In Odoo, sometimes we have to set a specific value for a field by default every time we create a record of that model. To achieve this task we have two key options/methods.
1. Passing value through kwargs
2. Setting value with default_get function
1) Passing value through kwargs
A field in Odoo has multiple kwargs namely string, read-only, required, etc. Among one of them is the kwarg called default.
We can pass a value through default kwarg in two ways
* Set the value directly
* Execute a function and return the value
- We can set the default value directly by assigning the value to kwarg like this
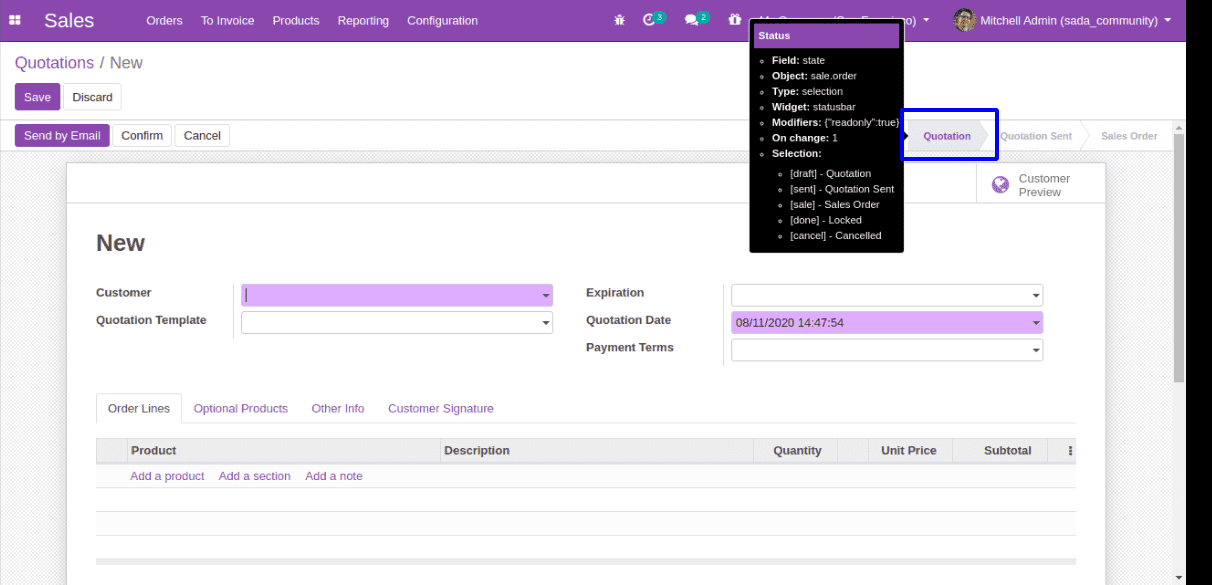
state = fields.Selection([
('draft', 'Quotation'),
('sent', 'Quotation Sent'),
('sale', 'Sales Order'),
('done', 'Locked'),
('cancel', 'Cancelled'),
], string='Status', readonly=True, copy=False, index=True, tracking=3, default='draft')
This is the code for the state of sale.order model, here default is set as ‘draft’, which is the Quotation state, so every time a new sale order is created, by default the state will be Quotation.
- For returning a value from a function to kwarg, we can run an anonymous lambda function or write the function name to be called.
