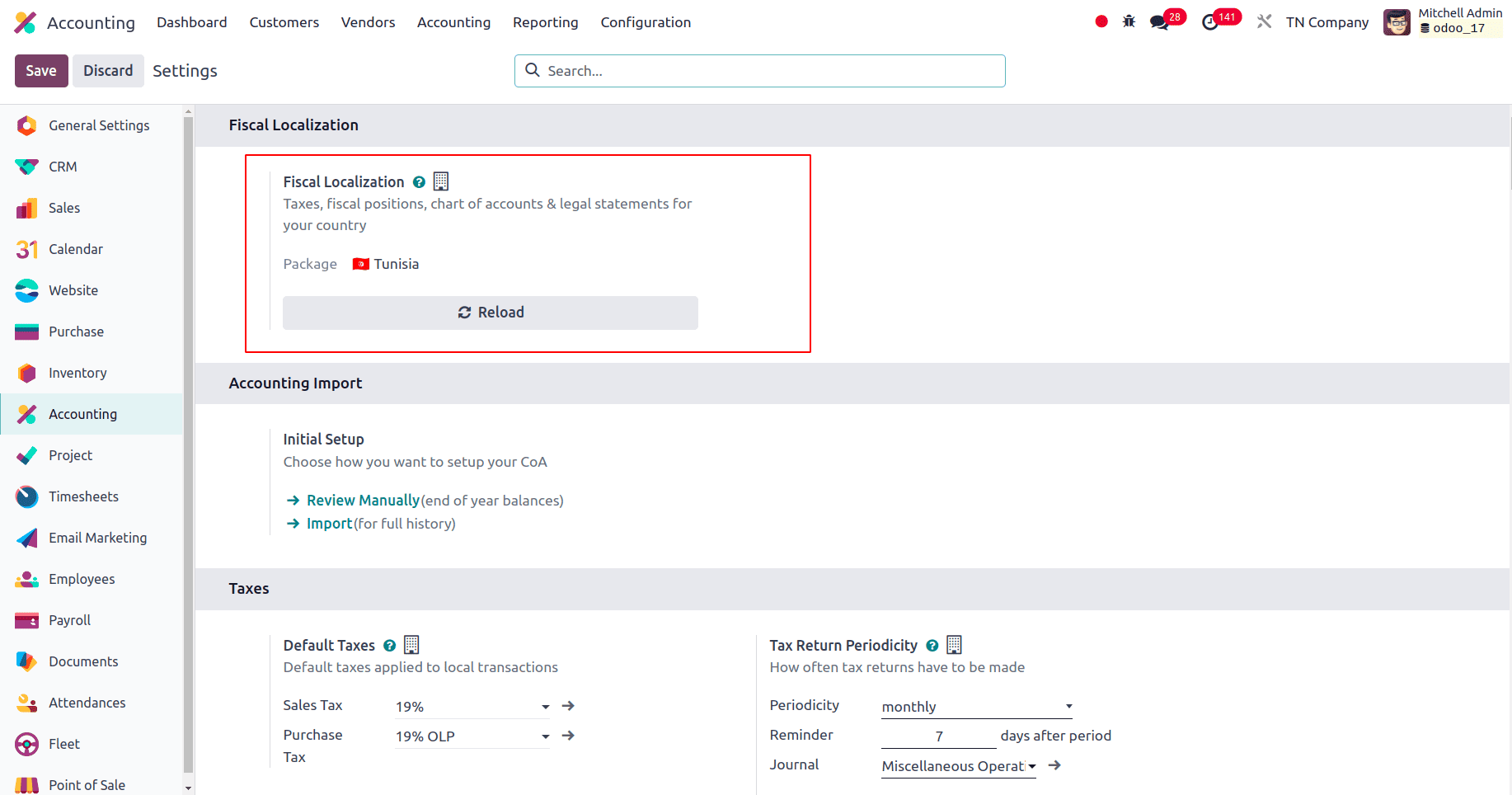
Default taxes are utilized to automatically apply tax rules to your financial transactions and invoices, and with this, accounting becomes more precise and efficient. Here, for this localization, the Default Taxes are set to 19% Sales Tax and 19% OLP for Purchase Tax.
The official currency of Tunisia is the dinar (TND), so the Main currency will be set to that.
