Introduction to IoT Devices
In today's technologically advanced world, a variety of devices such as smart TVs, speakers, toys, wearables, and appliances, have revolutionized the way we interact with our environment. These devices, commonly referred to as Internet of Things (IoT) devices, connect wirelessly to networks and continuously broadcast data. This interconnected network of gadgets forms an ecosystem that automates tasks both in homes and workplaces, sharing valuable sensor data with consumers and businesses alike. IoT devices can be categorized broadly into consumer, business, and industrial sectors.
Consumer IoT Devices
Consumer IoT devices are designed to sense and react to a person’s presence, making them integral components of the IoT ecosystem. For instance, a smart thermostat adjusts the temperature based on occupancy and preferences, while wearable fitness trackers monitor physical activity and health metrics. These devices enhance convenience and efficiency in daily life by automating routine tasks and providing real-time data.
Industrial and Business IoT Devices
In the business and industrial sectors, IoT devices include sensors, security cameras, and industrial machines. These devices are physical objects equipped with the capability to communicate with the external world. They typically have an integrated CPU, network adapter, and firmware, often utilizing open-source designs. For network connectivity, these devices connect to a Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server to obtain an IP address. While many operate on private networks, some have limited availability on the public internet. The majority of traffic to and from IoT devices is outbound, controlled through software programs or integrated web servers.
Challenges in IoT System Adoption
Despite their significant advantages, IoT systems face several challenges that hinder their widespread adoption. Key issues include security, interoperability, power and processing capability, scalability, and availability. Addressing these challenges is crucial for the successful implementation and management of IoT devices.
