In Odoo, the balance sheet is a financial statement that summarizes the company's assets, liabilities, and equity, providing a clear idea of what the company owns and owes.
The balance sheet is an essential financial report for any business as it helps determine the company's financial health, liquidity, and overall performance. Odoo's accounting module makes it easy to generate balance sheets for any date range, and the reports can be customized to display data in different formats, making it easier for users to analyze financial information.
Overall, Odoo's balance sheet functionality helps businesses keep track of their financial position and make informed decisions based on accurate and up-to-date financial data.
In this blog, we will be discussing the balance sheet in Odoo 16.
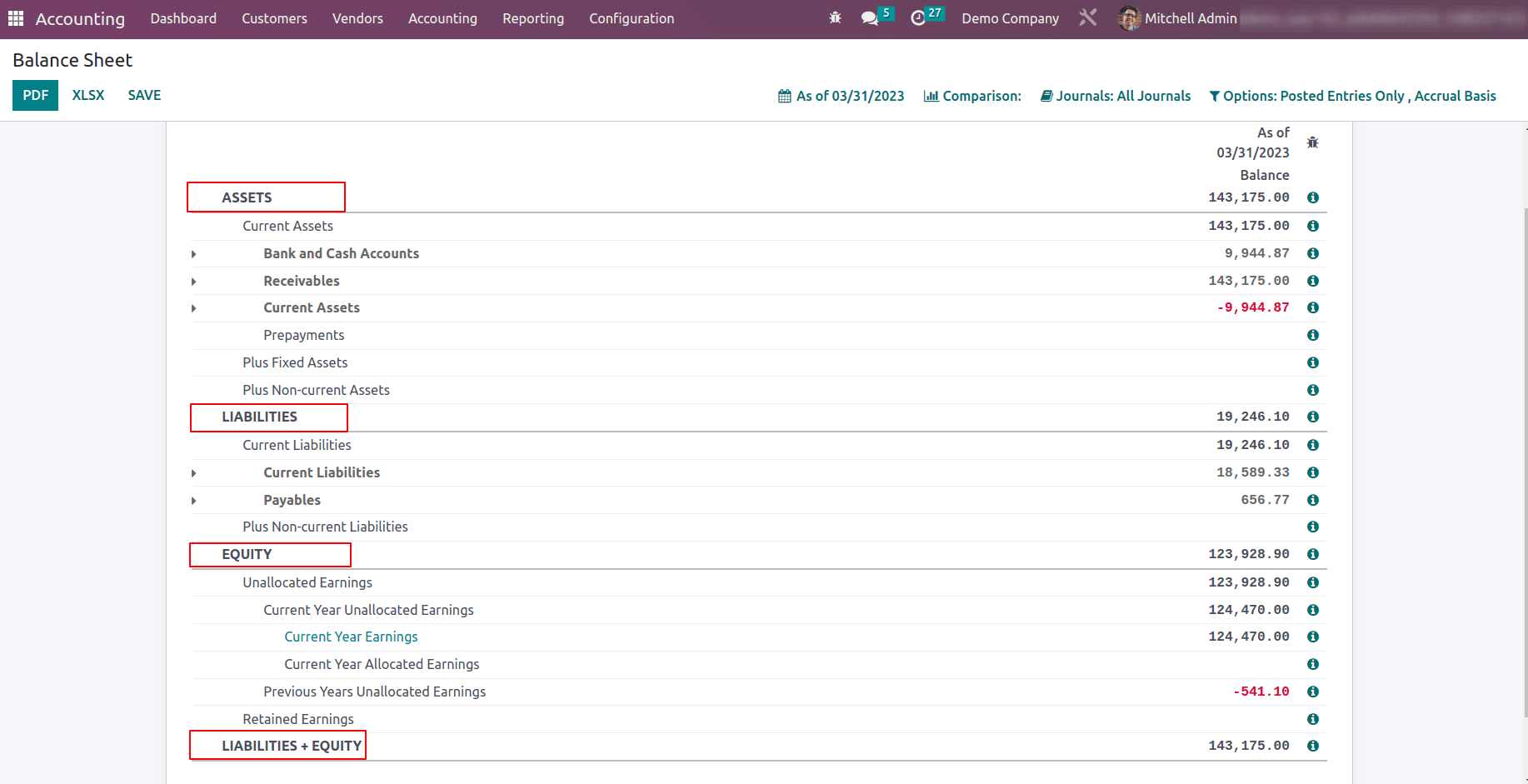
The balance sheet depicts the companies' Assets, Liabilities, and equity details are available. So before going to the balance sheet report, first discuss the Assets and what are the asset types that can be configured in odoo.
ASSETS
An asset is any resource hosted or possessed by a business organization. The asset can be anything, it can include land, buildings, Office appliances, furniture, cash deposits, etc which brings a positive economic value. They can be converted into cash in the future.
When you configure the Chart of Accounts in Odoo, there are different account types for assets, since each type of asset can be recorded separately in the balance sheet.
As you filter the COA by active asset account, one can see all the asset type accounts.
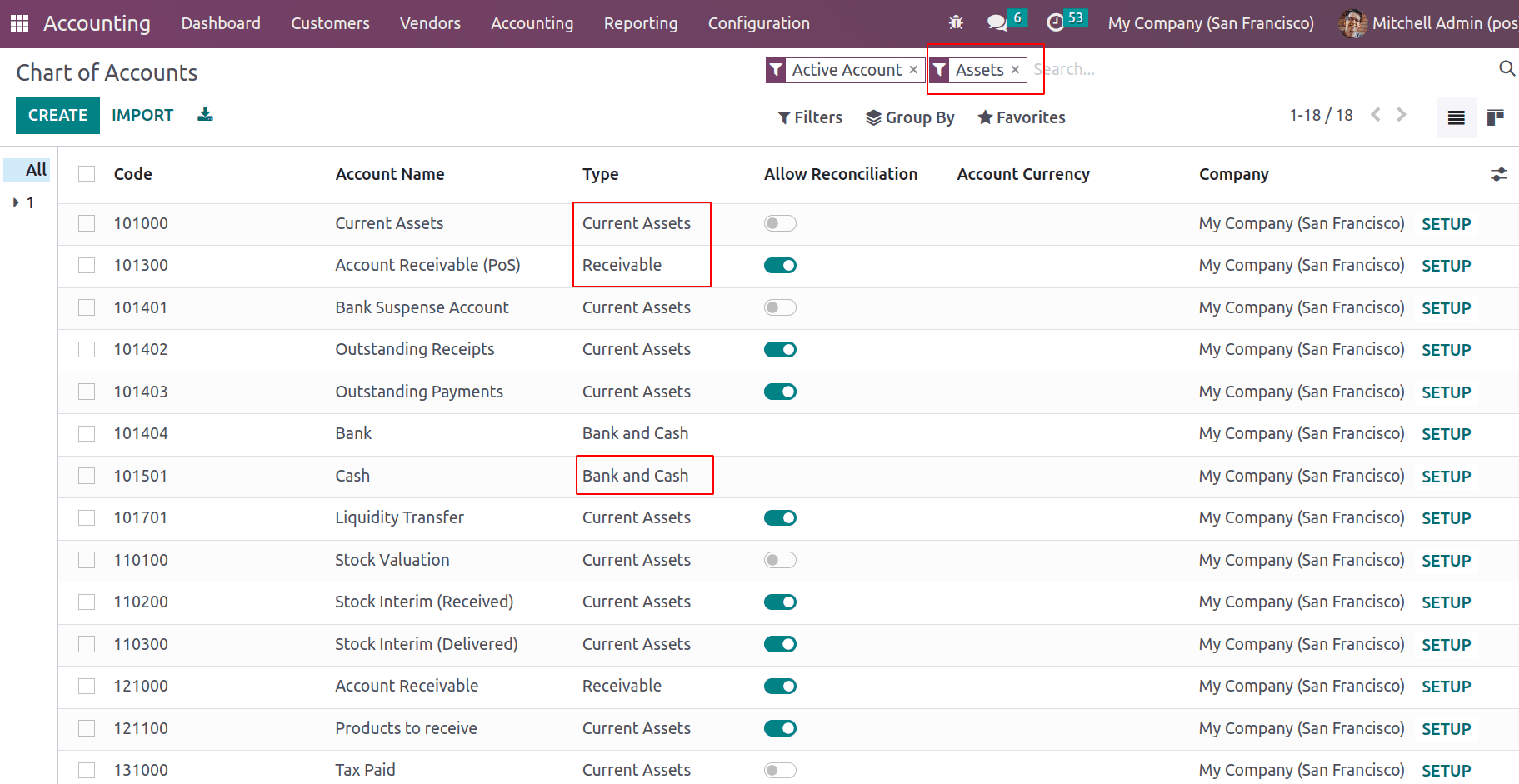
The Account Type Asset has some classifications including Current Assets, Non-current Assets, Receivables, Fixed assets, Bank and Cash, etc.

Receivables:
Suppose a company is selling goods or services to a customer and the customer need to make payment for the received goods and services. These are the amount of money that needs to be received from the company’s customers for any sales or services. The receivables are a cash amount and cash is considered an asset that has a positive value.
Bank and Cash:
A Company may have a bank account in which some cash deposits will be there. Also, in the company’s cash drawer, some money will be there. Suppose the company needs to make a payment to a partner, so either money can be transferred from the bank account or can use the liquid money in the cash drawer. This may be determined by variables such as the availability of funds in each account, any transaction fees or charges, and the urgency of the payment.
Thus the cash accounts which keep the details of cash and bank accounts which keep the details of money in the bank are of type bank and cash.
Current Assets:
Current assets are short-term assets that can be converted into cash within a year or one working cycle. Cash and cash equivalents represent the most liquid current assets and can be used to cover immediate cash needs. Cash receivables, short-term investments, stock, etc are considered current assets, which means they are converted into cash within a year.
