Data fields
Models are used to store information, which is organised into fields. Here we can learn
about the type of data stored on a field and how to add them into a model.
First we have to create a python file on the models directory for defining the basic
model.
models > patient.py
1. Use some simple code to add the patient record and create a new model for that.
import datetime
from odoo import api, fields, models, _
class HospitalPatient(models.Model):
_name = "hospital.patient"
_rec_name = 'reference_no'
_description = "Hospital Patient"
name_id = fields.Many2one('res.partner', string="Name", required=True)
reference_no = fields.Char(string='Order Reference', required=True,
copy=False,
readonly=True, default=lambda self: _('New'))
bdate = fields.Date(string='DOB', related='name_id.dob')
age = fields.Char(string="Age", compute='_compute_age')
mobile = fields.Char(string='Mobile', related='name_id.mobile')
phone = fields.Char(string='Phone', related='name_id.phone')
gender = fields.Selection([
('other', 'Other'),
('male', 'Male'),
('female', 'Female'),
], srting='Gender', default='other')
blood_grp = fields.Selection([
('a+', 'A+'),
('b+', 'B+'),
('ab+', 'AB+'),
('ab-', 'AB-'),
('o+', 'O+'),
('o-', 'O-'),
], string="Blood Group")
note = fields.Text(string='Note')
prescription = fields.Text(string="Prescription")
ticket_id = fields.One2many('hospital.ticket', 'patient_card', string='Ticket')
Fields are added to models by defining an attribute in their python classes. The non
relational field types are as follows.
- Char - Used for string values
- Text - Is used for multi line string values
- Selection - Used for selection list, allows for dynamically generated lists of
option
- Binary - Used for store binary field
- Html - It is similar to html fields
- Boolean - Store True or False values
- Date - Store date values, it have some utilities that are:
- fields.Date.to_date(string_value) : Convert string to date object
- fields.Date.to_string(date_value) : Convert date to string value
- fields.Date.today() : Current date in string format
- fields.Date.context_today(record, timestamp): Returns the day of the timestamp
in a string format
- Datetime - Used to store date time values (dd/mm/yyyy HH:MM:SS), have some utils
- fields.Datetime.to_datetime(string_value) : String into datetime object
- fields.Datetime.to_string(datetime_value): Datetime object to a string
- fields.Datetime.now() : Current datetime value
- fields.Datetime.context_timestamp(record, timestamp) : Converts a
timestamp-native datetime object into zone-aware datetime object
- Float - Store numerical values
- Monetary - Store amount in a certain currency
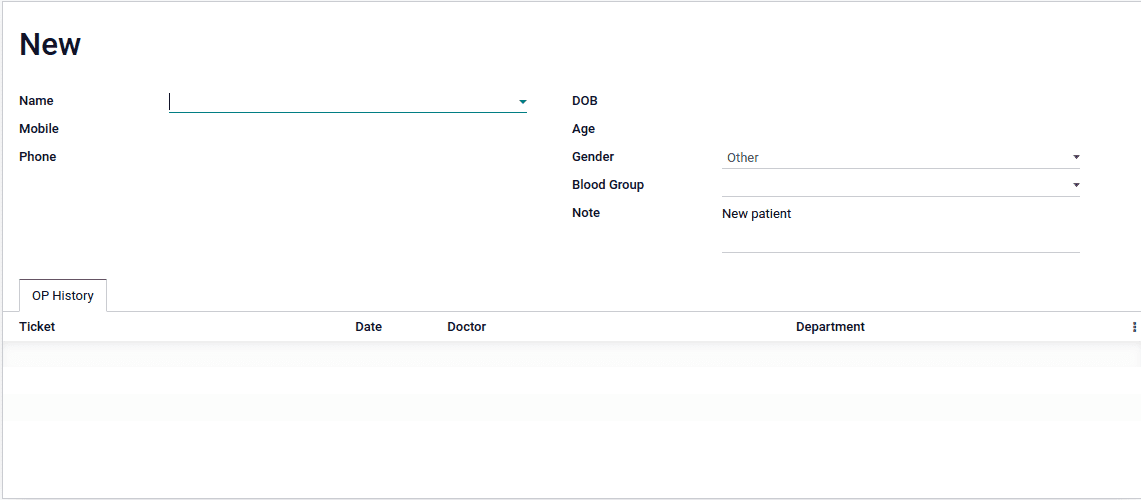
2. We have added new fields to the model. We need to add the fields into a form view in
order to reflect the changes on the user interface. The below code is used for view the
field on the user interface
<form>
<sheet>
<div class="oe_title">
<h1>
<field name="reference_no" readonly="1"/>
</h1>
</div>
<group>
<group>
<field name="name_id" widget="res_partner_many2one"
context="{'res_partner_search_mode': 'customer', 'show_address': 1 }"
options="{"always_reload": True}"/>
<!--<field name="address"/>-->
<field name="mobile"/>
<field name="phone"/>
</group>
<group>
<field name="bdate"/>
<field name="age"/>
<field name="gender"/>
<field name="blood_grp"/>
<field name="note"/>
</group>
</group>
<notebook>
<page string="OP History">
<field name="ticket_id">
<tree create="0" delete="0" edit="0">
<field name="tocken_no"/>
<field name="date"/>
<field name="doctor_id"/>
<field name="department"/>
</tree>
</field>
</page>
</notebook>
</sheet>
</form>
3. Upgrade the module and go to the user interface we can see the form view