A model represents the structure or blueprint for different
types of data objects or entities. A model is a class that
contains all of the fields along with actions for the data you
want to store, and it translates to the data relation (table).
We can discuss the different types of data that are kept on a
field and how to include them in a model here.
To define the basic model, we must create a Python file in the
models directory.
models > school_student.py
1. To add the student’s details, use some basic Python code; a
new model must be developed for that.
from datetime import date, timedelta
from odoo import models, fields, _, api
class SchoolStudent(models.Model):
"""
Model for managing student details within the school.
This class defines fields related to student information
such as name, admission number, date of birth, age, parents' names,
and contact details.
"""
_name = "school.student"
_rec_name = 'admission_no'
_description = "Student Details"
name_id = fields.Many2one('res.partner', string="Name", required=True)
admission_no = fields.Char(string='Admission No:', required=True,
copy=False,
readonly=True, default=lambda self: _('New'))
b_date = fields.Date(string='DOB', related='name_id.dob')
age = fields.Integer(string="Age", compute='_compute_age')
father_name = fields.Char(string="Father's Name")
mother_name = fields.Char(string="Mother's Name")
mobile = fields.Char(string='Mobile', related='name_id.mobile')
phone = fields.Char(string='Phone', related='name_id.phone')
gender = fields.Selection([
('other', 'Other'),
('male', 'Male'),
('female', 'Female'),
], srting='Gender', default='other')
blood_grp = fields.Selection([
('a+', 'A+'),
('b+', 'B+'),
('ab+', 'AB+'),
('ab-', 'AB-'),
('o+', 'O+'),
('o-', 'O-'),
], string="Blood Group")
nationality_id = fields.Many2one('res.country', string='Nationality')
class_history_ids = fields.One2many('school.class.history', 'student_id', string='Class History')
class SchoolClassHistory(models.Model):
"""
Model for recording the class history of students in the school.
This class manages historical data related to students' class details,
including class number, academic year, division, and associated student.
"""
_name = "school.class.history"
_description = "Class History"
student_id = fields.Many2one('school.student')
class = fields.Integer("Class")
academic_year = fields.Date('Academic Year')
division = fields.Char('Division')
In the model class, fields are declared as attributes,
specifying both their storage location and the type of data
the model can contain. The non-relational field types
encompass the following.
- Char - It is used for string values
- Text - It is used for multi-line string values
-
Selection - This field is used for a selection list, and
allows for dynamically generated lists of options
- Binary - It is used for storing binary field
- Html - It is similar to HTML fields
- Boolean - Store True or False values
-
Date - It store date values and, it has some utilities that
are:
-
- fields.Date.to_date(string_value): It will convert
string to date object
-
- fields.Date.to_string(date_value): It will convert
date to string value
-
- fields.Date.today(): Current date in string format
-
- fields.Date.context_today(record, timestamp): It will
return the day of the timestamp in a string format
-
Datetime - It is used to store date time values (dd/mm/yyyy
HH:MM:SS), and have some utils
-
- fields.Datetime.to_datetime(string_value): It will
convert String into DateTime
-
- fields.Datetime.to_string(datetime_value): It will
convert the DateTime object to a string
-
- fields.Datetime.now(): It is the current DateTime
value
-
- fields.Datetime.context_timestamp(record, timestamp):
Converts a timestamp-native DateTime object into a
zone-aware DateTime object
- Float - To Store the Float values
- Monetary - To Store amount in a certain currency
-
Many2one - The Many2one fields relate the many records of
the co-model, which is the second model, to the current
model’s record.
-
One2many - The One2many field relation is the inverse of the
Many2one relation. It relates one record of the co-model to
many records of the model.
-
Many2many - The Many2many fields are bidirectional multiple
relationships. It means that the number of records in one
direction will be directed to the number of records in the
other direction.