IoT Device Management
Effective IoT device management is essential to overcome these challenges. It involves integrating, organizing, monitoring, and remotely managing internet-enabled devices to ensure their health, connectivity, and security throughout their lifecycle. This management process is vital for maintaining the functionality and efficiency of IoT ecosystems.
Odoo 17 IoT Boxes Application
One innovative solution for IoT device management is the Odoo 17 IoT Boxes application. Odoo offers an external IoT Box device paired with associated application software. The Internet of Things (IoT) box, a micro-computer, enables the connection of input and output devices to an Odoo database. To use the IoT box with a secure connection, a subscription is required. The Odoo 17 IoT Module provides a platform to manage IoT services with both external and internal database systems.
Connecting Devices to Odoo Database
Connecting external devices to your Odoo database is straightforward with the IoT Box. It enhances productivity by integrating seamlessly with existing corporate procedures. Even without technical knowledge, devices can be linked through common connectors like WiFi, Bluetooth, USB, or HDMI. This simple and quick approach ensures efficient connectivity and management of IoT devices.
Installation and Setup of Odoo 17 IoT Application
To manage IoT devices using Odoo, the application can be installed from the Odoo 17 ERP Package.

Upon installation, the dashboard will display the available IoT Boxes.
IoT Boxes Menu
The IoT Boxes menu offers a Kanban view of the IoT Boxes, showing their connection links and the number of linked devices.
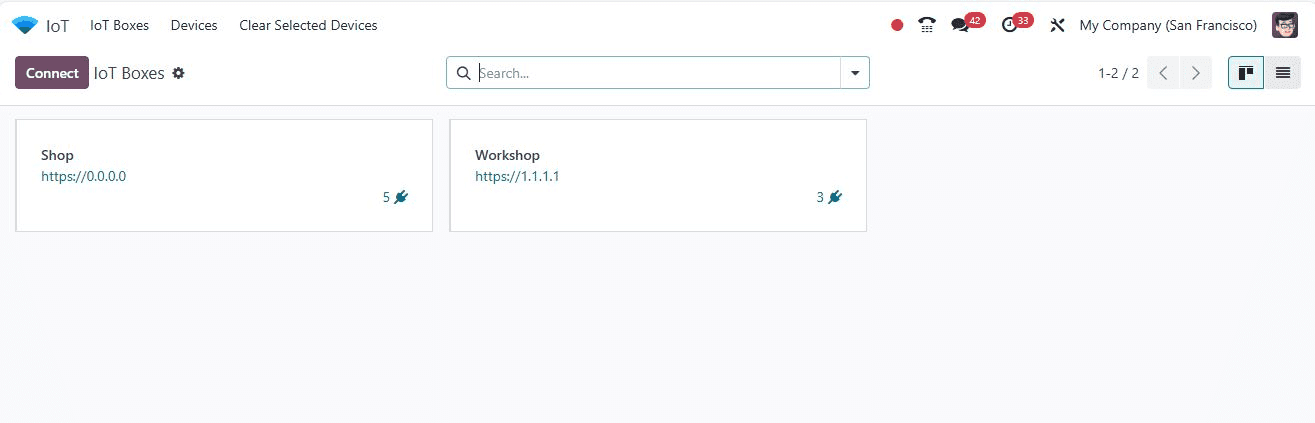
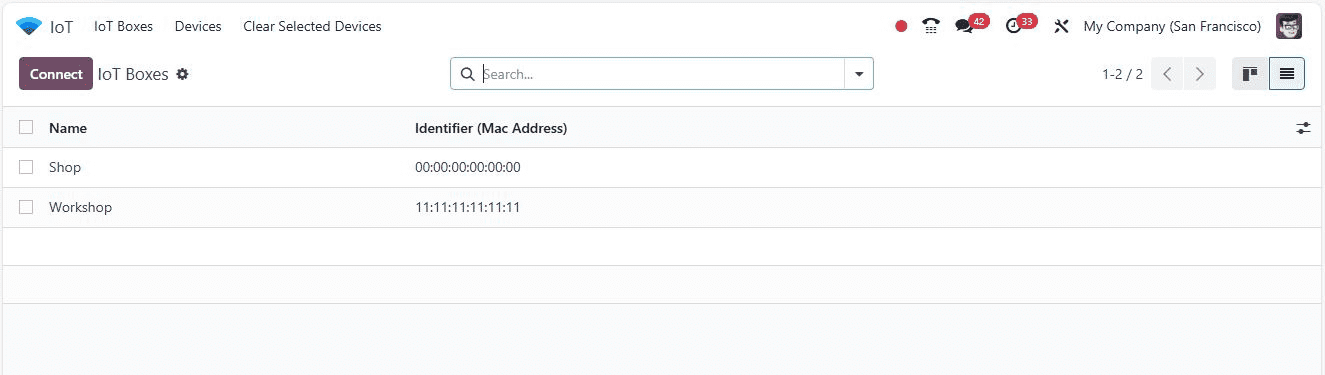
Users can switch to a list view using the “List” icon on the upper right side of the page.
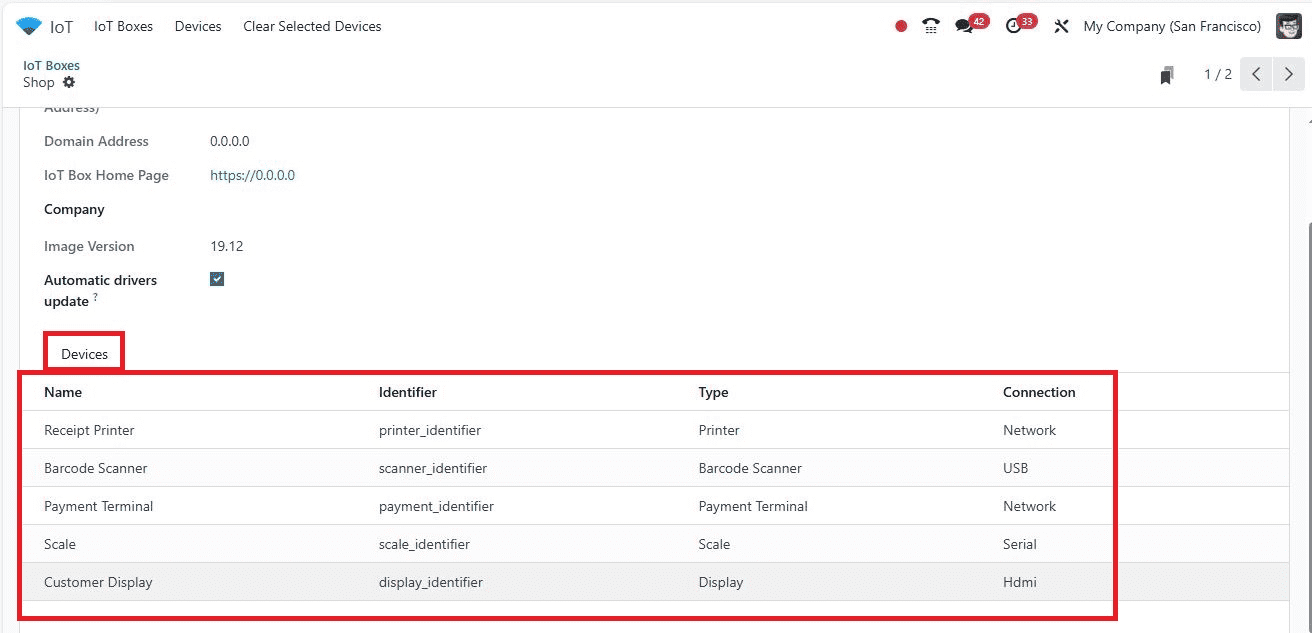
By opening the Kanban Card, users can check the devices connected to each IoT Box.