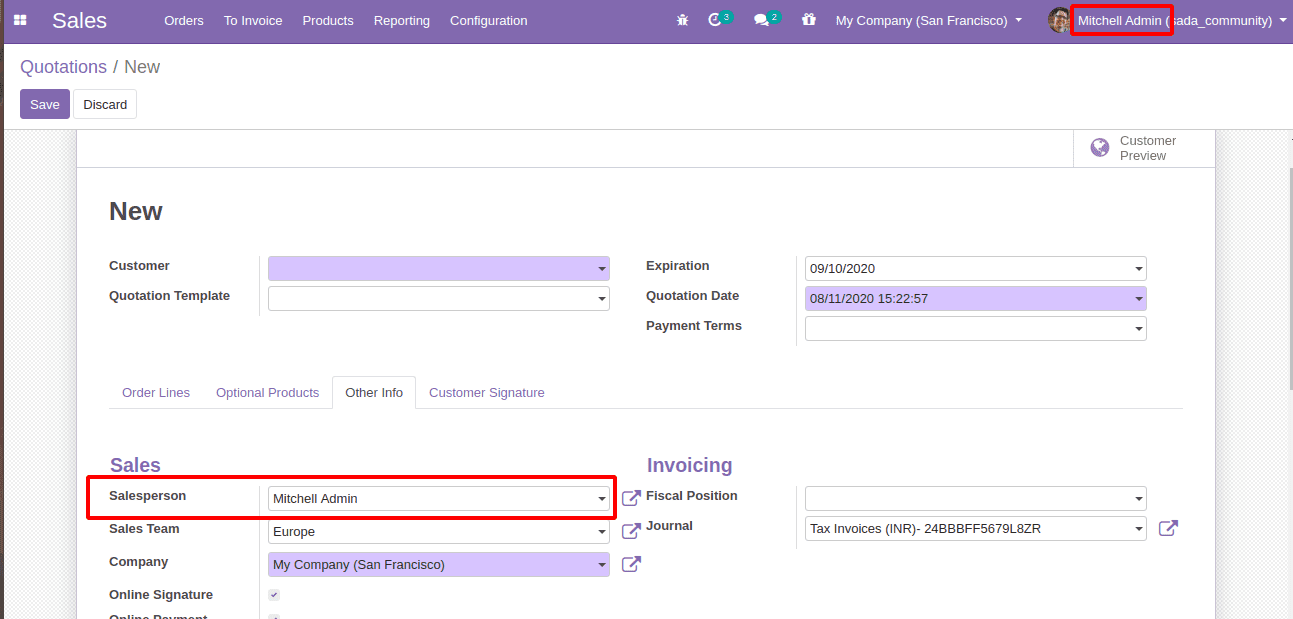
With lambda function: let's look at the ‘Salesperson’ field of sale.order
user_id = fields.Many2one(
'res.users', string='Salesperson', index=True, tracking=2, default=lambda self: self.env.user,
domain=lambda self: [('groups_id', 'in', self.env.ref('sales_team.group_sale_salesman').id)])
Here the currently logged in user is calculated with the lambda function lambda self: self.env.user and is set as the default Salesperson as shown below,
With function call: To compute a default value through a function call, the function should be defined before the field is defined. For example, we will look at the code of the ‘Expiration’ field in sale.order model called validity_date.
First, the function is defined
def _default_validity_date(self):
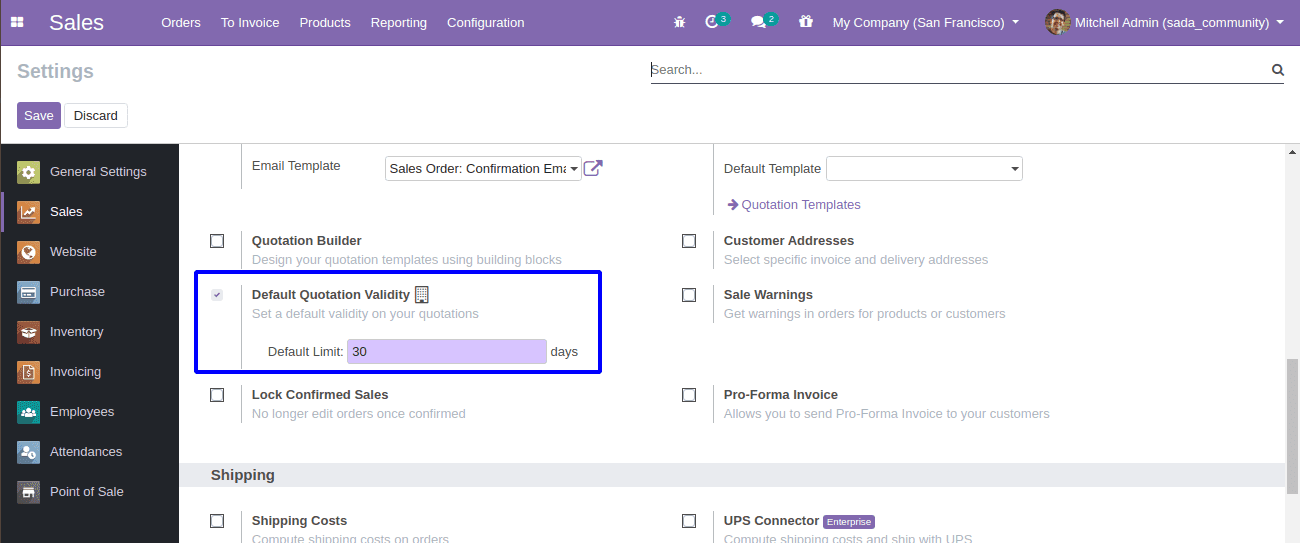
if self.env['ir.config_parameter'].sudo().get_param('sale.use_quotation_validity_days'):