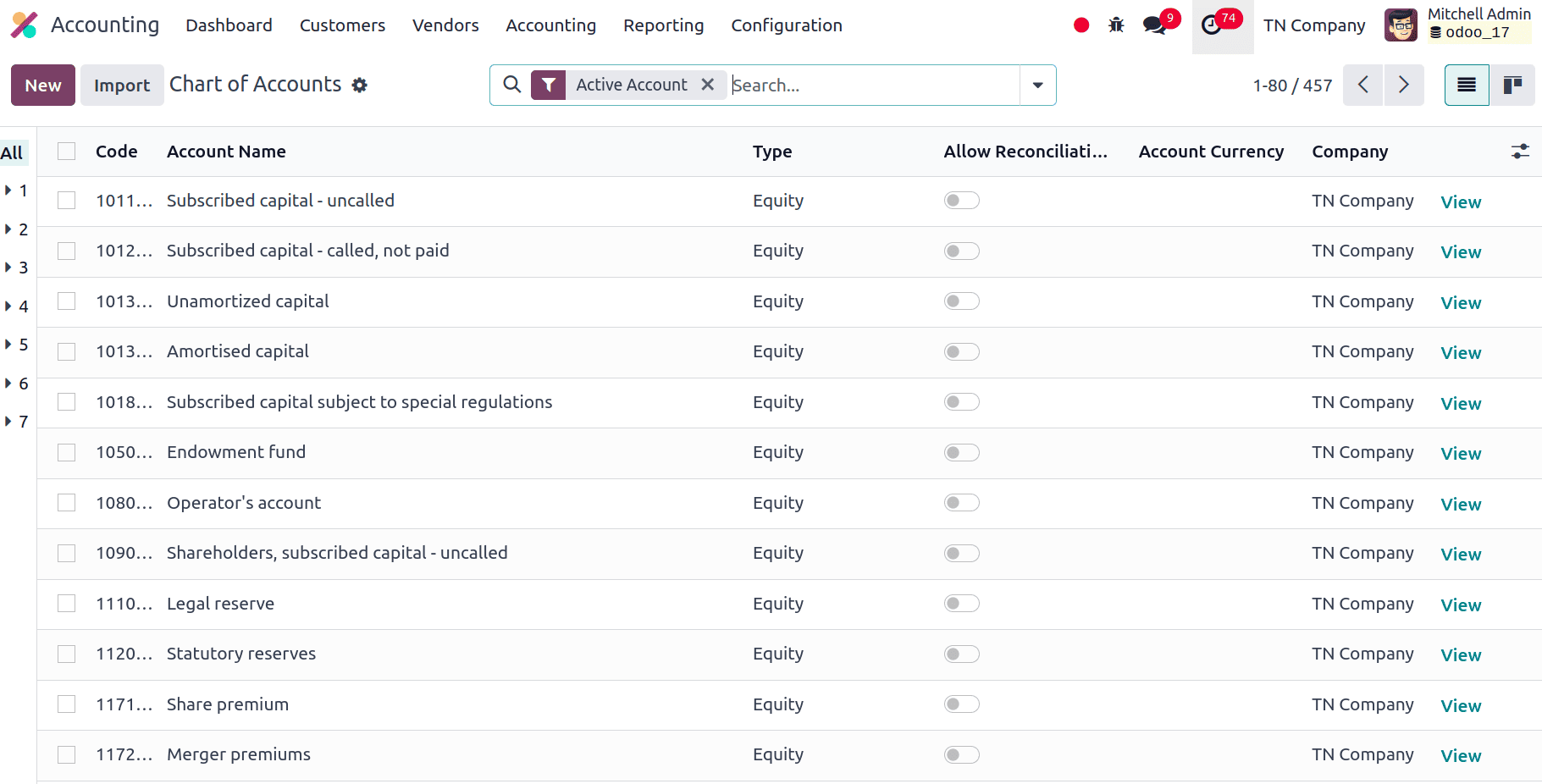
Chart of Accounts
All financial accounts that a business uses are listed in a chart of accounts. It arranges financial transactions into groups such as income, expenses, assets, and liabilities, much like a directory. It's a vital feature in Odoo for handling money and producing precise reports. The Tunisian Chart of Accounts follows the accounting standards and the framework established by the country's tax authorities. It contains particular account classifications and codes needed for local reporting. It complies with regional tax laws, such as TVA (Taxe sur la Valeur Ajoutée) and other regional taxes that apply in Tunisia. To guarantee correct tax reporting and regulation, default tax codes are put up. Financial statements and tax filings, among other local reporting needs, are made easier by the Chart of Accounts.
