Overriding name_search()
Sometimes, it becomes a tedious process to search for desired records, among a large
number of records. In such cases, name_search plays a vital role. It's an ORM
(Object-Relational Mapping) method that assists in searching records by specific values or
using fields other than the default name of the record, especially in a relational field.
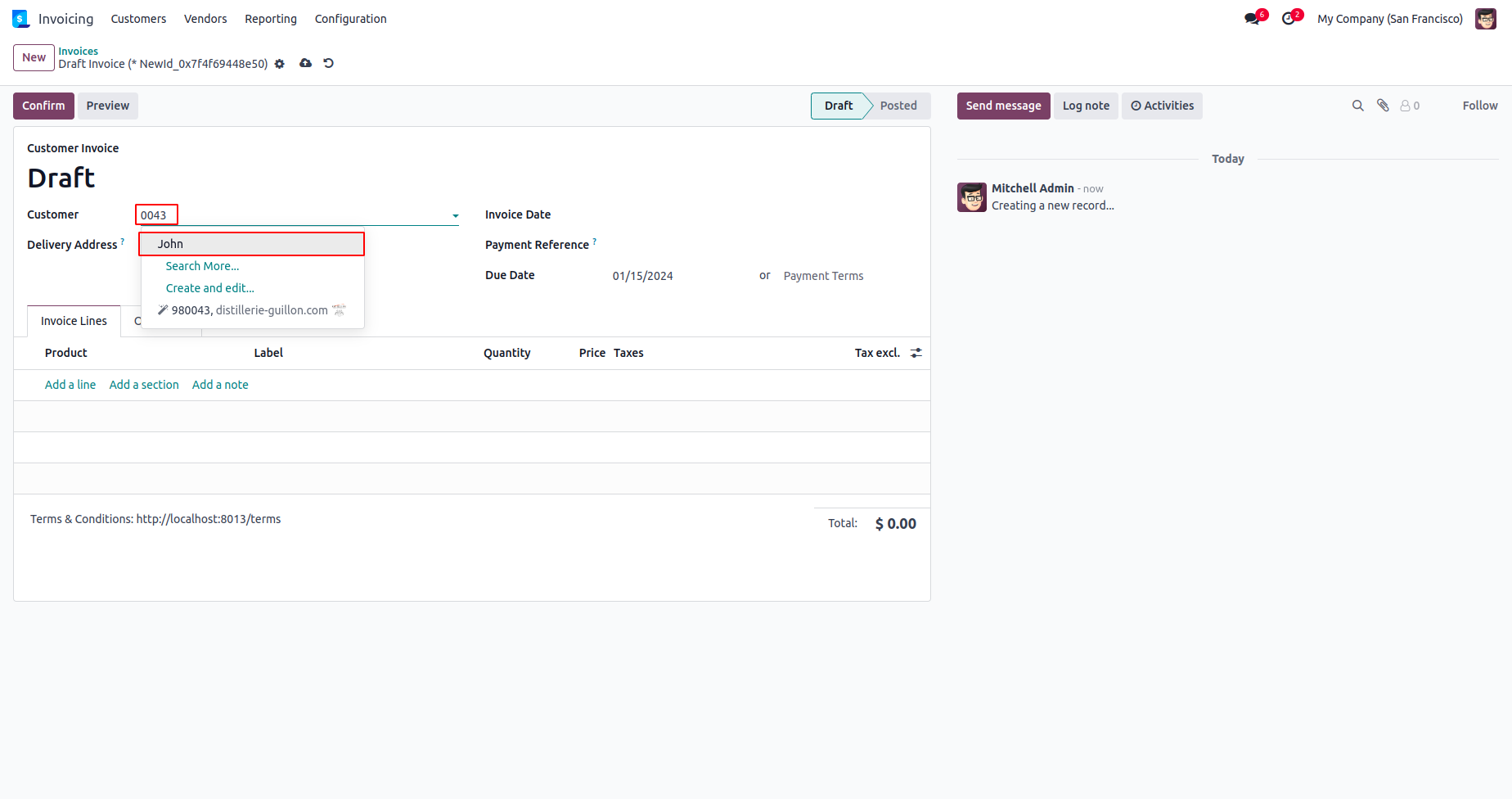
Let's take an example in Odoo. When creating a new sale order or invoice, we can choose the customer by searching from existing records by typing the customer's name or email id and partial address.This is made possible by using name_search function.Let’s take a look at the structure of name_search function in odoo.