days = self.env.company.quotation_validity_days
if days > 0:
return fields.Date.to_string(datetime.now() + timedelta(days))
return False
Then this function is called in the field definition,
validity_date = fields.Date(string='Expiration', readonly=True, copy=False, states={'draft': [('readonly', False)], 'sent': [('readonly', False)]},
default=_default_validity_date)
Here the _default_validity_date function takes the number that is set in the configuration and computer date with today and returns the value
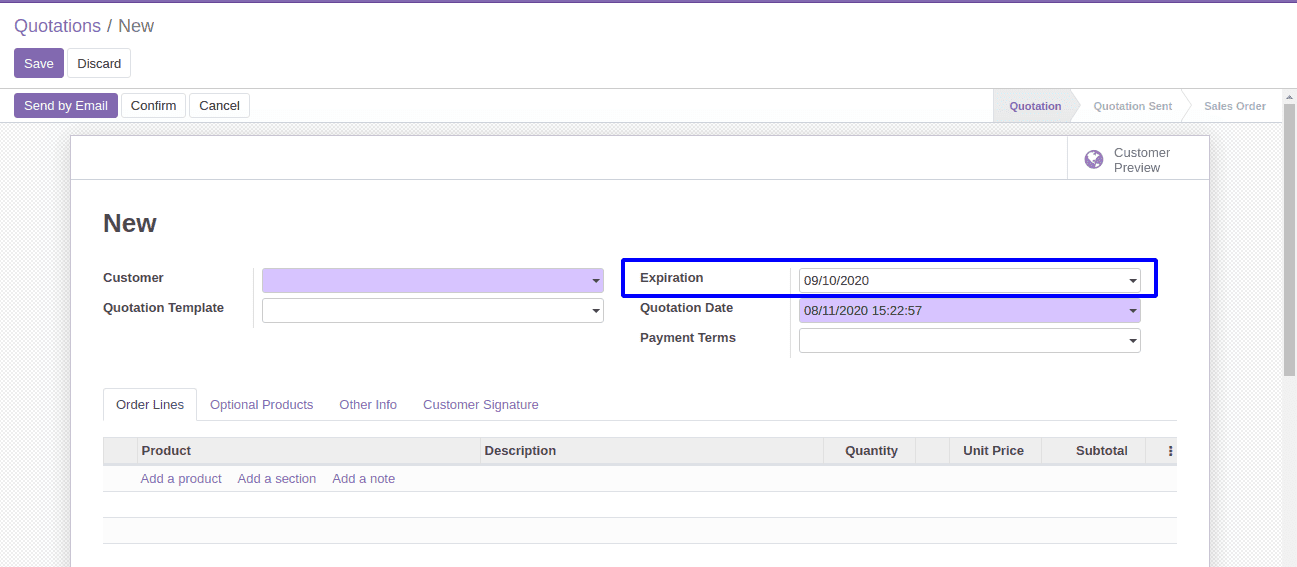
So when a new sale order is created, 30 days after today will be shown as default Expiration date as shown below
2) Setting value with default_get function
In this method, we can set and compute the default values of multiple fields by inheriting the default_get function and updating values into it.