These assets are essential for a company's day-to-day operations, as they provide the liquidity necessary to cover short-term obligations, such as payroll, accounts payable, and other operating expenses.
Non-Current Assets
Non-current assets are not expected to be converted to cash within the next 12 months. These assets are typically held by a company for a longer period and are used in the operation of the business. Property, plant, and equipment, investments in other companies, intangible assets like patents and copyrights, and long-term receivables are non-current assets.
Non-current assets are recorded on a company's balance sheet and are generally valued at their original cost, minus any accumulated depreciation or impairment charges. Because these assets are expected to be held for a longer period, they are not valued at their current market value like some current assets.
Companies need to manage their non-current assets effectively to ensure that they are being utilized efficiently and generating value for the company. Companies may also need to periodically revalue their non-current assets to reflect changes in their value or to account for impairment charges.
Prepayments
Prepayments are a type of asset that represents payments made by a company/customer in advance of receiving goods or services. Prepayments are recorded as assets on a company's balance sheet and are considered current assets because they are expected to be used or consumed within the next 12 months. As the goods or services are received, the prepayments are gradually recognized as expenses in the company's income statement. For example, if a company pays for a 12-month insurance policy upfront, the cost of the policy would be recognized as an expense over the 12 months, with a portion of the cost being recognized each month.
Fixed Assets
Property, plant, and equipment are tangible assets that a company acquires for long-term use in the operation of its business are fixed assets. These assets are used to generate revenue for the company and are not intended for resale. Fixed assets are recorded on a company's balance sheet.
Adding Opening Balance
At the start of any company, the opening balance needs to be updated before starting the operations. Opening balances are the initial balance that refers to the amount of money or assets that a business or individual has at the beginning of a financial period, such as a month, quarter, or year. It is the starting point for any financial statement or accounting record and is used to calculate the financial position of the entity at the end of the period.
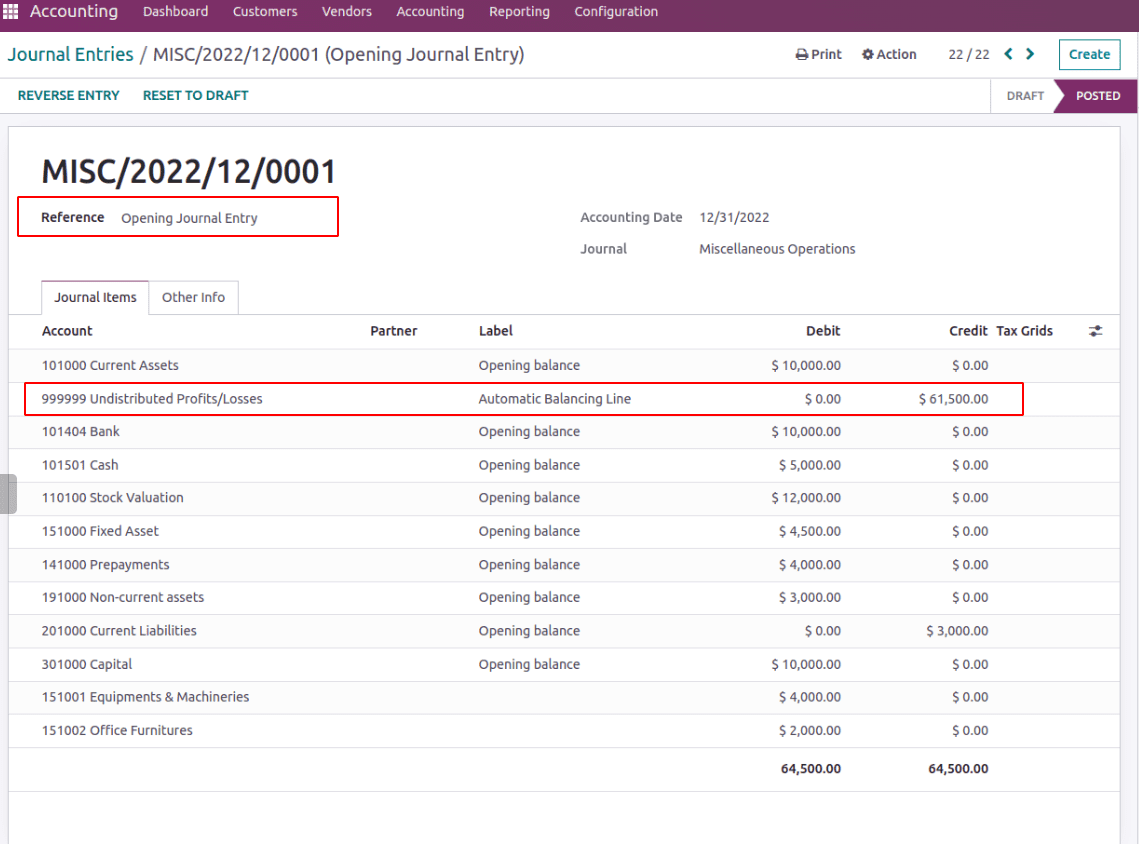
If a business has $10,000 in cash and $20,000 in inventory at the start of a month, lands will be there which is worth $25,000, and furniture and equipment of $11,000, etc. Adding an opening balance will create a journal entry and be posted to the balance sheet on an accounting date.
For the opening balance, the opening debit and credit might not same. So to post the journal entry odoo itself provides a ‘999999 Undistributed Profits/Losses’ account whose account type is ‘Current Year Earnings’. Thus the unbalanced amount will be recorded as unallocated earnings in the balance sheet.
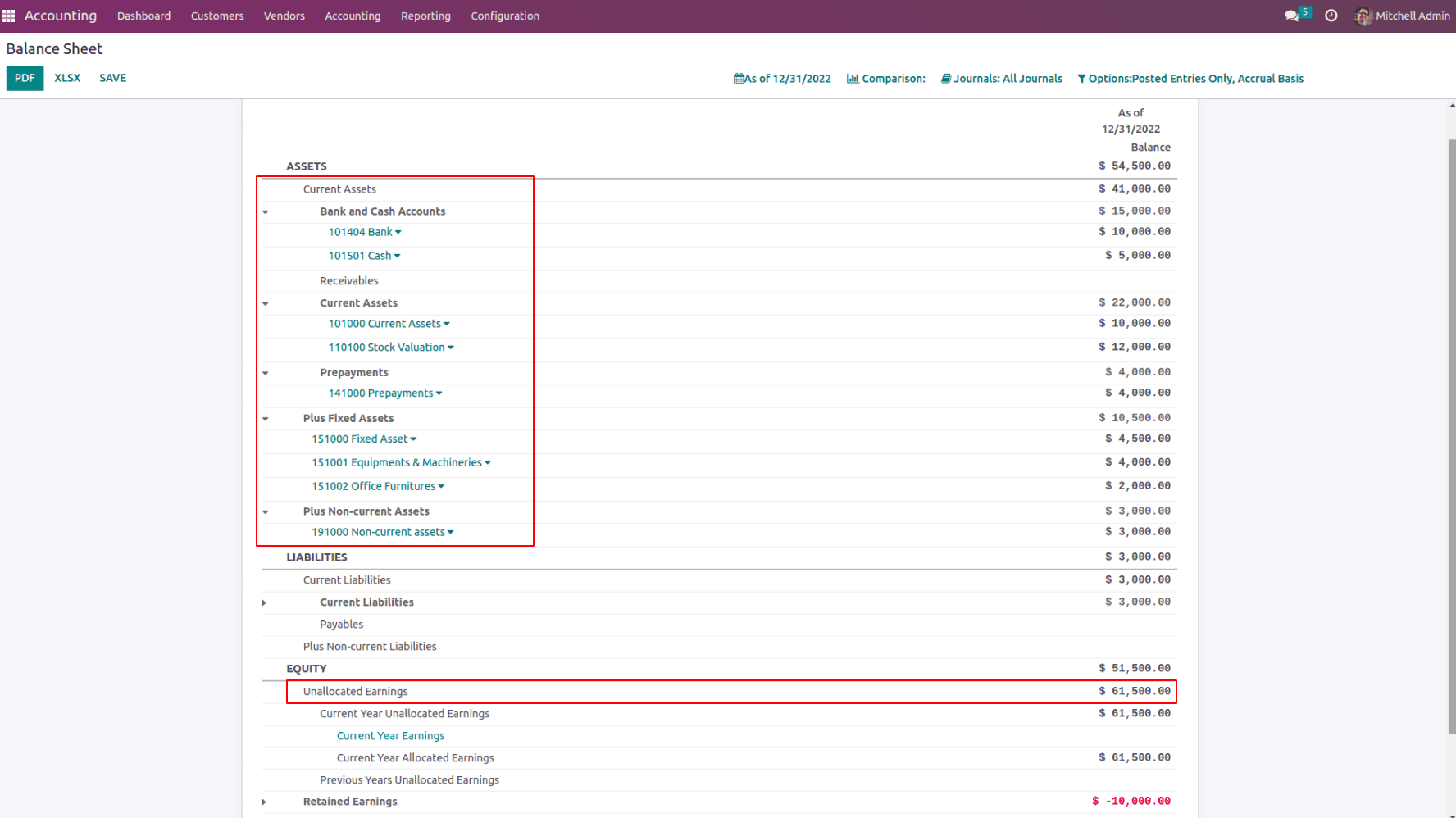
All the initial assets are updated in the balance sheet and the balancing differences will be kept as unallocated earnings.
Now as the company starts operating, it involves so many operations. In the following operations, the balance sheet gets updated accordingly.
Consider an Invoice for the customer, where the receivables are recorded in the Account Receivables.