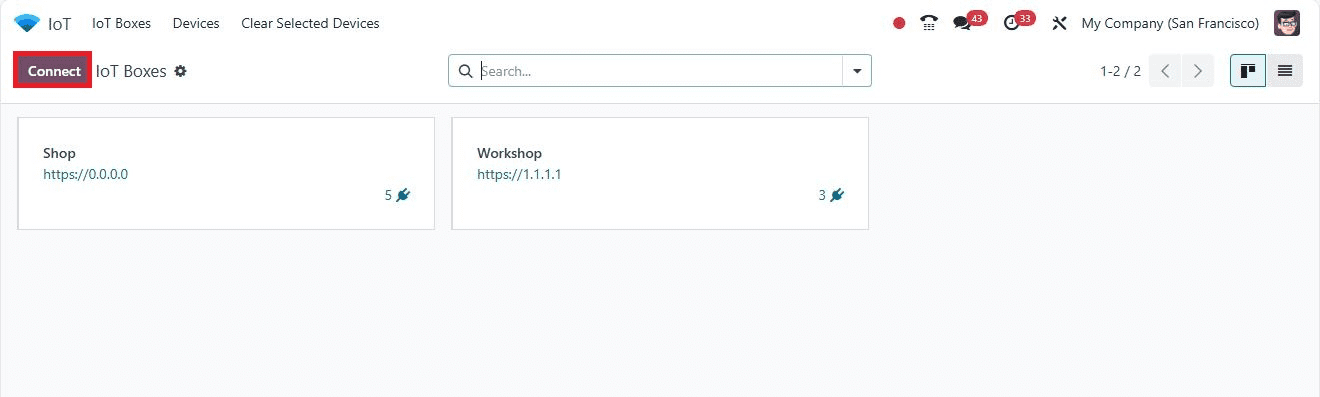
Connecting Devices to the Odoo IoT Box
To connect devices, navigate to the IoT Boxes Application Platform and click the “Connect” button on the “IoT Boxes” dashboard.
This action opens a pop-up window with two recommended techniques for connecting the IoT box to the database: Ethernet Connection and WiFi Connection.