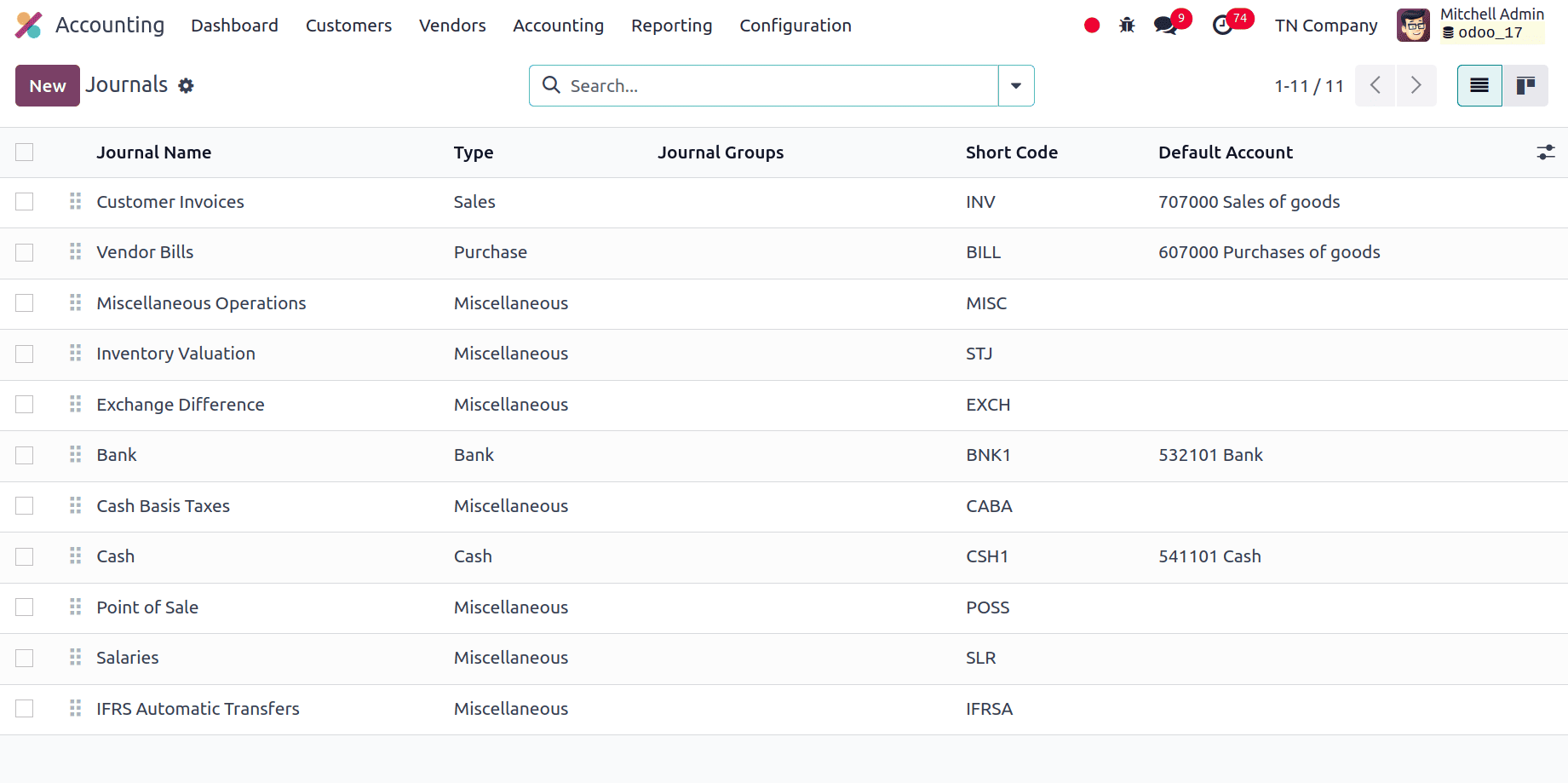
Journals
Maintaining an organized record of all kinds of transactions requires journals. Every sort of journal keeps track of particular financial transactions and guarantees proper bookkeeping. Typical varieties comprise Purchase, Bank, Sales, and Expense journals. Every journal has a specific purpose that aids in transaction segregation for improved reporting and clarity. The configuration of Odoo's Journals complies with Tunisian accounting norms and laws. This covers the proper configurations for VAT and other regional tax obligations. To ensure proper transaction recording and reporting, journals are linked to certain accounts from the Chart of Accounts that are adapted to Tunisian rules.