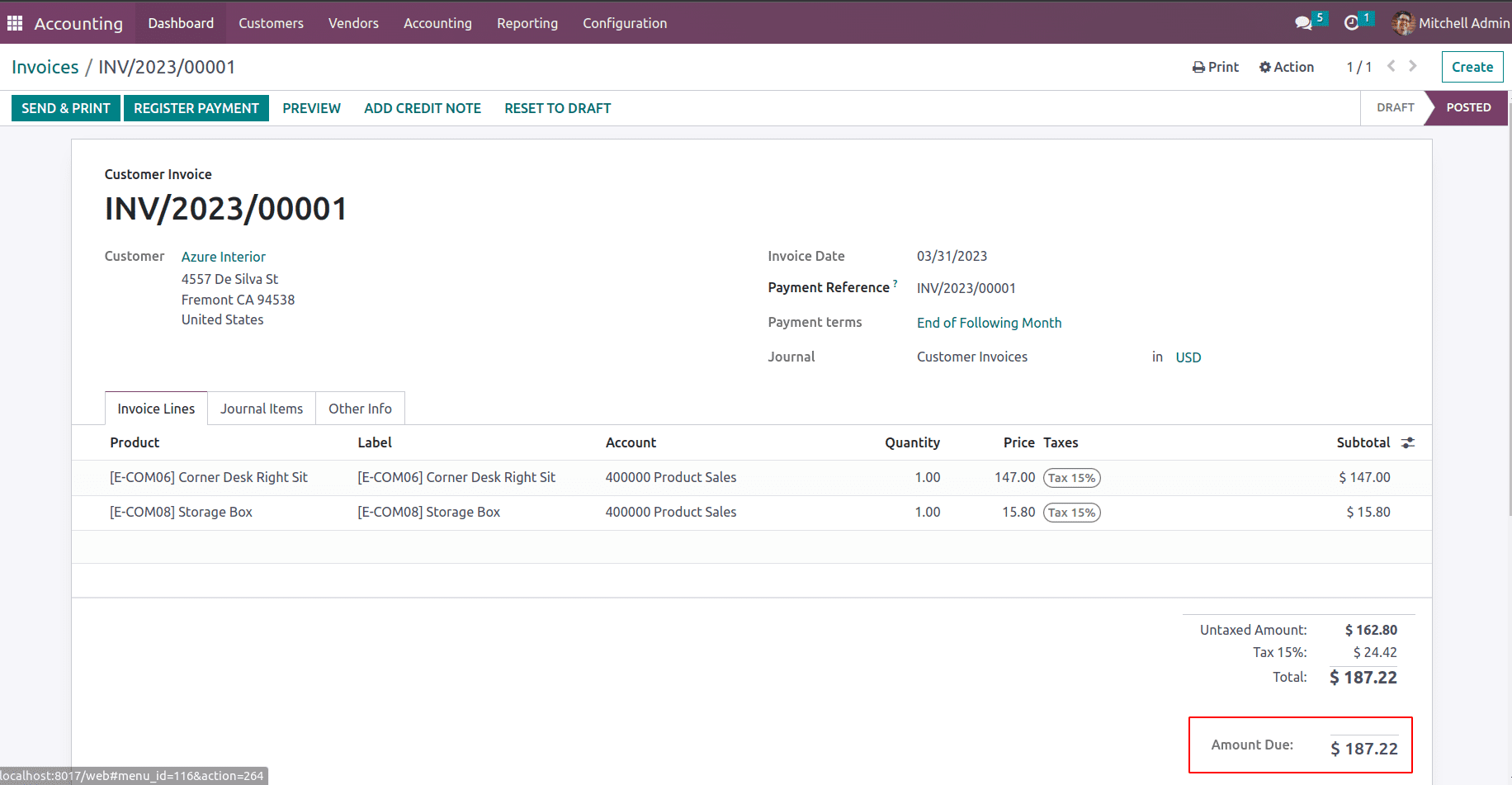
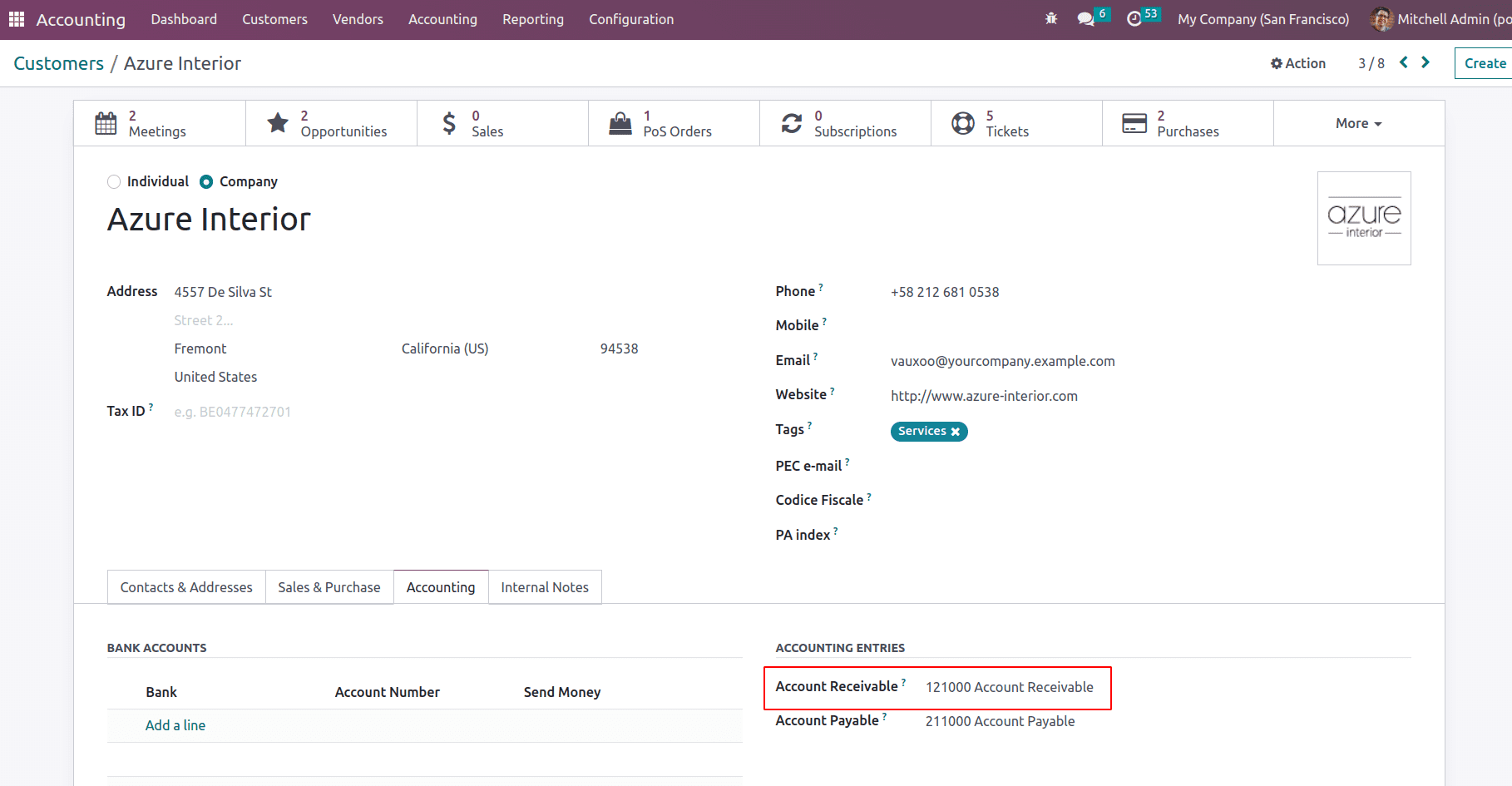
In this invoice, $187.22 needs to be received from the customer. Receivable accounts are mentioned in the partner form.
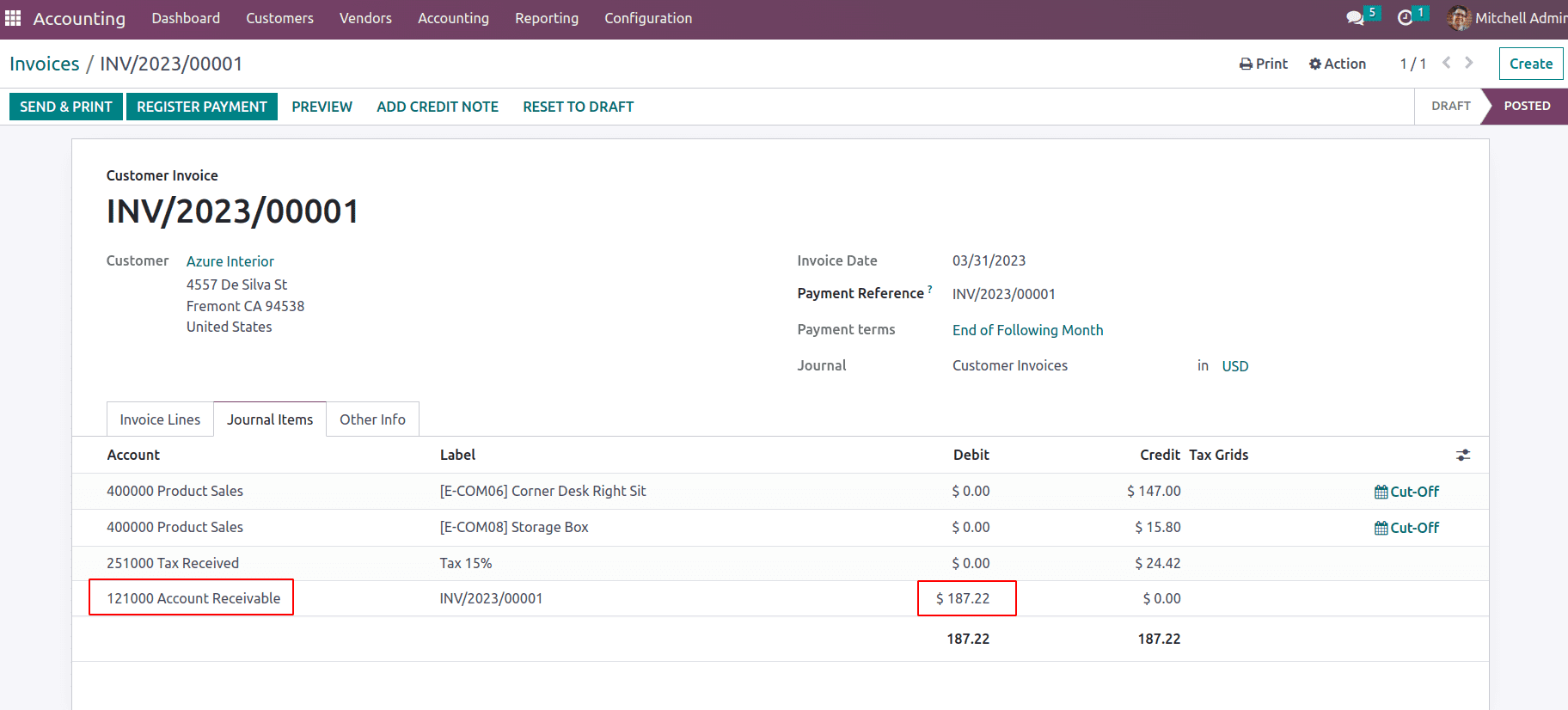
In the journal items of the tab, you will able to see the account receivable is affected as an invoice is posted.