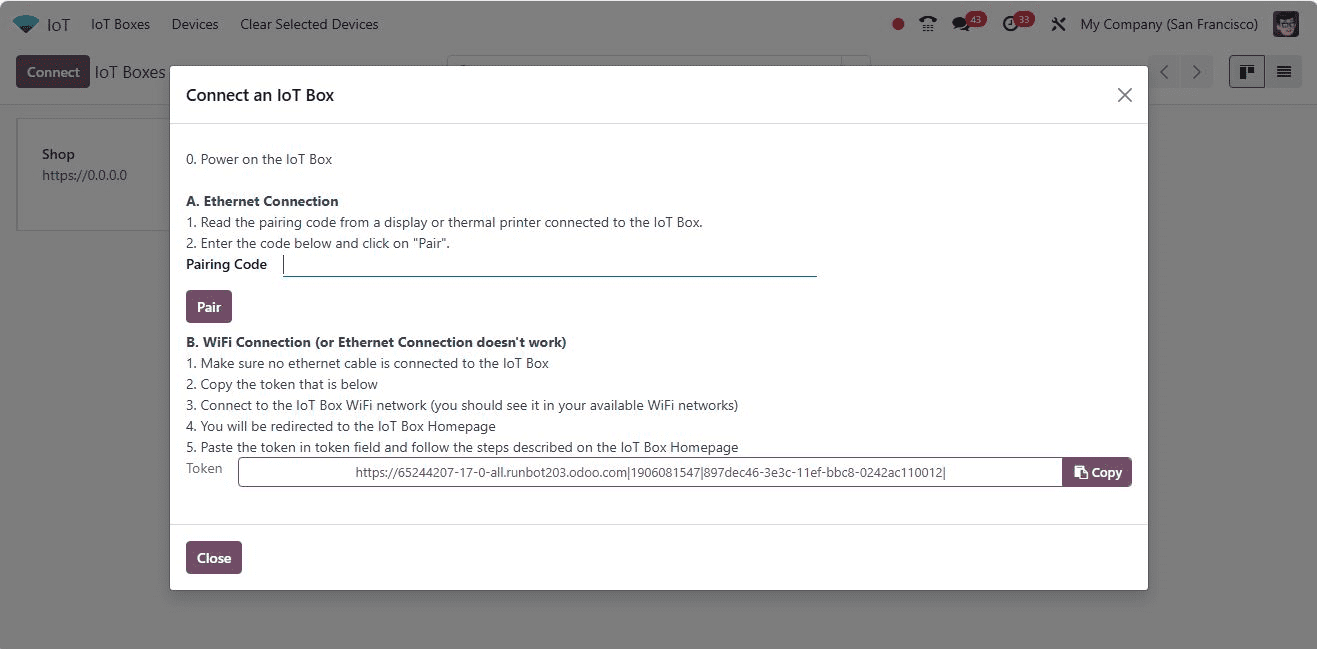
Ethernet Connection
For an Ethernet connection, enter the “Pairing Code” in the designated field and press the "PAIR" button. The IoT box will then link to the database and appear on the IoT Boxes page.
WiFi Connection
For a WiFi connection, use the link in the “Token” field from the “WiFi Connection” area to connect the IoT box and Odoo database. From your computer or laptop, connect to the IoT box WiFi network by navigating to the available WiFi networks. This process is as simple as setting up a Bluetooth or wireless connection.
Devices Menu
The Devices menu displays IoT-connected devices arranged in a Kanban view based on groups. This view shows the various devices connected to your IoT box, including their connection types (Ethernet or WiFi). Users can manage these devices and check their connectivity status from this dashboard.
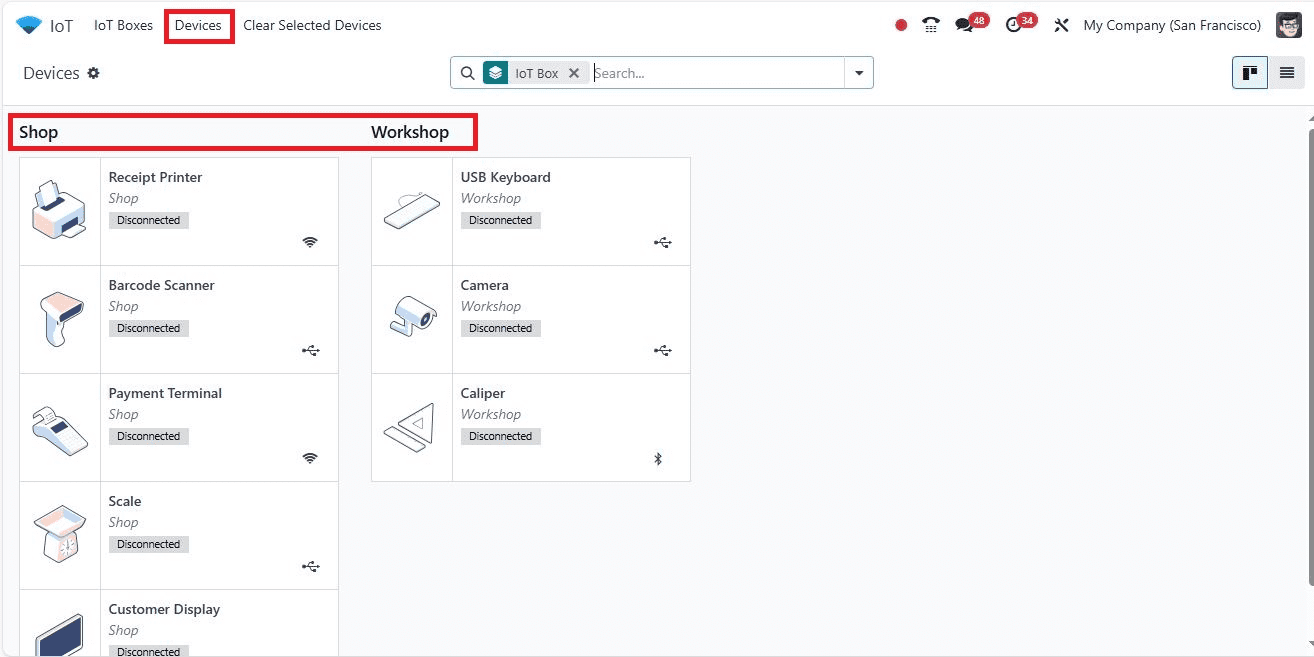