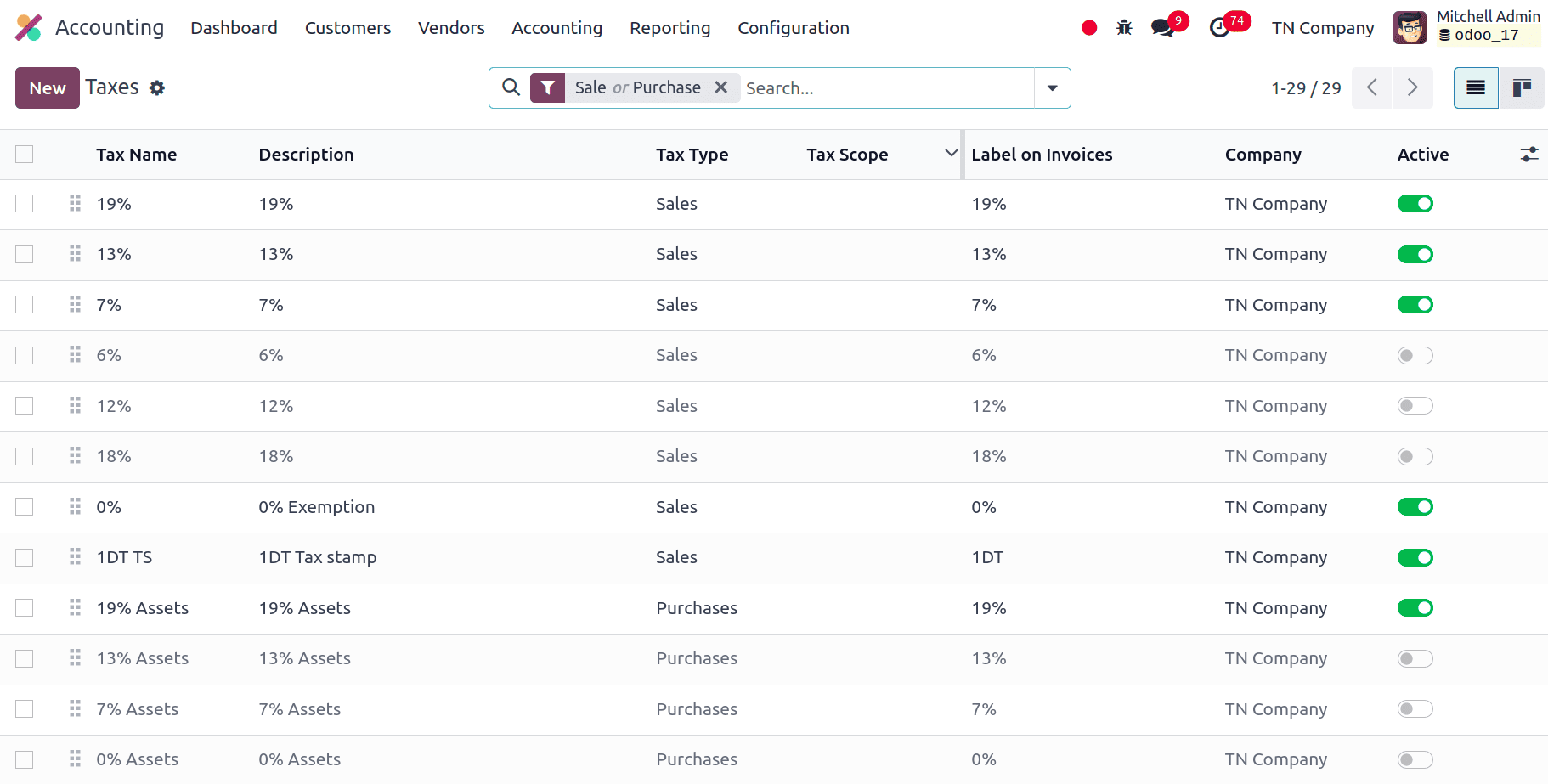
Taxes
In Odoo, taxes are applied to transactions by automated computations. These consist of purchase taxes, sales taxes, and others. By managing rates, regulations, reporting, and guaranteeing accuracy and compliance, Odoo streamlines tax administration. Taxes are used in Odoo Accounting to track and apply different tax laws to financial activities, such as purchases and sales. Odoo's tax setup for Tunisia localization is designed to be bound by regional tax laws, including VAT and other applicable taxes.
Fiscal Positions
With the use of fiscal positions, various tax laws and account mappings can be automatically applied depending on the details of the transaction, such as the customer's location or the nature of the transaction. Businesses can apply particular tax laws and account mappings according to predetermined standards by using fiscal positions. They simplify the administration of taxes and guarantee accurate transaction recording in compliance with regional tax regulations. Based on variables like the location of the consumer or the type of transaction, they automatically modify the taxes and accounts on invoices and other financial documents. The configuration of fiscal positions in Tunisia complies with local tax laws and VAT rates, among other tax regulations. They take into account local tax variations or particular tax laws that apply to certain kinds of transactions in Tunisia.