As the customer made a payment to the invoice and reconciled it with the bank statement, the received cash will be reflected in the bank account.
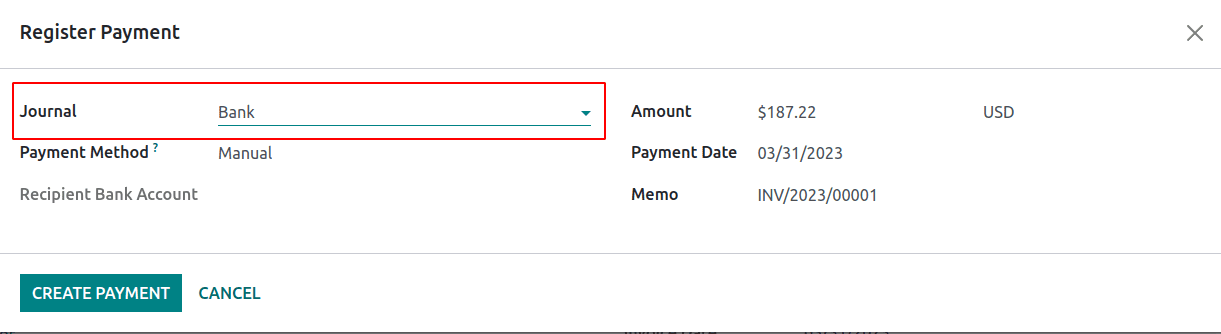
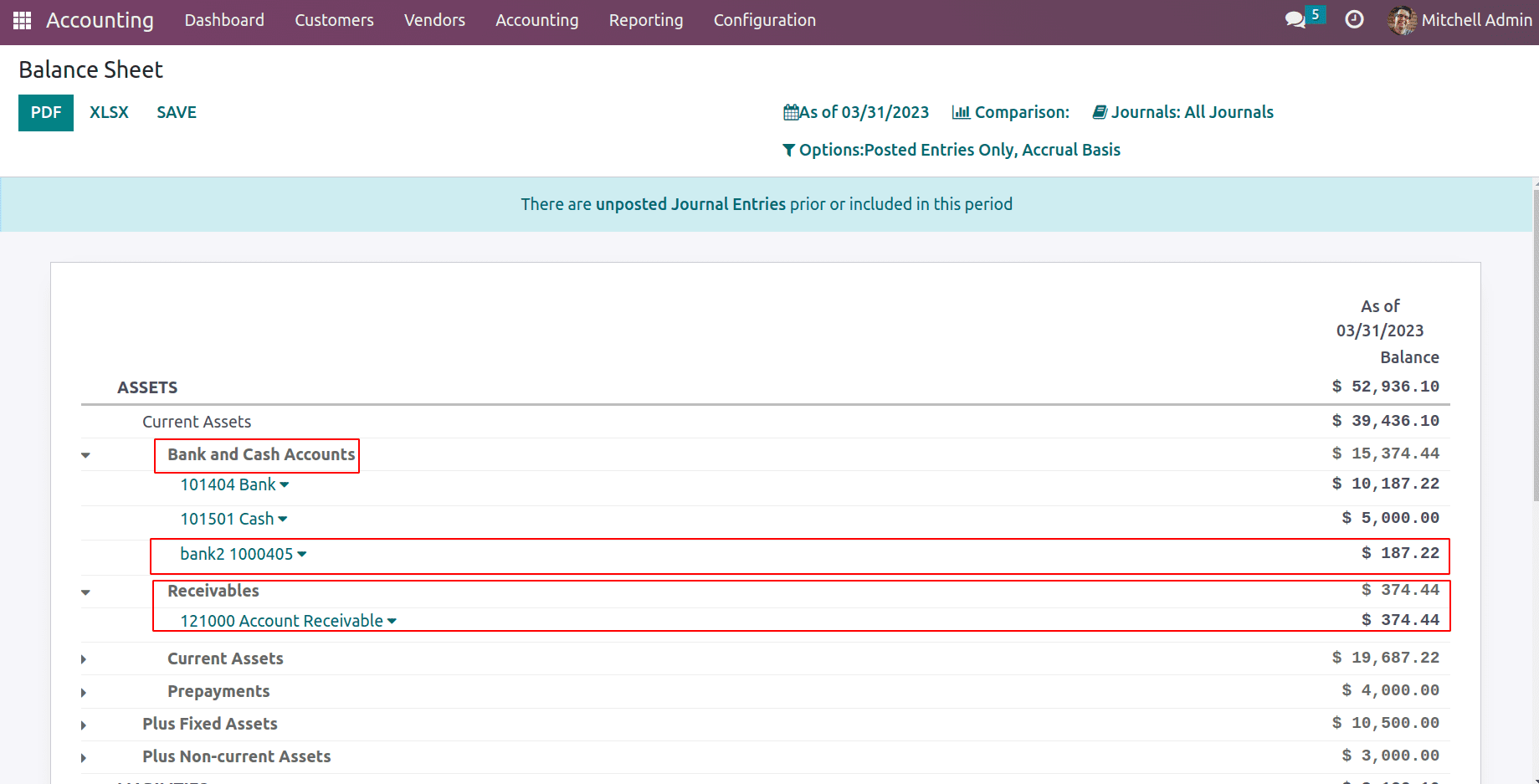
Thus the receivables are received at the bank. Now receivables become zero and the bank is debited with the asset or cash amount.
Now consider a deferred expense is recorded in Odoo. Deferred expenses are prepaid expenses like insurance, building rent, etc, which is an assets for the company.
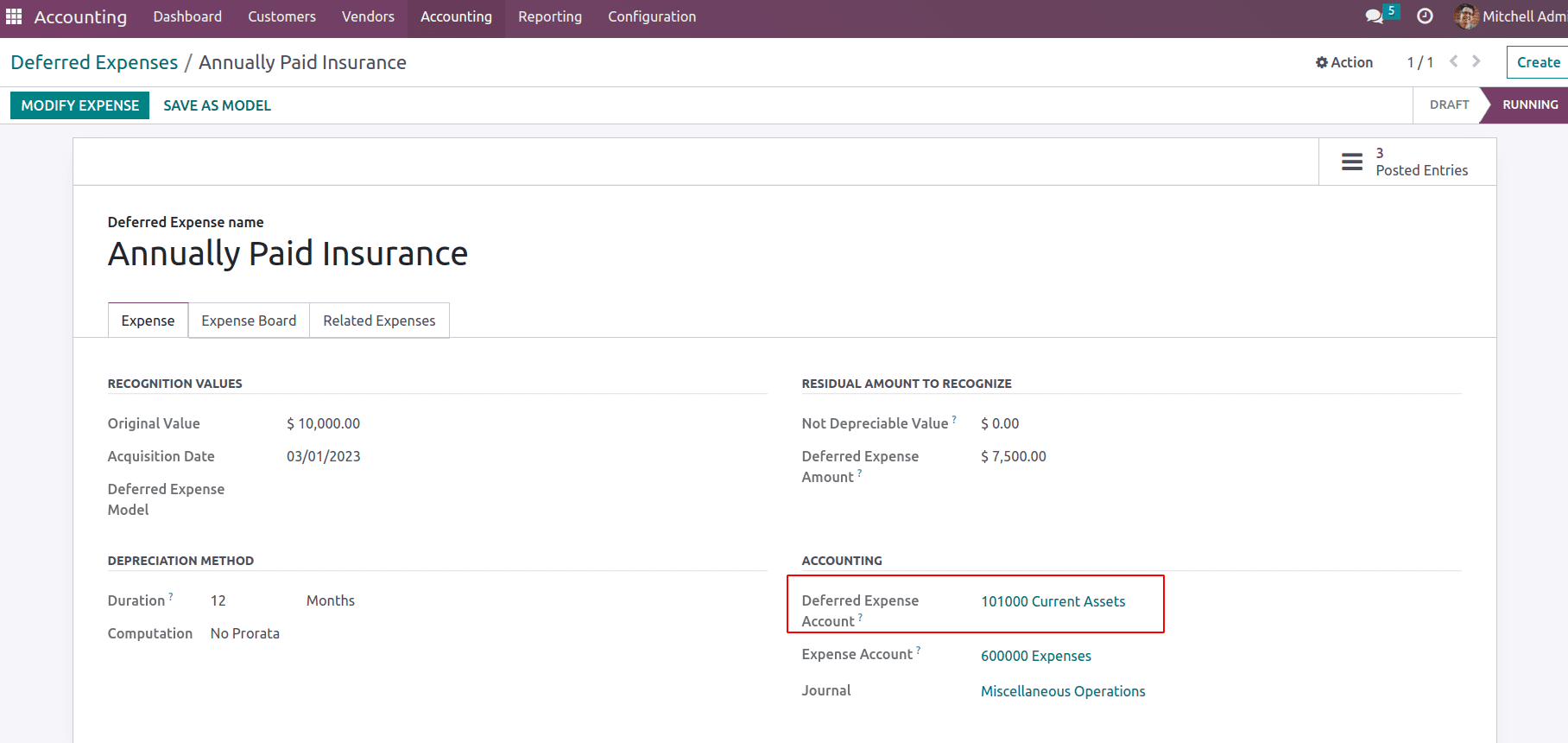
Once the journal entries for the deferred expense have been posted they will record under the current assets section of the balance sheet.
