Sitemap is important for every website, and It is a file that provides information about the website pages and other files on the website. The search engine uses a sitemap for indexing the website pages.
This blog will explain how we can change the already existing sitemap on the Odoo website.
open <odoo_server_url>/sitemap.xml for seeing the sitemap.
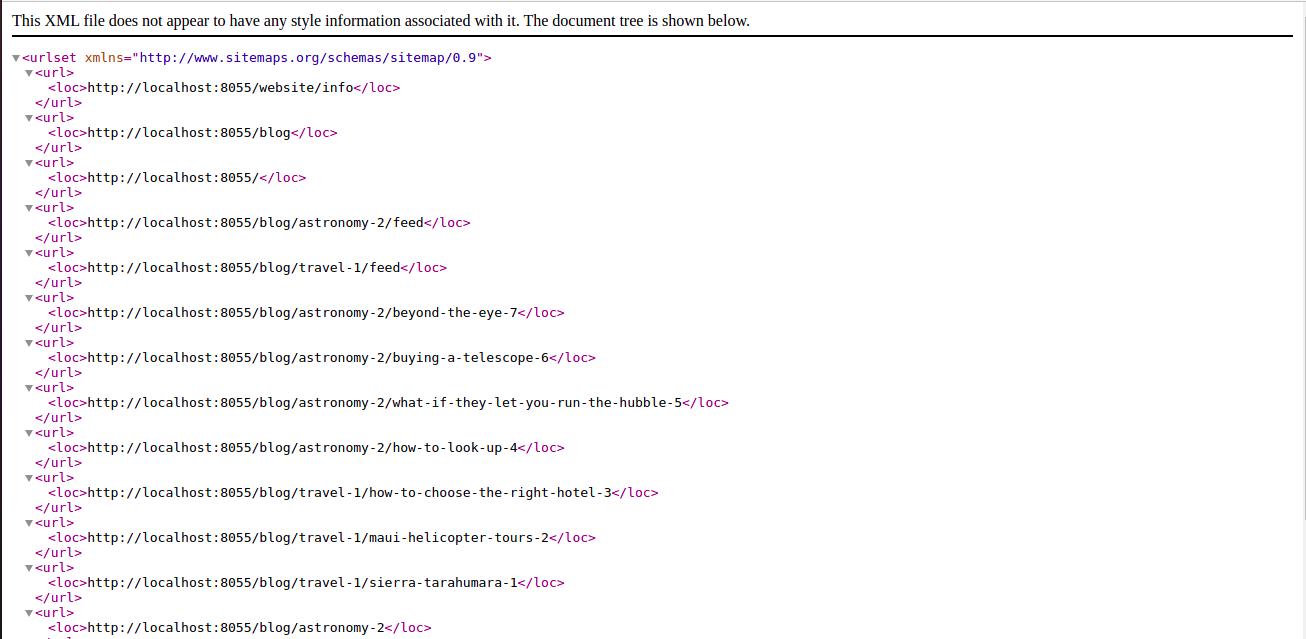
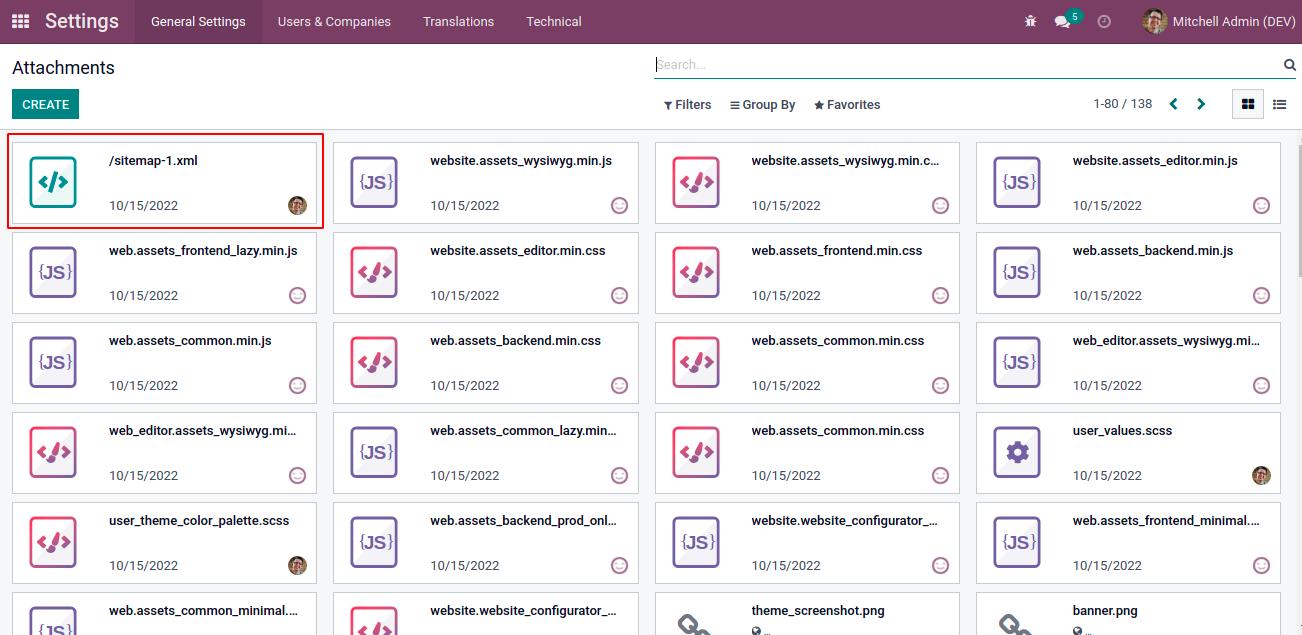
The sitemap.xml file will see on the attachments.