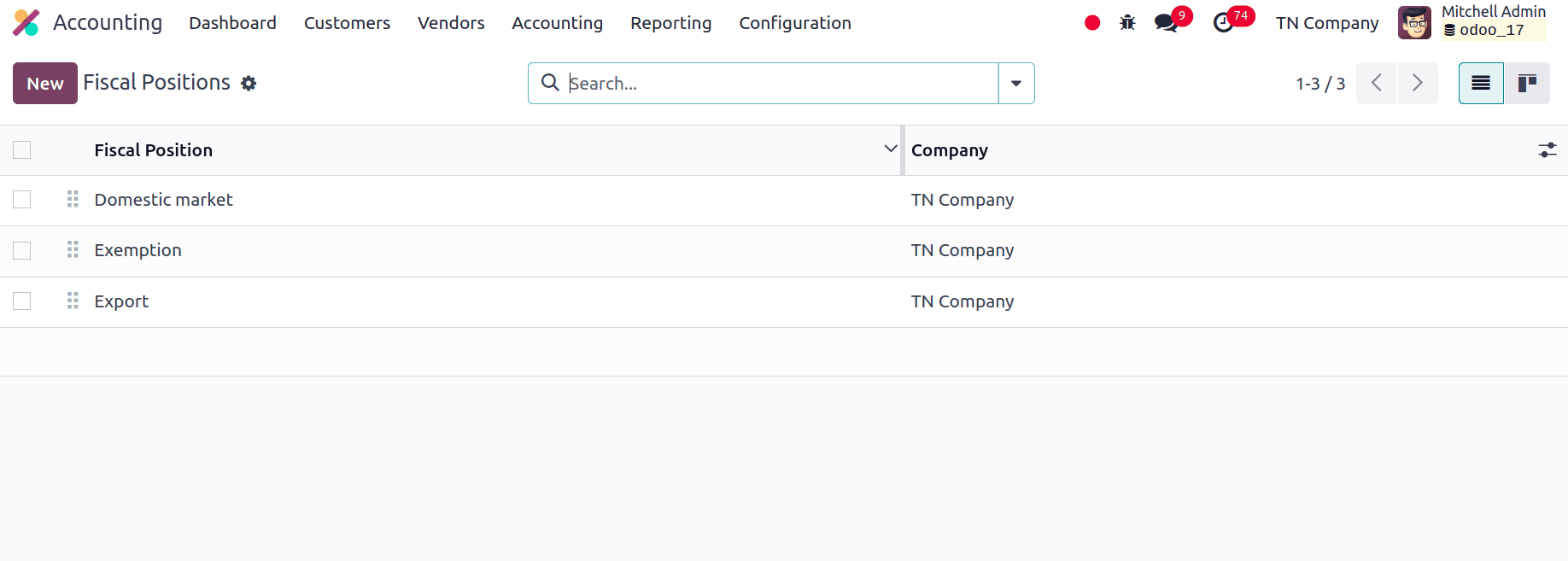
1. Domestic Market's Fiscal Position:
It is useful for transactions that take place in Tunisia's domestic market.
* Tax Application: Treats invoices and transactions according to the standard VAT rate or any other appropriate domestic tax rate. It guarantees adherence to regional VAT laws for transactions made within Tunisia.
It maps to the regular VAT rates or any discounted rates that apply to domestic transactions. Account mapping is the process of mapping Chart of Accounts accounts to typical domestic transaction entries. It is applied automatically to transactions involving local suppliers and customers, guaranteeing the use of accurate accounting entries and VAT rates.
2. Exemption Fiscal Position
Utilized for transactions that, in accordance with Tunisian tax laws, are free from VAT or other local taxes. It guarantees that transactions that are legally exempt from VAT, such as specific categories of services or items that meet tax exemption requirements, are not subject to tax.
3. Export Fiscal Position
It is used in transactions where products or services are exported from Tunisia. Uses a standard 0% VAT rate for export transactions since, according to Tunisian VAT rules, exports are usually zero-rated. This implies that companies can frequently recover VAT on inputs connected to these exports, even though the exported items are free from VAT.