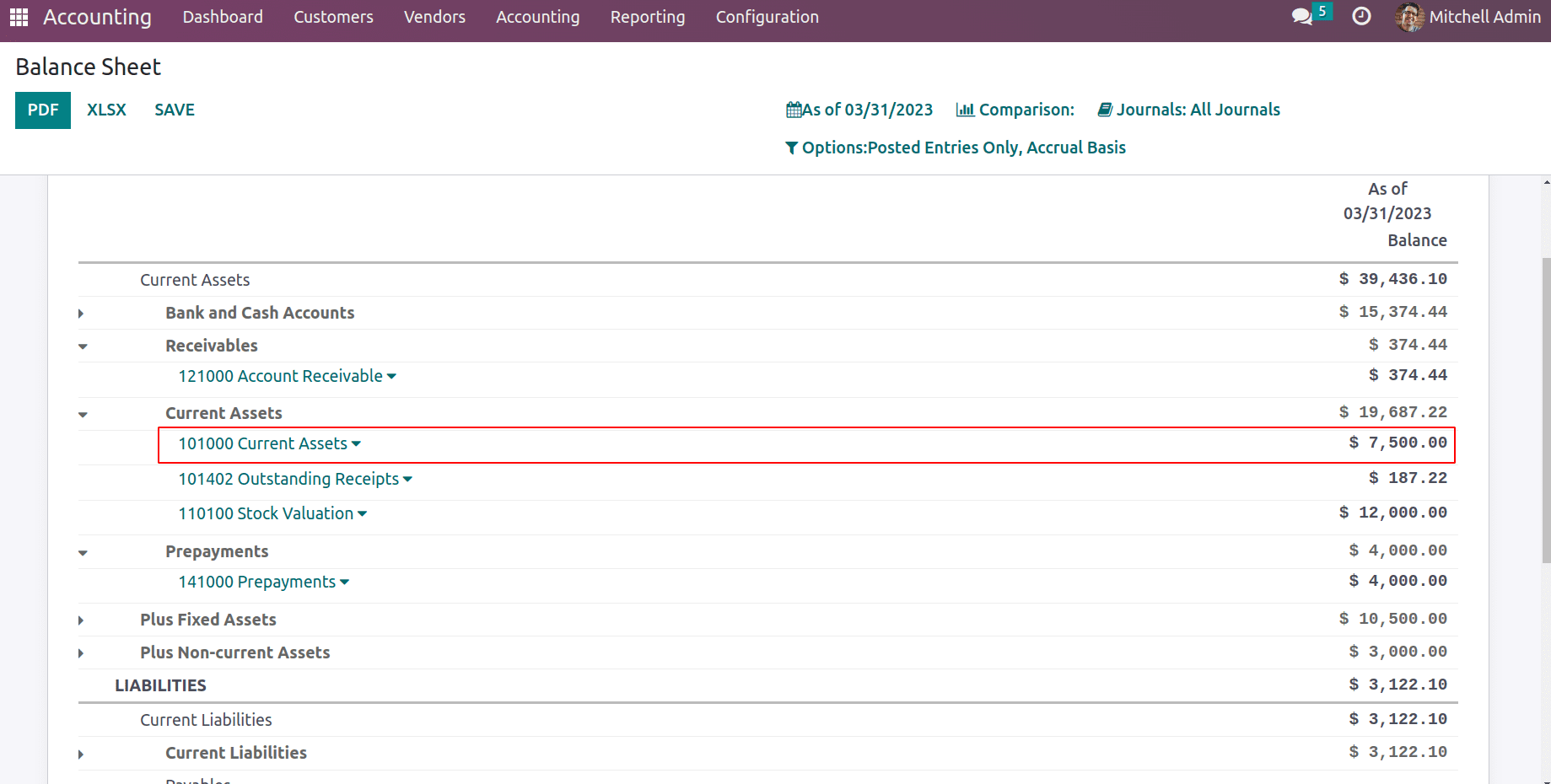
Next is fixed assets and if any fixed asset entry is posted, which will be seen under the fixed assets section of the balance sheet.
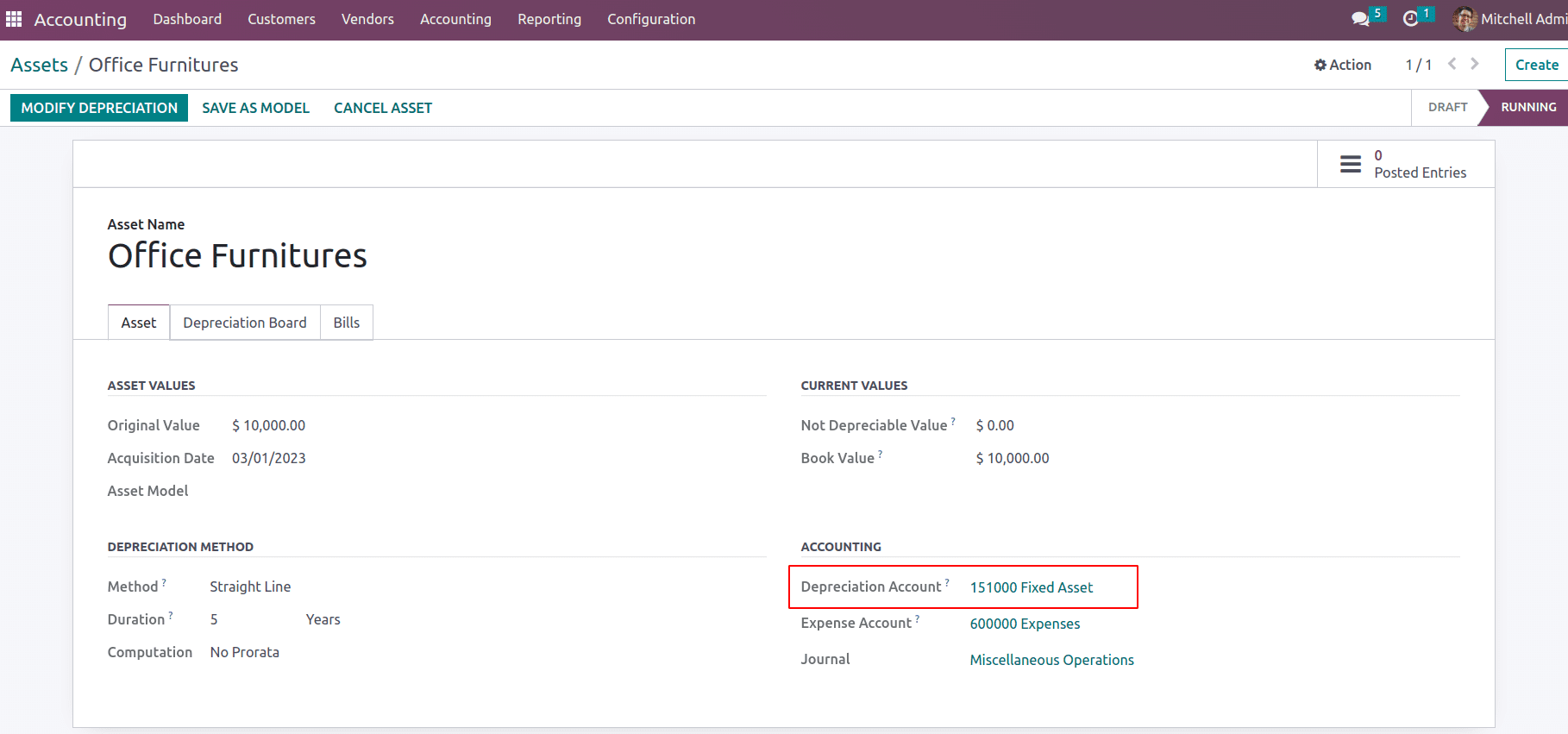
At each period the asset depreciation will be posted to the fixed asset account. Thus each year the asset value will be reduced.