Eg: Two custom fields are created in the sale order module, sales_person_contact and sales_person_email. We then set the default value of these as shown below
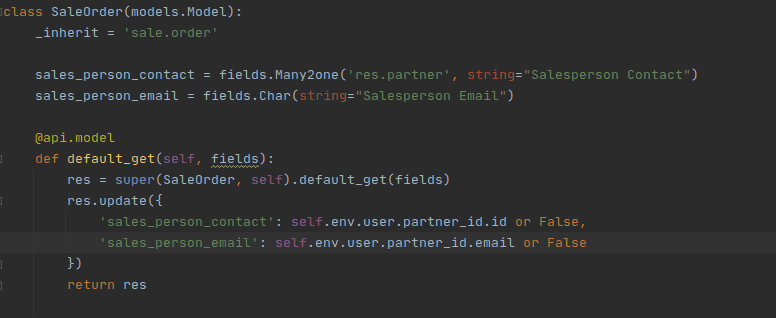
So when you create a new sale order, these fields will be set by default like this
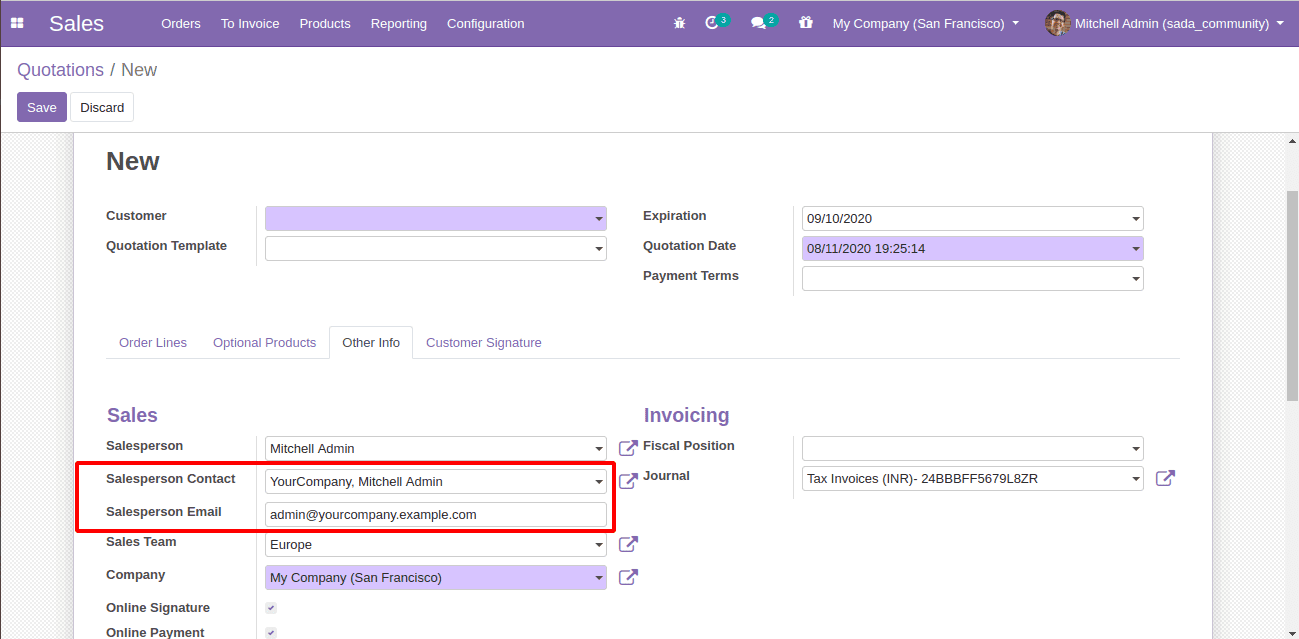
These are the main methods of setting default values for fields in Odoo.
To know more about a similar topic on computed fields, Read Blog: How to add computed fields to a model in Odoo 13