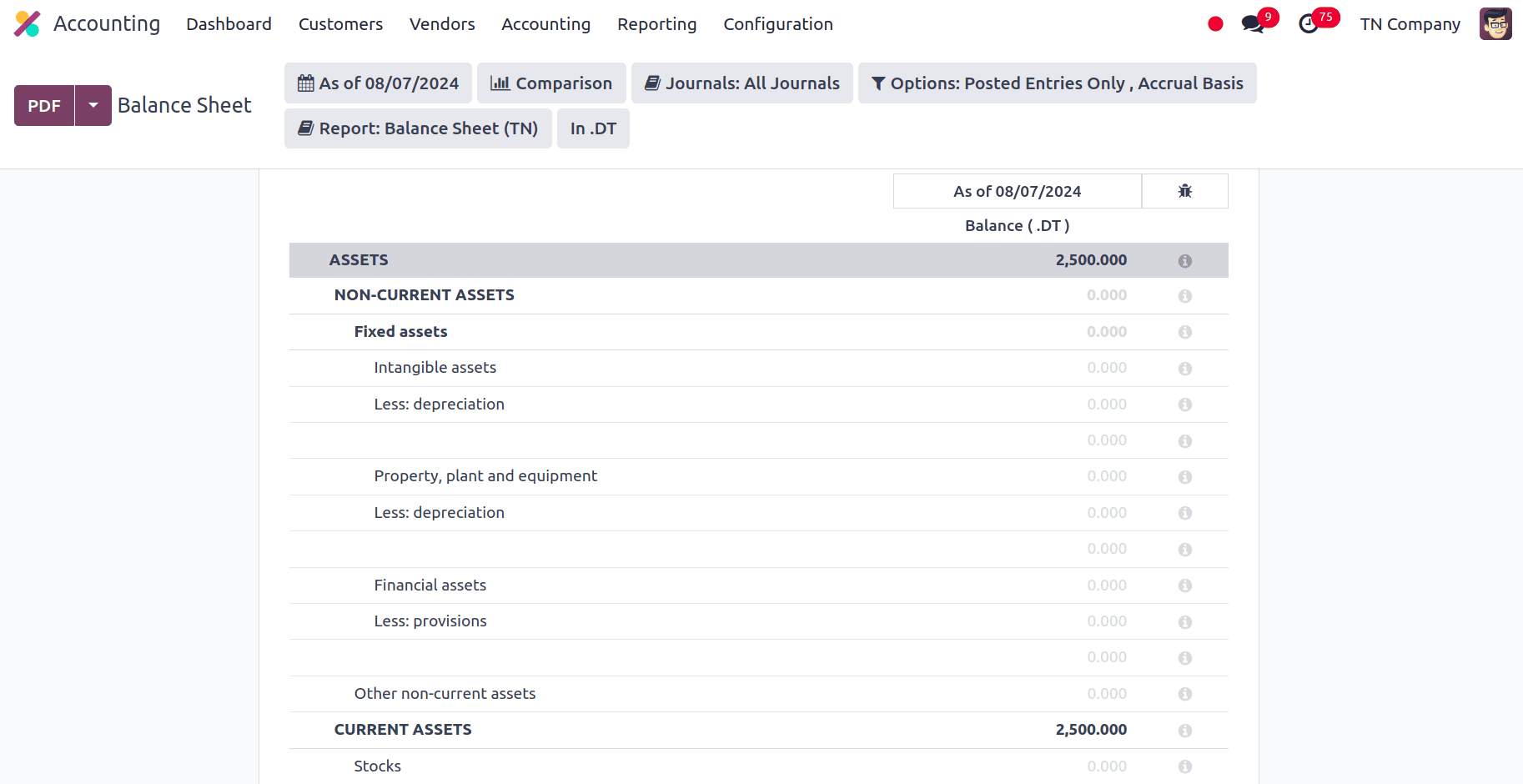
Balance Sheet
Important financial information on a company's financial situation at a particular moment is provided by the balance sheet. The business's equity, liabilities, and assets are summed up on the balance sheet to show its overall financial status. Liabilities plus equity and assets make up its two primary components. Obligations are divided into current and non-current obligations, while assets are further divided into current and non-current assets.
Profit and Loss Report
A business's financial performance over a given time period is summarised in the profit and loss report. It provides information on sales, costs, and earnings and provides a window into the profitability and operational effectiveness of the business. This report has been localized to Tunisia, following the local tax laws and accounting norms.