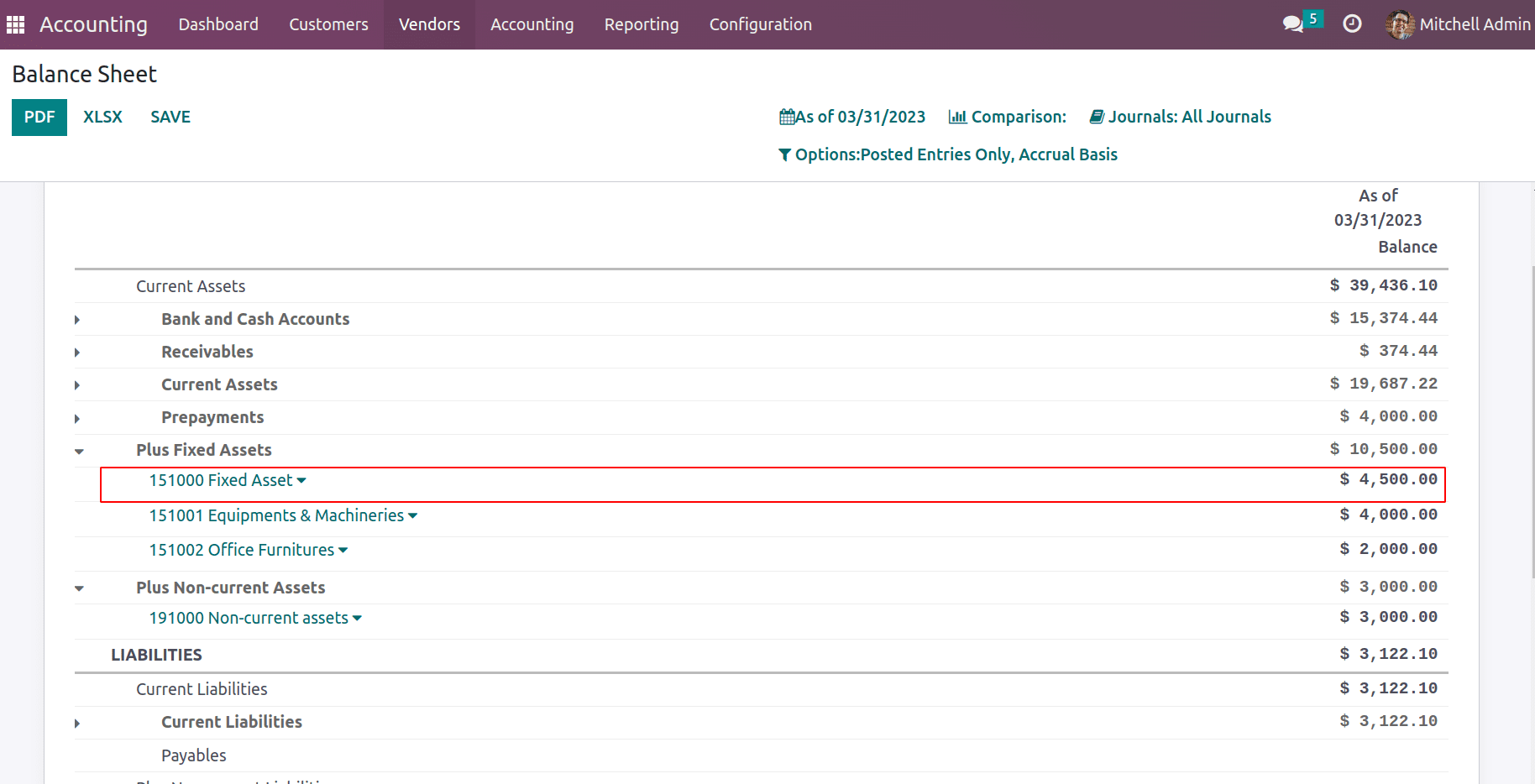
LIABILITIES
Liabilities are obligations or debts that an individual, organization, or business owes to vendors. They are recorded on the balance sheet of an entity and represent the amount of money or resources that must be repaid to creditors or other stakeholders.
Different types of liabilities can be viewed in the chart of accounts.
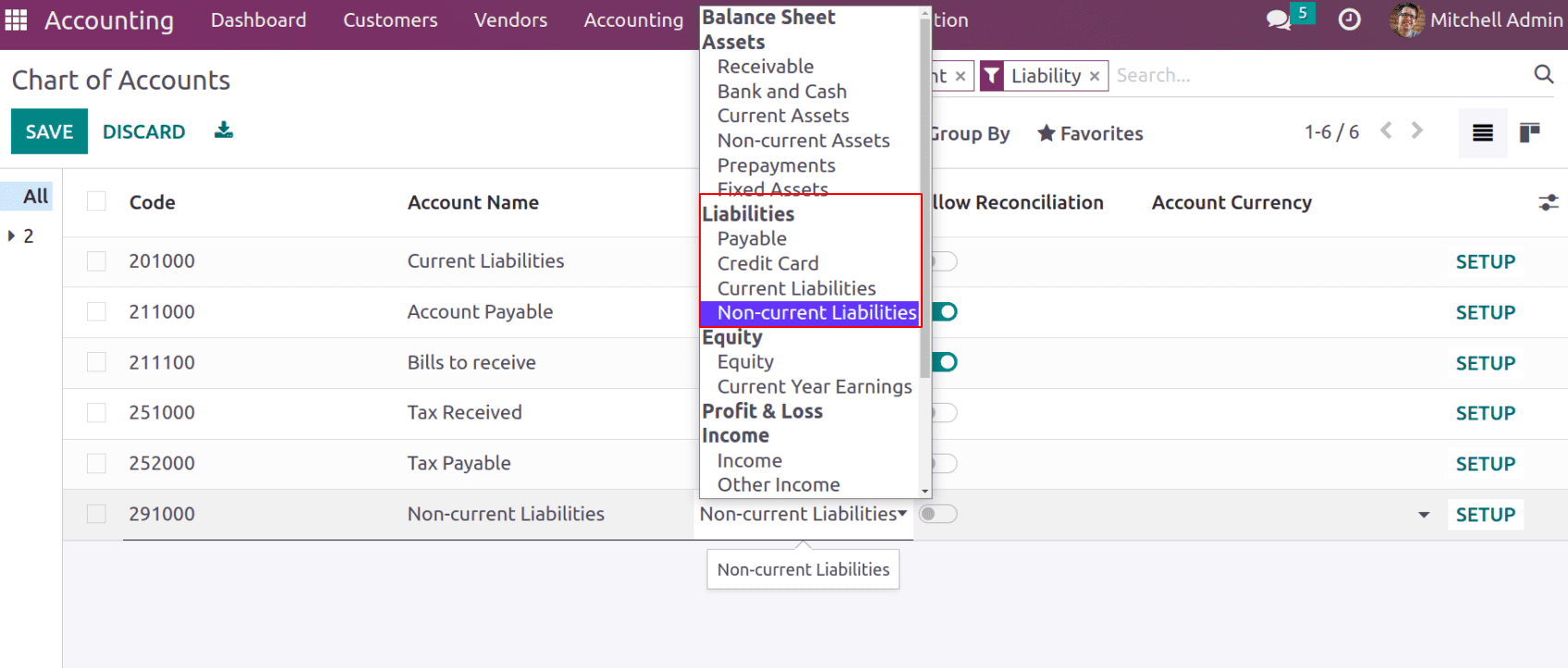
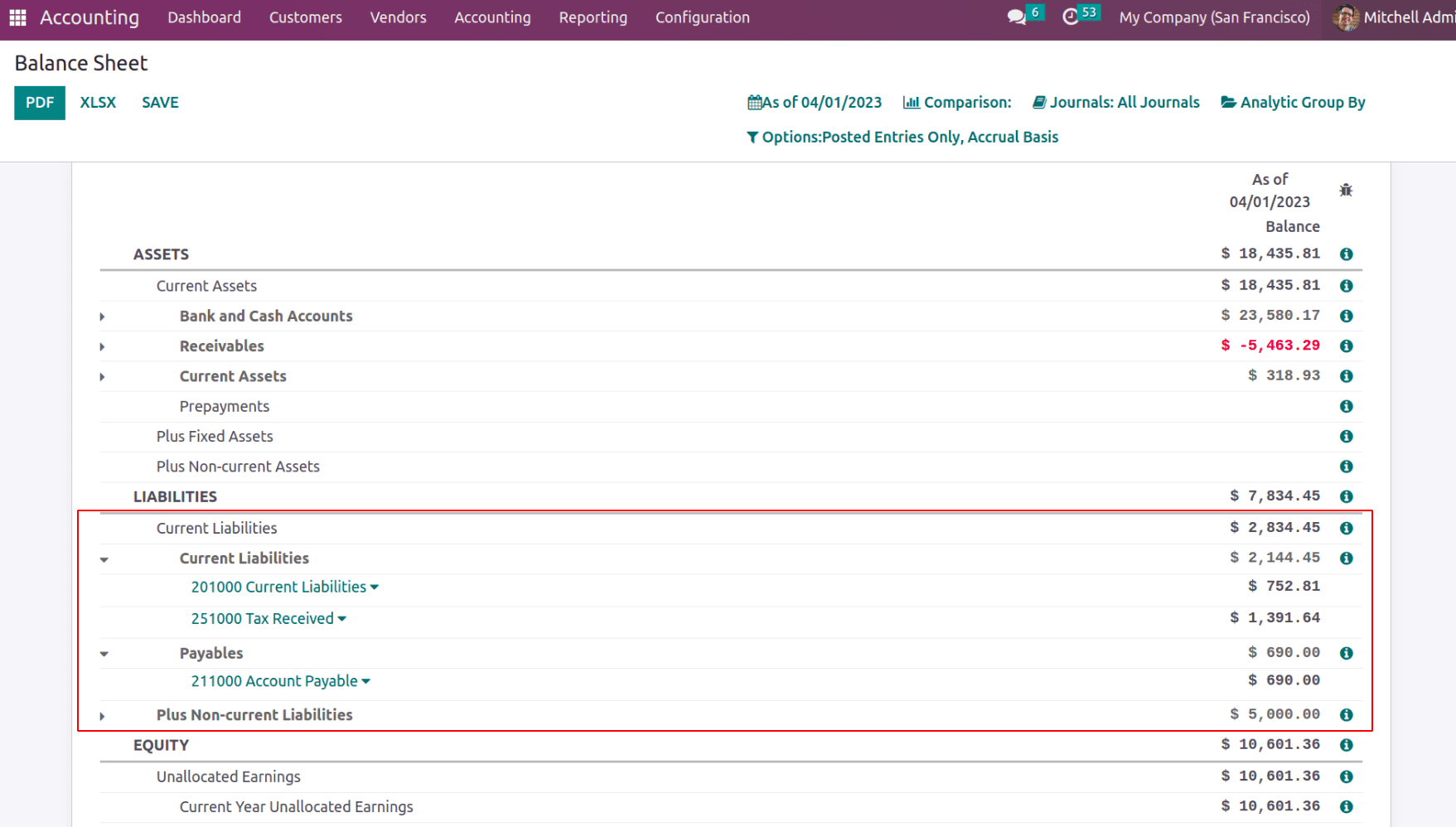
Current Liabilities
They are liabilities or debts that must be paid within one year, such as accounts payable, taxes owed, and short-term loans. These liabilities are recorded on the balance sheet of an entity and represent the amount of money or resources that must be paid to creditors or other stakeholders in the near term.