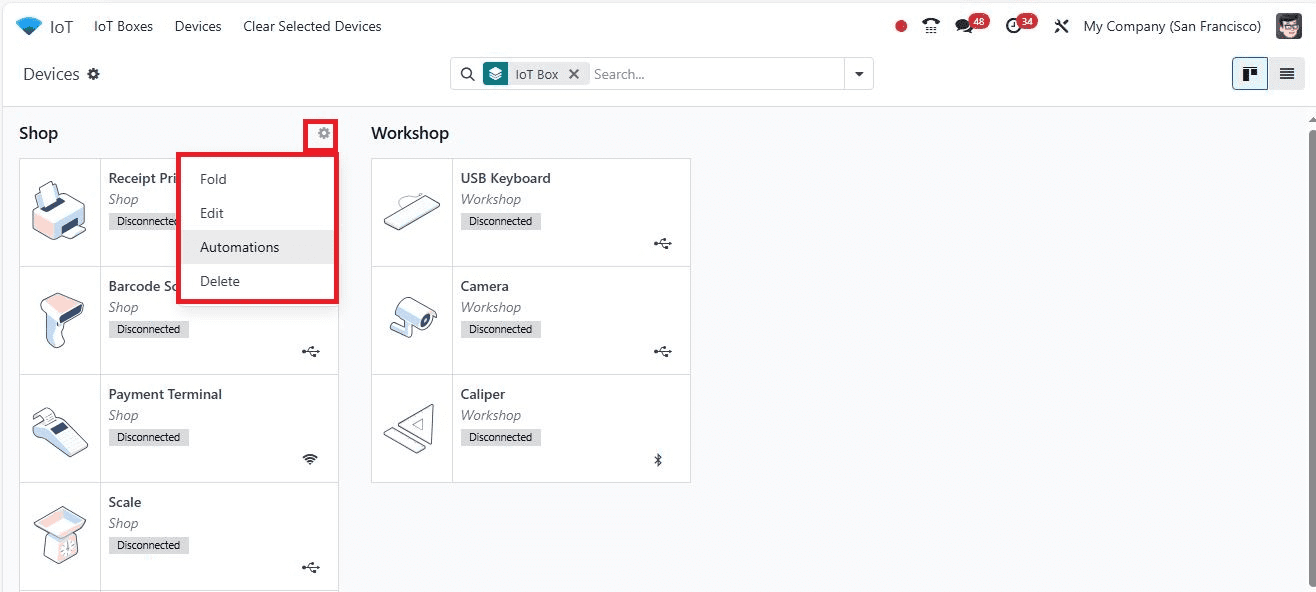
Managing Devices
The “Settings” icon near the device category title allows users to Edit, Fold, or Delete the Kanban view.
Conclusion
The Odoo 17 IoT Application platform offers robust capabilities for managing multiple IoT connections and devices. Its user-friendly interface and comprehensive management tools enable efficient handling of IoT ecosystems. By addressing the challenges of security, interoperability, power and processing capability, scalability, and availability, Odoo 17 IoT Boxes provide a secure and straightforward platform for IoT device management. This innovative solution not only enhances productivity but also ensures seamless integration with existing business processes, making it an invaluable tool in the modern technological landscape.
To read more about What are the Features of Odoo 16 IoT Module, refer to our blog What are the Features of Odoo 16 IoT Module.