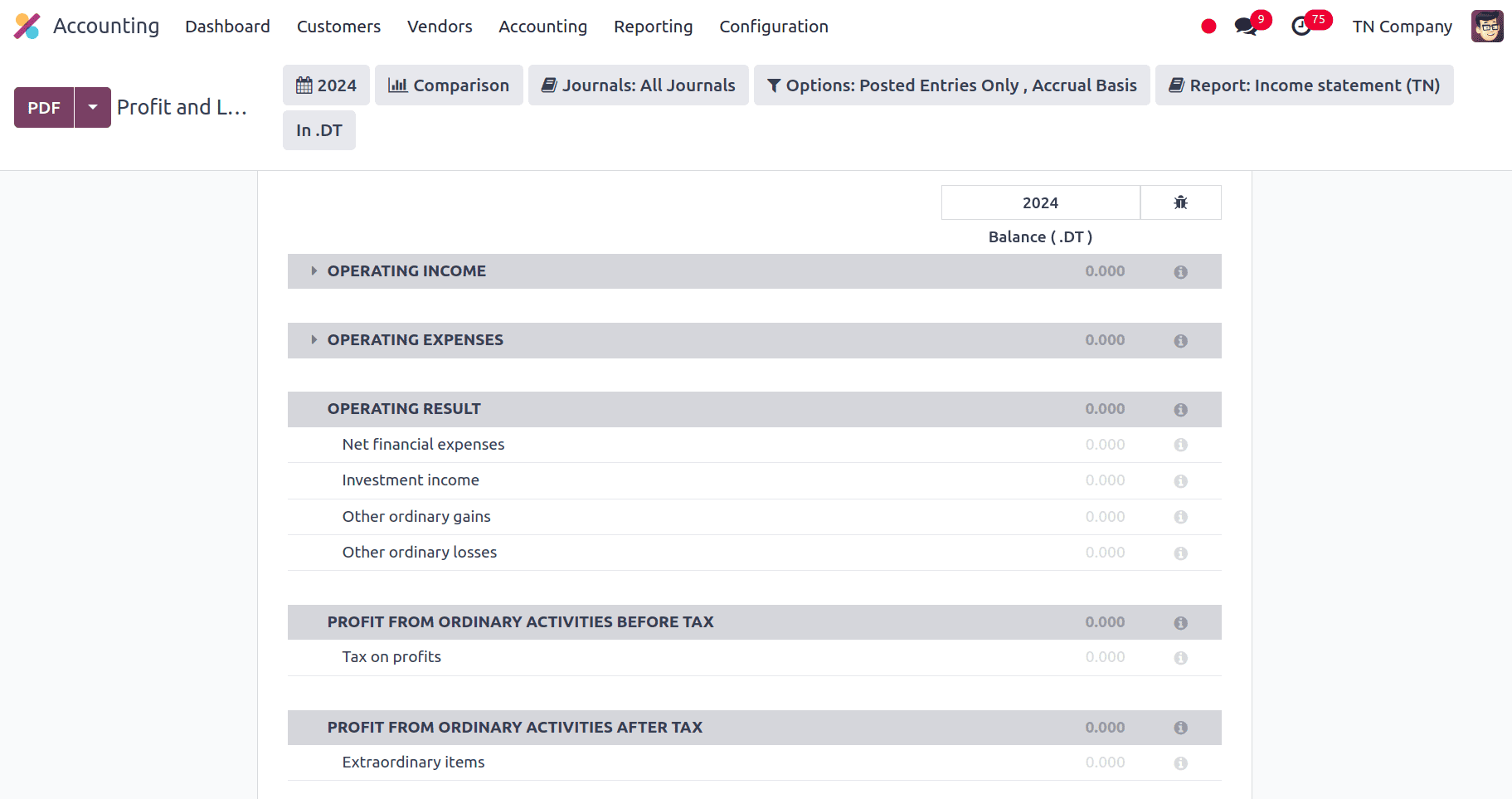
The money received by the business from its main lines of operation is known as Operating Income. Sales revenue from products or services is included in this figure, which is computed prior to deducting taxes, interest, and non-operating income. The costs associated with running a company on a daily basis, such as rent, utilities, salaries, and administrative expenses, are referred to as Operating Expenses. They exclude non-operating costs like taxes and interest as well as expenditures directly related to production (COGS). What's left over after operating expenses and operating income is known as the Operating Result. It indicates how well a corporation is performing in its primary business activities after taking non-operating variables into consideration.
Profit from Ordinary Activities Before Tax is the amount left over after deducting income tax expenses and adjusting for non-operating income and expenses from the company's primary operational activities. It displays the profitability and operational performance of the corporation from its main business operations. Profit from Ordinary Activities After Tax is the amount of profit left over from regular operations after income tax charges are subtracted, which is known as "After Tax." After deducting tax requirements, the net income from the company's main business operations is shown. The Net Result of the Period is the total profit or loss for the reporting period, determined by deducting all taxes and all other operational and non-operational revenue and expenses.