Non-Current Liabilities
Long-term liabilities are billed with maturities of more than a year, such as long-term loans and bonds payable.
Payables
Payables are any amounts owed by an entity to its vendors or suppliers for items that were bought on credit. Payables are a type of liability and are recorded on the balance sheet of an entity.
Now let us see how various operations affect the liability section on the balance sheet.
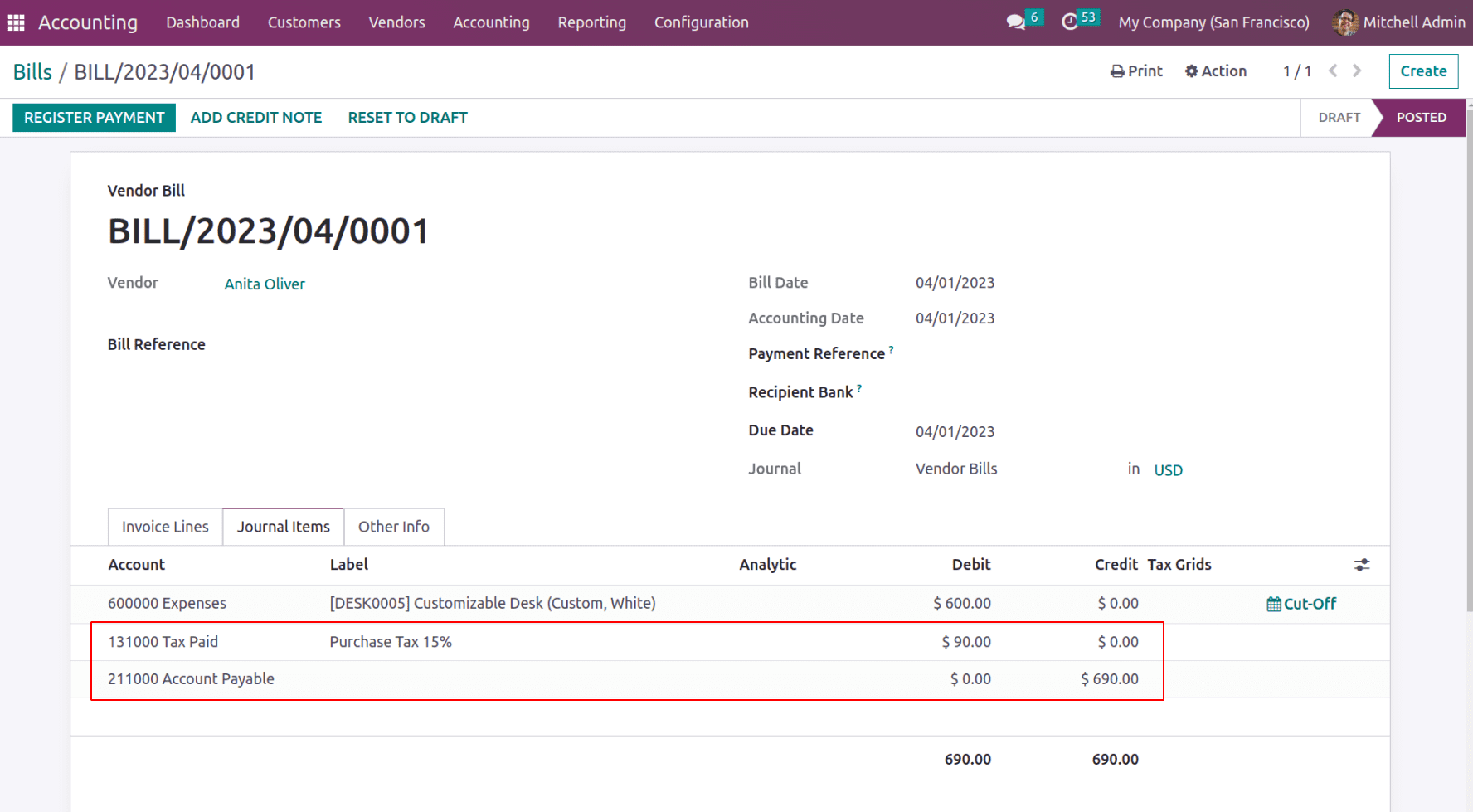
The Account Payable records all payable amount to the vendor and Tax Paid record the tax amount which is a current asset.
In the case of opening stock, there might be some current liabilities like short-term bonds, or in the case of deferred revenue say some warranty amount is received from the customer. Even if it is revenue, this is considered a current liability since the service is not completely rendered.
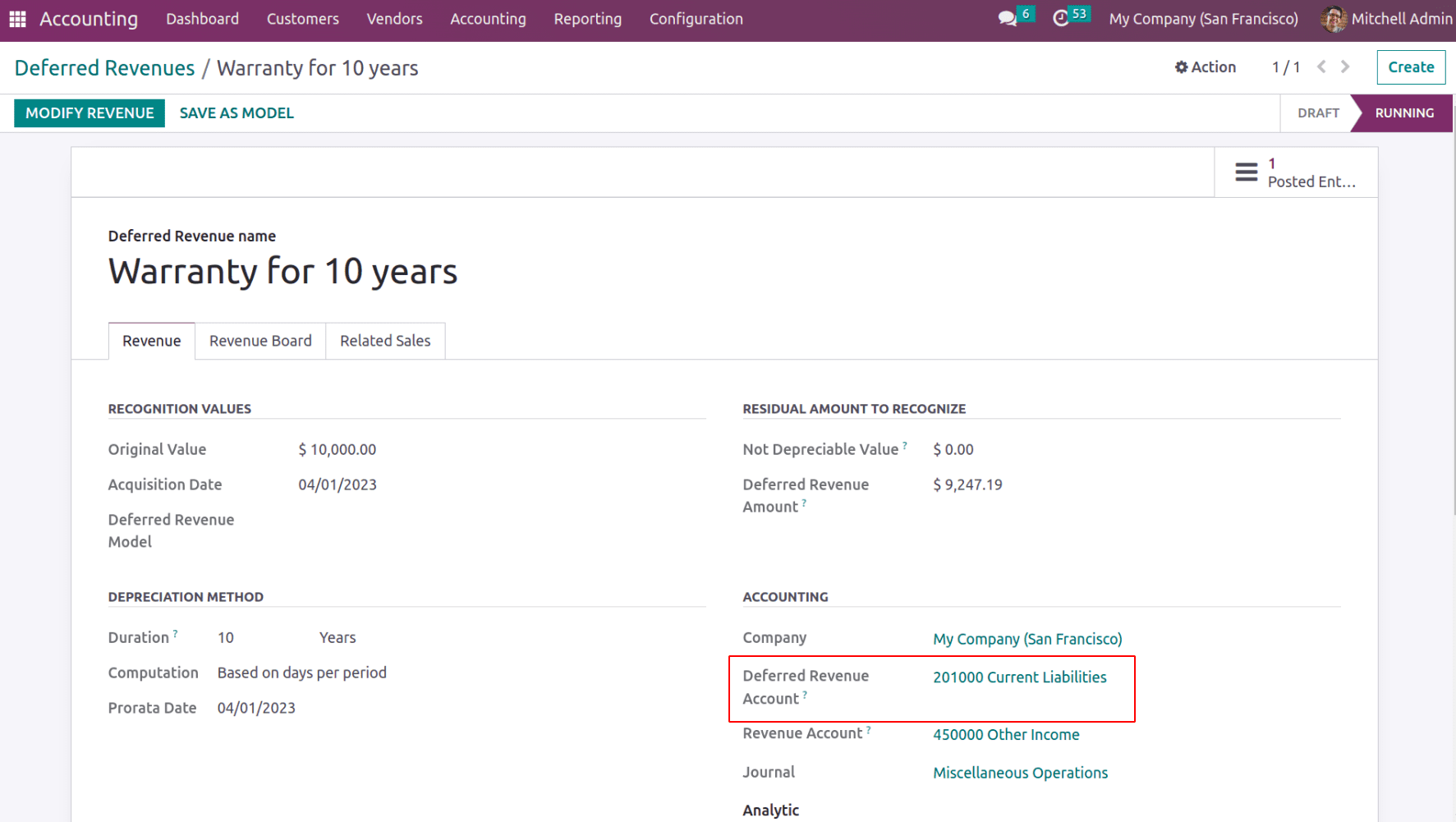
As this deferred revenue is posted, current liabilities are posted, and hence the balance sheet is updated accordingly.
EQUITY
Equity is the quantity of money that a company's owner has invested in or owns. The difference between a business's liabilities and assets on its balance sheet indicates how much equity it has.
Unallocated Earnings
Once the opening balance is added, there will be some amount that should be added to the account ‘ 999999 Undistributed Gain/Loss ‘ to balance the journal entry which will be taken as the unallocated earnings of the current. It can depict a source for that money in the balance sheet. Total unallocated earnings are the sum of the current year's unallocated earnings and the previous year’s unallocated earnings. Later this will be the retained earnings.
