Redirect old URL
You must migrate from a current system or website to the Odoo website. Replace your old
URLs with a new URL. While using redirection of URLs, all of your SEO ranks will
improve. In this, we will be discussing how to transfer to new. And also, We'll examine
how to redirect old URLs to new ones in this recipe.
For using the Redirects, Go to Website > Configuration > Redirects.We can see a tree view
of the redirects; just click on the create button to create a new record.
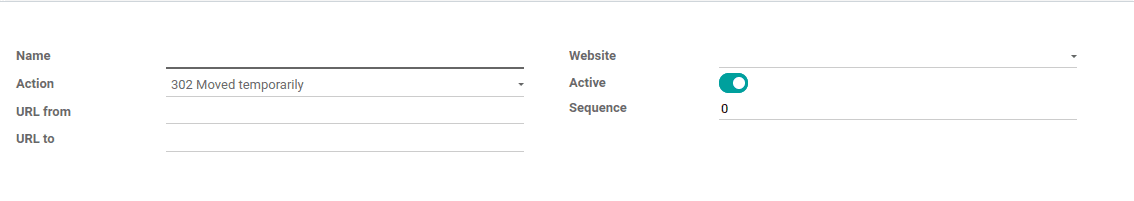
The form view of the redirect is shown.Here we can see some fields. Just take a look at
which are that and those uses.
Name: Name of the website rewrite
Action: Which action will perform on that rewrite. There are mainly four
types of actions
- 302 Moved Temporarly
- 404 Not Found
- 301 Moved Permanently
- 308 Redirect/ Rewrite
302 Moved Temporarily: An HTTP status code of 302 means the page the
user is trying to access has been temporarily moved to a different location. The server
returns the user to the new destination with a 302 "Found" or "Moved Temporarily"
redirect, even though the original location is still being used for requests.
404 Not Found: A 404 error is an HTTP Status number that indicates that
the page you attempted to access on a website was not located on their server.
301 Moved Permanently: The 301 Transferred Permanently redirect status
response code from the HyperText Transfer Protocol (HTTP) indicates that the requested
resource has been definitively moved to the URL specified in the Location headers.
Search engines update their links to the resource after a browser redirects to the
updated URL.
308 Redirect/ Rewrite: The 308 Permanent Redirect redirect status
response code indicates that the resource requested has been permanently redirected to
the URL specified in the Location headers. A browser redirects to this page, and search
engines update their links to the resource (the 'link-juice' is transmitted to the new
URL in SEO parlance).
Url from: Old url
Url to: new url
Website: The Website field is used when you are using the multi-website feature and you
want to limit the redirection rule to one website only. By default, however, the rule
will be applied to all websites.
Active: Which can used if you want to enable/disable rules from time to time.
Manage website record
Website record are the records that everything on the website. The everything created or
checking on the front end of the website will be stored on the back end of the website.
We can see that the all details of the website that are stored on the backend.
We can take a look at how to create a website form and how to store that value on to the
backend.
First of all we have to create a menu named Repair order for that
<record id="menu_repair_form" model="website.menu">
<field name="name">Repair Order</field>
<field name="url">/repair_webform</field>
<field name="parent_id" ref="website.main_menu"/>
<field name="sequence">55</field>
</record>
By clicking this created menu we can see a form view for that we have to design that form
view.
<template id="create_repair" name="Repair Order">
<t t-call="website.layout">
<div id="wrap">
<div class="oe_structure">
<div class="container">
<form role="form" action="/create/webrepair" method="POST">
<input type="hidden" name="csrf_token" t-att-value="request.csrf_token()"/>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="product_id" class="control-label"> Product </label>
<select name="product_id" class="form-control link-style">
<t t-foreach="product_rec" t-as="product">
<option t-esc="product.name" t-att-value="product.id"/>
</t>
</select>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="product_qty" class="control-label"> Quantity </label>
<input type="number" name="product_qty" t-att-value="product_qty" id="product_qty" class="form-control"/>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="product_uom" class="control-label"> UOM </label>
<select name="product_uom" class="form-control link-style">
<t t-foreach="uom" t-as="uom">
<option t-esc="uom.name" t-att-value="uom.id"/>
</t>
</select>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="partner_id" class="control-label"> Customer </label>
<select name="partner_id" class="form-control link-style">
<t t-foreach="customer_id" t-as="customer">
<option t-esc="customer.name" t-att-value="customer.id"/>
</t>
</select>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="location_id" class="control-label"> Location </label>
<select name="location_id" class="form-control link-style">
<t t-foreach="location_id" t-as="location">
<option t-esc="location.name" t-att-value="location.id"/>
</t>
</select>
</div>
<div class="clearfix oe_login_buttons">
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary pull-left">Submit</button>
</div>
</form>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</t>
</template>
Next we can write a controller for this on that python file we have to write the things
which fields and what are the things we can seen on the website form.
class Request(http.Controller):
@http.route(['/repair_webform'], type='http', auth="public", website=True)
def repair_webform(self, **kw):
product_rec = request.env['product.product'].sudo().search([])
uom = request.env['uom.uom'].sudo().search([])
customer_id = request.env['res.partner'].sudo().search([])
location_id = request.env['stock.location'].sudo().search([])
return request.render("website_demo.create_repair", {
'product_rec': product_rec,
'uom': uom,
'customer_id': customer_id,
'location_id': location_id,
})
@http.route(['/create/webrepair'], type='http', auth="public", website=True)
def create_webrepair(self, **kw):
request.env['repair.order'].sudo().create(kw)
return request.render("website_demo.repair_thanks", {})
Here we can see that on the repair_webform() the fields that are shown on the form are
specifield. But on the create_webrepair() function just create a new record based on the
previous functions values