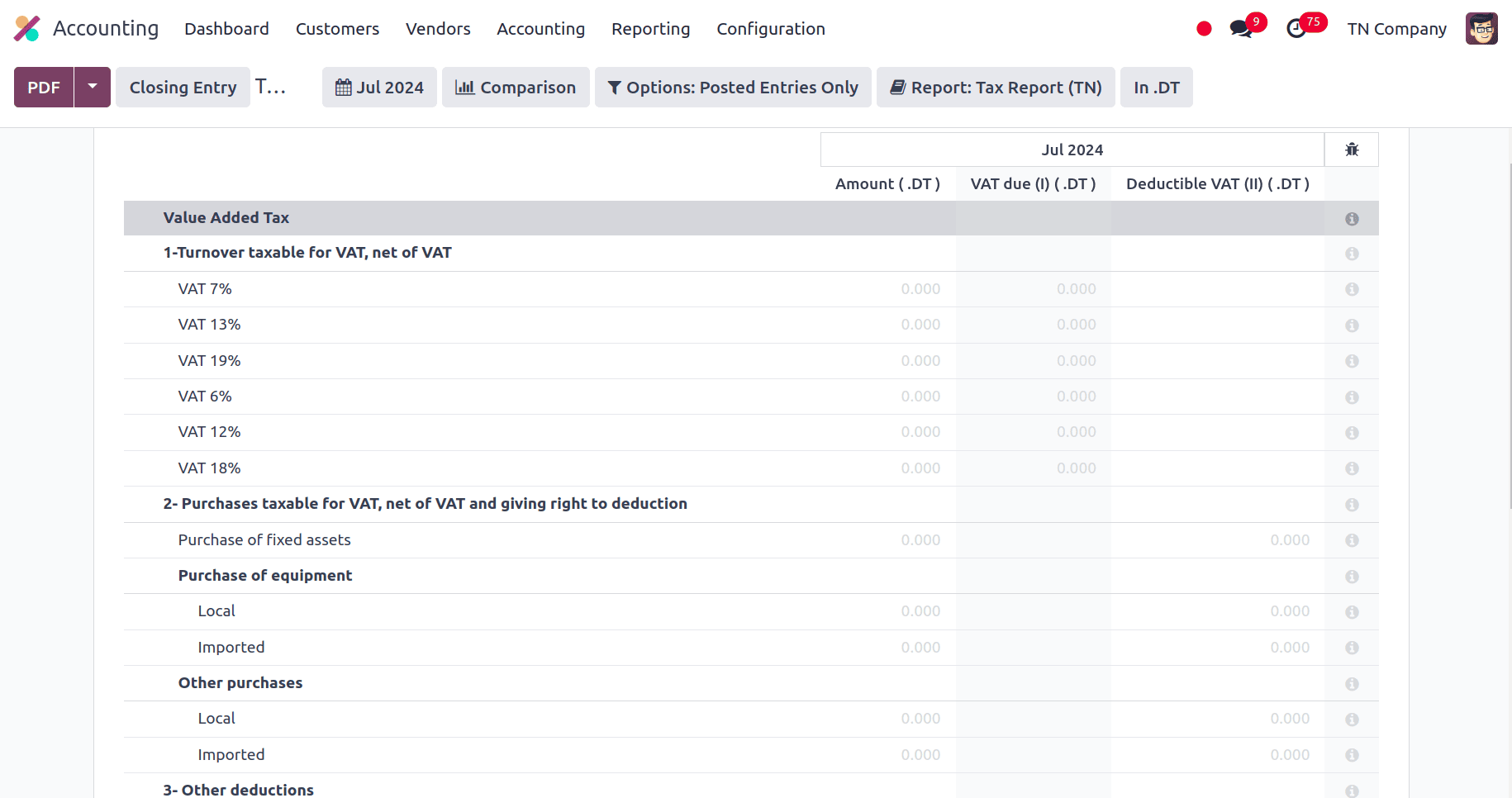
Tax Report
An essential instrument for monitoring and controlling a business's tax liabilities and guaranteeing adherence to tax laws is the Tax Report. Businesses can better prepare for tax filings and audits with the assistance of the Tax Report, which offers a comprehensive account of all tax-related transactions, including VAT (Value Added Tax) and other applicable taxes. The tax amounts contain information on VAT paid on purchases and VAT collected on sales. This is essential for reporting and complying with VAT. Tax categories are a list of several tax categories, including purchase and sales VAT and other tax kinds. Tax Amounts displays the total amount of tax collected and paid, usually divided by the tax period and type.
To sum up, the accounting localization of Odoo 17 for Tunisia provides a stable and flexible solution that is suited to the particular financial and legal needs of Tunisian companies. Businesses may function effectively while following national norms with Odoo's integration of crucial local practices like particular tax laws, adherence to the Tunisian Chart of Accounts, and customized reporting formats.
The extensive features enable Tunisian businesses to handle their accounting procedures more precisely and conveniently. These features include customizable tax reports, comprehensive financial statements, and accurate fiscal positioning. This localization improves the overall effectiveness of financial management while also making it easier to follow local regulations.
To read more about An Overview of Accounting Localization for Ecuador in Odoo 17, refer to our blog An Overview of Accounting Localization for Ecuador in Odoo 17.