@api.model
def _name_search(self, name, args=None, operator='ilike', limit=100,
order=None):
domain = domain or []
# code
return self._search(expression.AND([your_domain, domain]),
limit=limit, order=order)
Similarly, we can configure searching using any other existing fields. Let's explore how we can search for customers by typing their mobile numbers.
class ResPartner(models.Model):
_inherit = 'res.partner'
@api.model
def _name_search(self, name='', args=None, operator='ilike', limit=100,
order=None):
args = list(args or [])
if name:
args += ['|', '|', ('name', operator, name),
('email',operator, name),
('phone', operator, name)]
return self._search(args, limit=limit, order=order)
Lets’ add phone number for any contact,
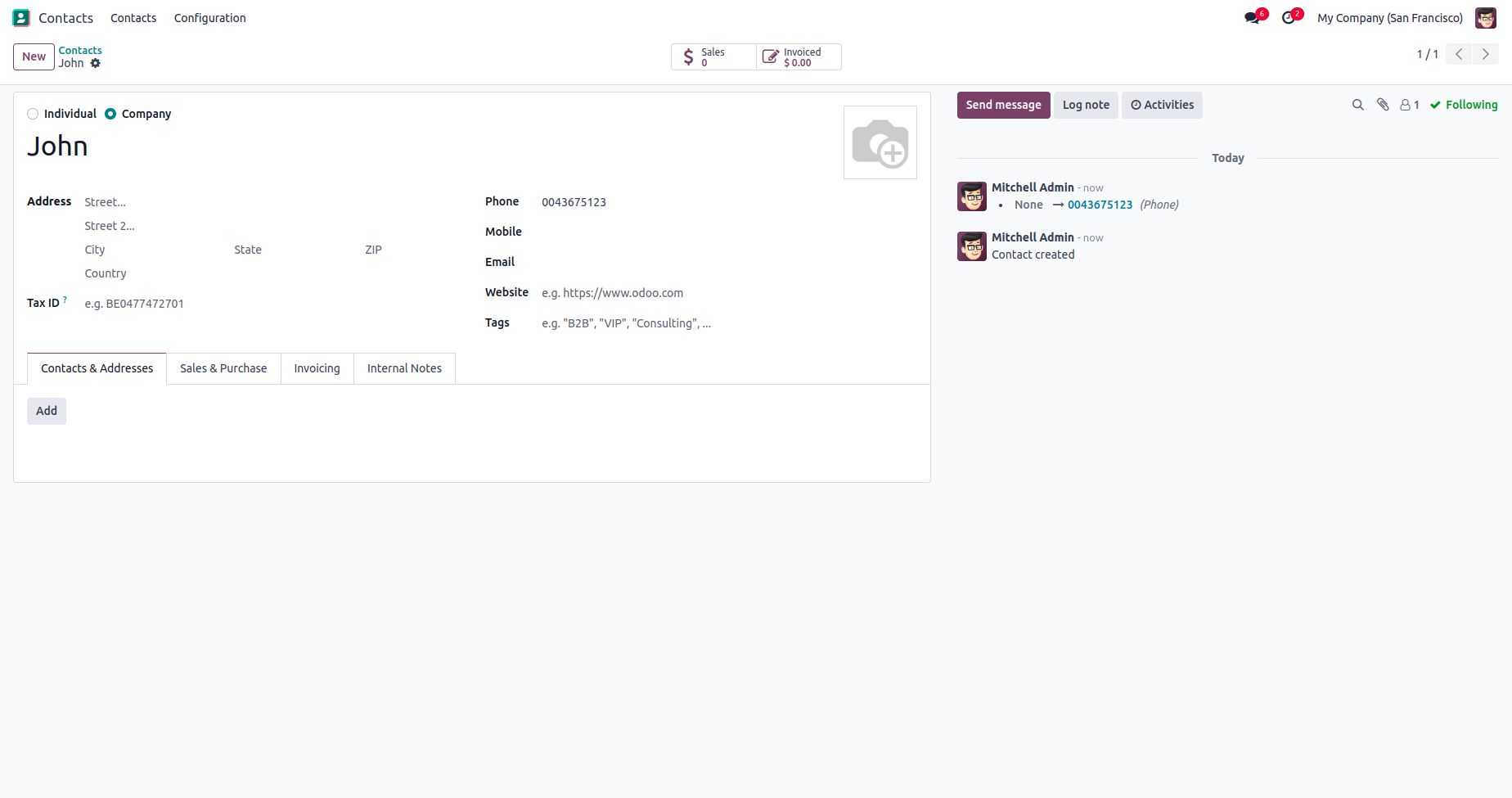
Now create an invoice and search for the contact by typing this phone number.