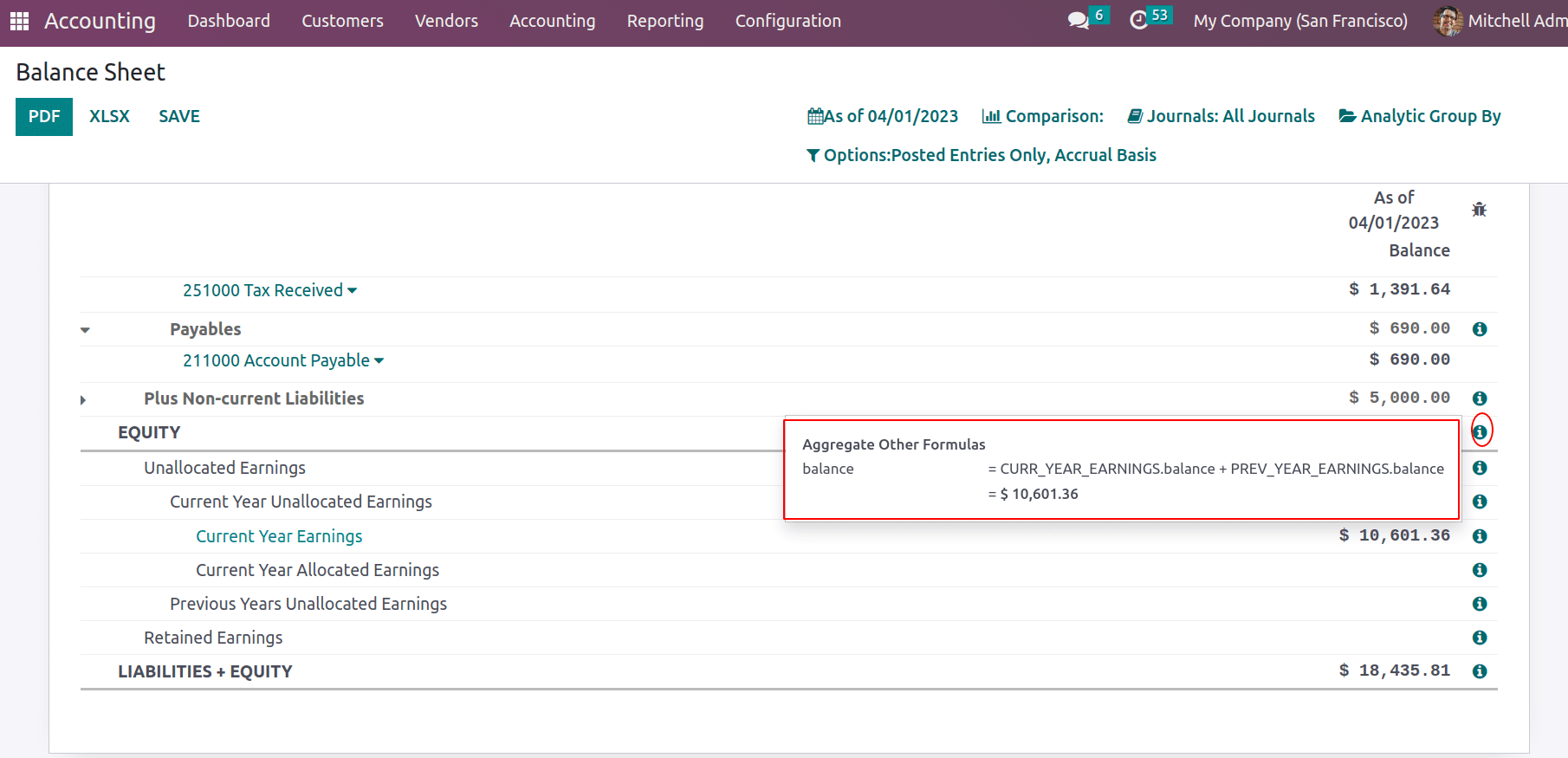
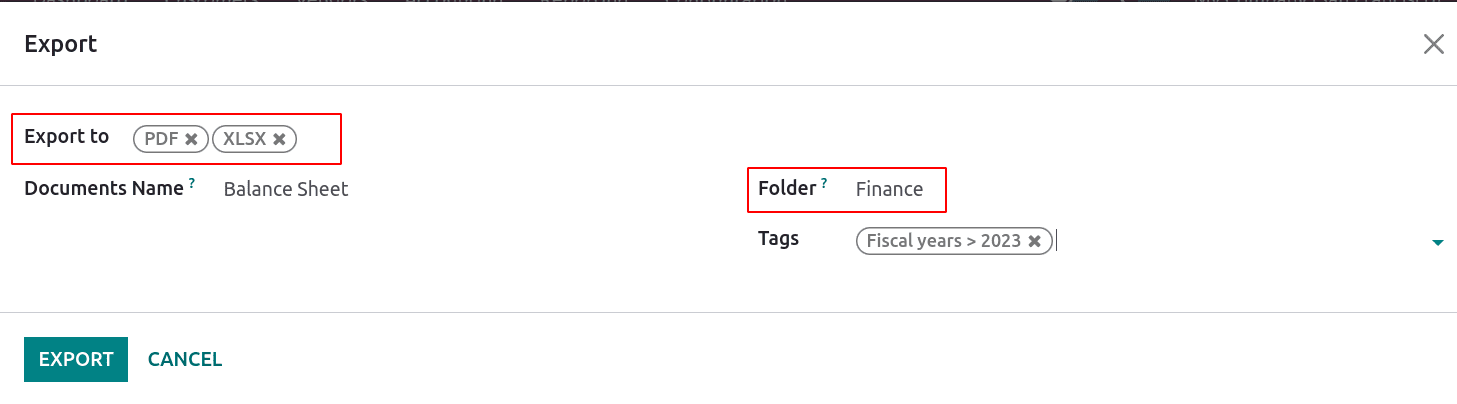
The little “i” icon gives formulae for each line. The balance sheet data can be taken with filters. The filters can be applied based on dates, journals, analytic accounts, and plans. Also, unposted data can be taken to the balance sheet by choosing draft entries from the options.
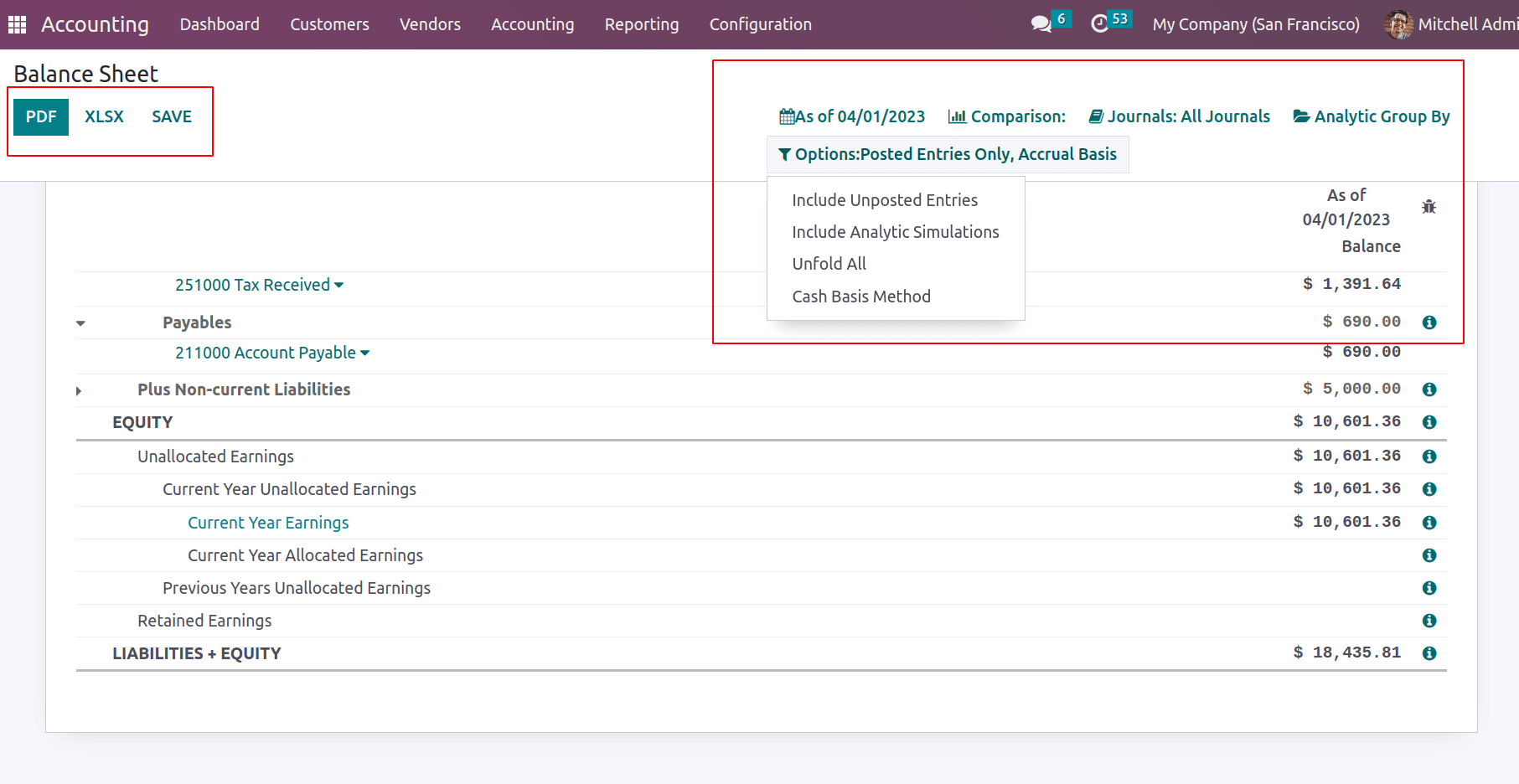
The PDF and XLSX buttons print the balance sheet in PDF and XLSX format. The SAVE button saves the balance sheet in a specified format in the documents module under the ‘Finance’ workspace.