We can use the sitemap_xml_index method for changing the already existing sitemap. Ie,
@http.route('/sitemap.xml', type='http', auth="public", website=True, multilang=False, sitemap=False)
def sitemap_xml_index(self, **kwargs):
current_website = request.website
Attachment = request.env['ir.attachment'].sudo()
View = request.env['ir.ui.view'].sudo()
mimetype = 'application/xml;charset=utf-8'
content = None
def create_sitemap(url, content):
return Attachment.create({
'raw': content.encode(),
'mimetype': mimetype,
'type': 'binary',
'name': url,
'url': url,
})
dom = [('url', '=', '/sitemap-%d.xml' % current_website.id), ('type', '=', 'binary')]
sitemap = Attachment.search(dom, limit=1)
if sitemap:
# Check if stored version is still valid
create_date = fields.Datetime.from_string(sitemap.create_date)
delta = datetime.datetime.now() - create_date
if delta < SITEMAP_CACHE_TIME:
content = base64.b64decode(sitemap.datas)
if not content:
# Remove all sitemaps in ir.attachments as we're going to regenerated them
dom = [('type', '=', 'binary'), '|', ('url', '=like', '/sitemap-%d-%%.xml' % current_website.id),
('url', '=', '/sitemap-%d.xml' % current_website.id)]
sitemaps = Attachment.search(dom)
sitemaps.unlink()
pages = 0
locs = request.website.with_user(request.website.user_id)._enumerate_pages()
while True:
values = {
'locs': islice(locs, 0, LOC_PER_SITEMAP),
'url_root': request.httprequest.url_root[:-1],
}
urls = View._render_template('website.sitemap_locs', values)
if urls.strip():
content = View._render_template('website.sitemap_xml', {'content': urls})
pages += 1
last_sitemap = create_sitemap('/sitemap-%d-%d.xml' % (current_website.id, pages), content)
else:
break
if not pages:
return request.not_found()
elif pages == 1:
# rename the -id-page.xml => -id.xml
last_sitemap.write({
'url': "/sitemap-%d.xml" % current_website.id,
'name': "/sitemap-%d.xml" % current_website.id,
})
else:
# TODO: in master/saas-15, move current_website_id in template directly
pages_with_website = ["%d-%d" % (current_website.id, p) for p in range(1, pages + 1)]
# Sitemaps must be split in several smaller files with a sitemap index
content = View._render_template('website.sitemap_index_xml', {
'pages': pages_with_website,
'url_root': request.httprequest.url_root,
})
create_sitemap('/sitemap-%d.xml' % current_website.id, content)
return request.make_response(content, [('Content-Type', mimetype)])This original function is defined inside the controller of the website module. And whenever the sitemap file is generated this function will call.
locs = request.website.with_user(request.website.user_id)._enumerate_pages()
From this code the website urls are generated for the sitemap. Here using the function _enumerate_pages it is defined in the model website.
def _enumerate_pages(self, query_string=None, force=False):
""" Available pages in the website/CMS. This is mostly used for links
generation and can be overridden by modules setting up new HTML
controllers for dynamic pages (e.g. blog).
By default, returns template views marked as pages.
:param str query_string: a (user-provided) string, fetches pages
matching the string
:returns: a list of mappings with two keys: ``name`` is the displayable
name of the resource (page), ``url`` is the absolute URL
of the same.