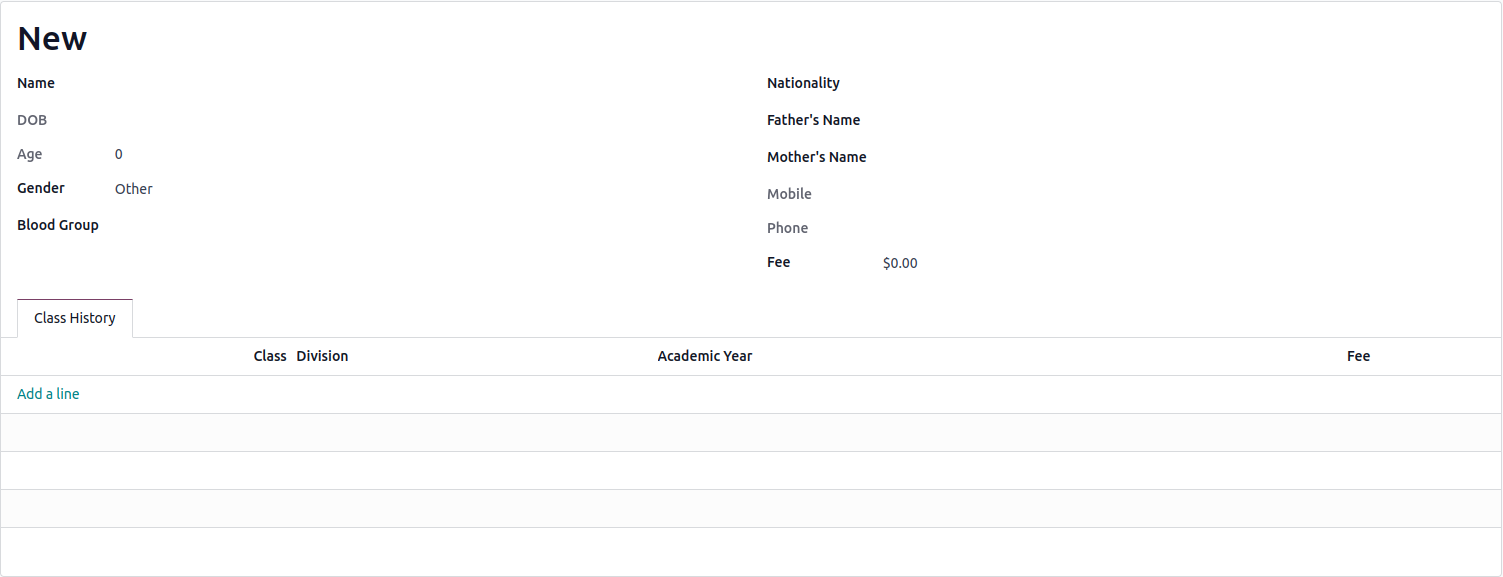
2. We've introduced new fields into the existing model. Now,
the next step involves configuring the form view within the
user interface to display these added fields. The following
code snippet is used to present these fields on the user
interface.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<odoo>
<record id="patient_card_view_form" model="ir.ui.view">
<field name="name">school.student.form.view</field>
<field name="model">school.student</field>
<field name="arch" type="xml">
<form>
<sheet>
<div class="oe_title">
<h1>
<field name="admission_no" readonly="1"/>
</h1>
</div>
<group>
<group>
<field name="name_id" widget="res_partner_many2one"
context="{'res_partner_search_mode': 'customer', 'show_address': 1 }"
options='{"always_reload": True}'/>
<field name="b_date"/>
<field name="age"/>
<field name="gender"/>
<field name="blood_grp"/>
</group>
<group>
<field name="nationality"/>
<field name="father_name"/>
<field name="mother_name"/>
<field name="mobile"/>
<field name="phone"/>
</group>
</group>
<notebook>
<page string="Class History">
<field name="class_history_ids">
<tree editable="bottom">
<field name="class_id" required="1"/>
<field name="division" required="1"/>
<field name="academic_year_id" required="1"/>
</tree>
</field>
</page>
</notebook>
</sheet>
</form>
</field>
</record>
</odoo>
3. The form view in the user interface is then visible after
upgrading the module.