Qunit Test
The Odoo framework utilizes the QUnit library testing system as a test sprinter. QUnit
characterizes the ideas of tests and modules (a bunch of related tests), and gives us an
web-based point of interaction to execute the tests.
web.test_utils will provide us with the test utilities required to build
the JavaScript test cases.
Adding Qunit Test Cases
your_module
-----
-----static
-------tests
---------test_file.js
While writing tests
- Define a tests sub-package in the static directory in your module.
- Create js test file inside the tests directory.
- Add a test case after the definition of the test suite
- Add the file to the main test assets (views/asset.xml).
- Visit /web/tests/ to make sure the test is executed
Let's go to an example of qunit test for some javascript code (for example, some utility
function myFunction, located in test_addon.utils). The process of adding a new test case
is the following:
First, create our test file inside static/tests/utils_tests.js
odoo.define('test_college.arithmatic', function (require) {
"use strict";
var pyUtils = require('web.py_utils');
var testUtils = require("web.test_utils");
QUnit.module('college',{}, function (){
});
});
Define the test case inside the test file.
odoo.define('test_college.arithmatic', function (require) {
"use strict";
var pyUtils = require('web.py_utils');
var testUtils = require("web.test_utils");
QUnit.module('college',{}, function (){
QUnit.test('simpletest', function (assert) {
assert.expect(2);
var result = pyUtils.py_eval("4 - 2");
assert.strictEqual(result, 2, "should properly evaluate difference");
result = pyUtils.py_eval("4 * 5");
assert.strictEqual(result, 20, "should properly evaluate multiplication operator");
});
});
});
Add our tests inside the asset (manifest file).
'assets': {
'web.qunit_suite_tests': [
'college/static/tests/arithmatc.js'
],
},
Running test by visiting /web/tests/.
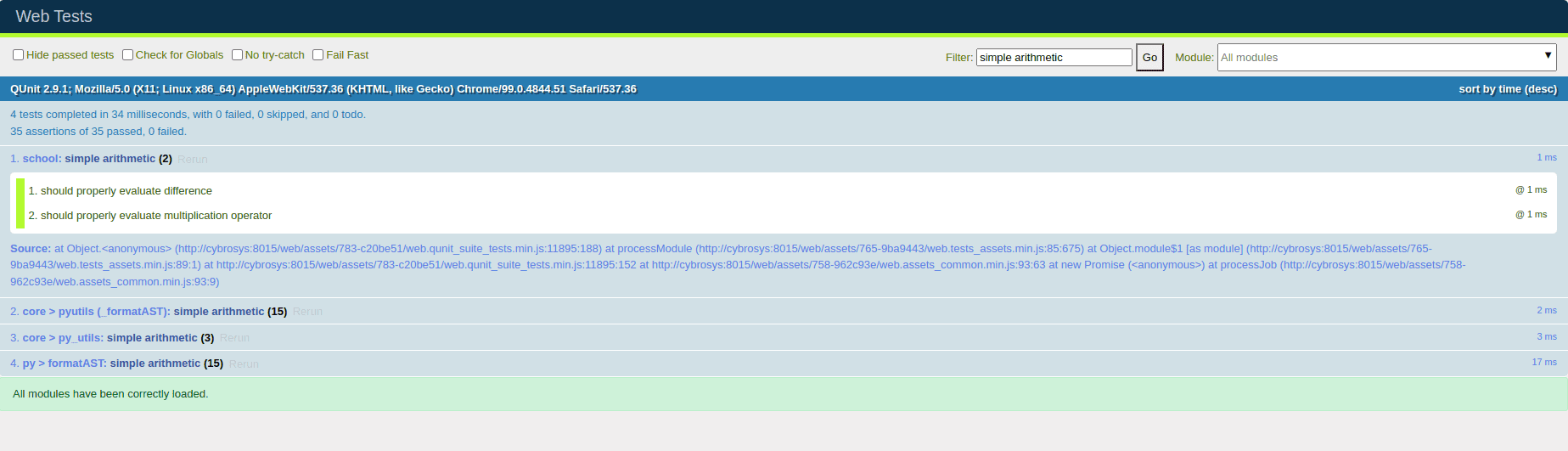
Testing by using Helper Function
Without help, it is quite difficult to test some parts of Odoo. Specifically, sees are
interesting, on the grounds that they speak with the server and may perform numerous
rpcs, which should be ridiculed. For this reason we fostered some specific assistant
capacities, situated in test_utils.js.
Some helper functions are:
- Mock test functions: These capacities assist with setting up a test
environment. The main use case is ridiculing the responses given by the Odoo server.
These functions utilize a fake server. This is a javascript class that recreates
replies to the most widely recognized model strategies: read, search_read, nameget
- DOM helpers: valuable to mimic occasions/activities on some
particular objective. For instance, testUtils.dom.click plays out a click on an
objective. Note that it is more secure than doing it physically on the grounds that
it additionally makes sure that the objective exists, and is visible.
- create helpers: they are presumably the main capacities traded by
test_utils.js. These helpers are valuable to make a widget, with a mock environment,
and a lot of little detail to reproduce however much as could be expected the
genuine circumstances. The most significant is unquestionably createView.
- qunit assertions: QUnit can be reached out with particular
assertions. For Odoo, we often test some DOM properties. To this end we made a few
assertions to assist with that. For instance, the containsOnce assertions takes a
widget/jQuery/HtmlElement and a selector and afterward checks in the event that the
objective contains precisely one counterpart for the CSS selector.
For example, with these helpers, here is what a simple form test could look like:
QUnit.test('Simple Form Testing ', async function (assert) {
assert.expect(1);
var form = await testUtils.createView({
View: FormView,
model: 'student.student',
data: this.data,
arch: '',
res_id: 1,
});
var line = form.$('[name="f_name"]').length
assert.strictEqual(line, 1,
"The field exist");
form.destroy();
});