:rtype: list({name: str, url: str})
"""
router = http.root.get_db_router(request.db)
# Force enumeration to be performed as public user
url_set = set()
sitemap_endpoint_done = set()
for rule in router.iter_rules():
if 'sitemap' in rule.endpoint.routing and rule.endpoint.routing['sitemap'] is not True:
if rule.endpoint in sitemap_endpoint_done:
continue
sitemap_endpoint_done.add(rule.endpoint)
func = rule.endpoint.routing['sitemap']
if func is False:
continue
for loc in func(self.env, rule, query_string):
yield loc
continue
if not self.rule_is_enumerable(rule):
continue
if 'sitemap' not in rule.endpoint.routing:
logger.warning('No Sitemap value provided for controller %s (%s)' %
(rule.endpoint.method, ','.join(rule.endpoint.routing['routes'])))
converters = rule._converters or {}
if query_string and not converters and (query_string not in rule.build({}, append_unknown=False)[1]):
continue
values = [{}]
# converters with a domain are processed after the other ones
convitems = sorted(
converters.items(),
key=lambda x: (hasattr(x[1], 'domain') and (x[1].domain != '[]'), rule._trace.index((True, x[0]))))
for (i, (name, converter)) in enumerate(convitems):
if 'website_id' in self.env[converter.model]._fields and (not converter.domain or converter.domain == '[]'):
converter.domain = "[('website_id', 'in', (False, current_website_id))]"
newval = []
for val in values:
query = i == len(convitems) - 1 and query_string
if query:
r = "".join([x[1] for x in rule._trace[1:] if not x[0]]) # remove model converter from route
query = sitemap_qs2dom(query, r, self.env[converter.model]._rec_name)
if query == FALSE_DOMAIN:
continue
for rec in converter.generate(uid=self.env.uid, dom=query, args=val):
newval.append(val.copy())
newval[-1].update({name: rec})
values = newval
for value in values:
domain_part, url = rule.build(value, append_unknown=False)
if not query_string or query_string.lower() in url.lower():
page = {'loc': url}
if url in url_set:
continue
url_set.add(url)
yield page
# '/' already has a http.route & is in the routing_map so it will already have an entry in the xml
domain = [('url', '!=', '/')]
if not force:
domain += [('website_indexed', '=', True), ('visibility', '=', False)]
# is_visible
domain += [
('website_published', '=', True), ('visibility', '=', False),
'|', ('date_publish', '=', False), ('date_publish', '<=', fields.Datetime.now())
]
if query_string:
domain += [('url', 'like', query_string)]
pages = self._get_website_pages(domain)
for page in pages:
record = {'loc': page['url'], 'id': page['id'], 'name': page['name']}
if page.view_id and page.view_id.priority != 16:
record['priority'] = min(round(page.view_id.priority / 32.0, 1), 1)
if page['write_date']:
record['lastmod'] = page['write_date'].date()
yield record
We can use this function for changing the website pages in the sitemap. We can use this function if we are required to add new pages or new URLs to the sitemap, we can use this function.
Add records page to sitemap
To add a records page to the sitemap, first we need to import the following methods.
from odoo.addons.http_routing.models.ir_http import slug
from odoo.addons.website.models.ir_http import sitemap_qs2dom
The slug is used to generate user-friendly URLs, and it is created based on the record name. The sitemap_qs2dom is mainly used to create a domain based on the route and query strings.
Then next, we can create a new method inside the main.py. Ie,
class Main(http.Controller):
def sitemap_records(env, rule, qs):
records = env[your.model]
dom = sitemap_qs2dom(qs, '/url', records._rec_name)
for r in records.search(dom):
loc = '/url/%s' % slug(r)
if not qs or qs.lower() in loc:
yield {'loc': loc}
Here sitemap_records is a python generator function. Whenever a sitemap is generated, this function will be called. This function generated a domain with sitemap_qs2dom. And then used this generated domain to search the records. Then generated the location through the method slug(). By using the slug method, we will get a user-friendly URL.
Then we can add the sitemap_records function reference in a record’s detailed routes. ie,
@http.route('/url/<model("your.model"):record>', type='http', auth="user", website=True, sitemap=sitemap_records)
def records_detail(self, record):Here we passed the sitemap_records() function reference to the route with a sitemap keyword.
This way, we can add record pages to the sitemap.xml. If we do not need to filter records and we need to list all the records in a sitemap, then we can just pass True instead of the function reference.
And last, update our module for the changes. The sitemap will update every 12 hours. So If we want to see the changes, go to the attachments and delete the already existing sitemap.xml. Then open <odoo_server_url>/sitemap.xml in the browser then we can see the changes.